Enterprise Software Development
Steps, Timelines, and Cost Factors
In software development since 1989, ScienceSoft helps enterprises design and develop modular multi-user software that efficiently controls complex business operations.
Enterprise Software Development: The Essence
Enterprise software development is a way for enterprises to increase operational efficiency and productivity with the help of secure, reliable business applications that are easy to maintain, integrate, scale, manage and are cost-effective with a lower cloud footprint.
- Time: The end-to-end development of the first version of enterprise software or several essential enterprise software modules usually takes around a year. The exact timelines depend on the business domain it is used in and the composition and complexity of the required modules.
- Key project steps: Discovery, enterprise software planning and design, UX and UI design, development and testing, data conversion and uploading, deployment, regulatory compliance assessment and certification procedures, iterative evolution.
- Cost: $50,000–$500,000 for a standalone enterprise app, $1,500,000+ for a large-scale enterprise system. Use our free calculator to estimate the cost for your case.
- Team: A project manager, a business analyst, a System Architect, a regulatory consultant, UI and UX designers, a database developer, front-end and back-end developers, QA and DevOps engineers.
Having 750+ skilled IT talents and vast experience in large-scale software engineering projects for Fortune 500 companies, ScienceSoft is ready to take over enterprise software delivery end to end – from planning to development to continuous support.
How to Build Enterprise Software in 8 Steps
Below are described the typical steps we at ScienceSoft take to complete enterprise application development projects.
Step 1. Analyze enterprise needs and engineer requirements
Duration: 1–2 months
- Documenting key business processes and how they’re covered with existing software, understanding the capabilities and limitations of the existing IT environment.
- Eliciting business needs and concerns regarding the existing and desired business process flows.
- Analyzing a broad business strategy (e.g., planned company growth and IT budgets) that can affect architectural and tech choices for planned software.
- Drawing up high-level functional and technical requirements to software.
- Evaluating risks of possible negative impact on business processes due to the introduction of the new system (e.g., lost productivity and downtime associated with transitioning to new digital processes, business user training).
Step 2. Plan and design the enterprise system
Duration: ~ 2 months.
- Drawing up technical requirements for the new enterprise software.
- Deciding on the architectural style of the new enterprise software system (mostly point-to-point/event-driven service-based or microservices) and developing its detailed design.
ScienceSoft's tip #1
Often, we see that it is more cost-efficient and less risky to re-use a part of our client's legacy enterprise systems than develop and implement new software modules and enable their communication with other enterprise systems. When we decide to re-use existing legacy modules in a new enterprise software development, we add to our project plan all or several of the following activities:
- Reverse engineering of the legacy system (including all connections and interdependencies), interfaces between software components, data structure, and data design.
- Code re-factoring to simplify conditionals, remove unneeded code parts, improve code structure, review complex or memory-intensive algorithms.
- Adding new intuitive and integrated interfaces.
- Designing and implementing the integration of the legacy modules with new software (see more info on software integration in Note 2).
ScienceSoft's tip #2
When integration with other enterprise or third-party software is required, we add to the plan:
- Identifying integration touchpoints.
- Choosing integration approaches (integrating via common data storage, mediated integration of SOA/microservices via message broker/ESB or PaaS, point-to-point integration, integration via UI/RPA, etc.) and technologies (e.g., for an ESB-based integration – Talend ESB and SAP PI, for iPaaS-based integration – Azure iPaaS or Informatica iPaaS).
Non-invasive integration (integration via UI/RPA, data storage) is less flexible but also less costly and risky. Invasive integration (e.g., via implementation of SOA with re-usable functional modules that communicate via ESB) can improve enterprise agility and be cost-efficient in the long-term, but it’s expensive in the short term, architecturally risky, and may require quite deep preliminary code changes (very dangerous for legacy applications with their old, not well-documented code). At ScienceSoft, we prioritize non-invasive integration approaches when it comes to legacy software and, for more complex invasive integrations, always consider the adoption of the iterative integration approach to better control risks and prove architecture feasibility in the early iterations.
- Enterprise application integration architecture design.
- Planning how data should flow and whether it needs to be transformed into a different format.
- Checking how many communication protocols between integrated applications will be used.
- Designing additional security enhancements.
- Preparing a comprehensive QA strategy to verify all uni- and bidirectional calls between the integrated systems, backup and recovery mechanisms, how well the integrated system works within established bandwidth limitations, etc.
Step 3. Design UX and UI for the enterprise app
Duration: 1–3 months.
- UX designers and Business Analysts collaborate on UX research to understand the target audience and their needs, goals, and mental models.
- UX designers describe how a user will interact with the system (identify digital touchpoints) and design information architecture.
- UX designers create wireframes that demonstrate basic content layout and functionality.
- We combine the wireframes into a prototype of the application and run prototype testing.
- Once the prototypes pass user testing, UI designers transform them into full-color graphic interface mockups that are then handed over to front-end developers.
Step 4. Develop and test the enterprise solution
Duration: from ~ 6 months to several years (depending on software complexity).
- Back-end development – building the server side and APIs of new enterprise software. It also includes integration with required business applications.
- Front-end development – transforming static interface images provided by UI designers into a fully functional enterprise client side and ensuring its communication with the server.
- Reviewing whether the system matches functionality, performance, security, and integration requirements. Testing usually runs in parallel with development.
- Preparing training materials to help employees promptly learn how to use the new system.
Our clients often like the idea of shortening the time to release and optimizing the development budget by developing an MVP. It is a software version with only the essential features, which helps us test whether software meets the key stated user needs. Upon confirming or adjusting the initial EAS idea, we add other features to the MVP. We deliver the first working version of enterprise software of small to medium complexity in 4–8 months, with new functionality being added during major releases every 2–6 weeks.
Step 5. Prepare and migrate enterprise data
Duration: 3–6 weeks.
- Inspecting the legacy data to migrate, avoiding duplicated or inconsistent data.
- Deciding on the supported data formats and handling the required conversions if several data formats are in use.
- Extracting, transforming, and loading the legacy data.
- Conducting ETL testing to ensure data stays complete and adequately transformed (also, where feasible, developing and running automated ETL testing, e.g., using tools such as QuerySurge, Informatica DVO, ETL Validator)
Step 6. Deploy EAS to production
Duration: 1–2 weeks.
We deploy the enterprise solution and integrate it with the required corporate infrastructure. We first move complex software through staging and testing environments so that the team could spot all potential issues before release and safely introduce changes.
For complex projects we perform a trial implementation to minimize possible downtimes in production. The trial implementation is done for a limited number of users and requires comprehensive technical support in case any problems are encountered. Trial stages usually take up to 1–3 months.
Step 7. Ensure regulatory compliance
Duration: up to several months.
This stage is relevant for enterprise software or its parts falling under government or industry regulations, e.g., HIPAA, CGMP, GLBA, PCI DSS, GDPR. At this stage, our team compiles comprehensive documentation created during all stages – from software design to verification and validation – to prove that software and software development life cycle meet all essential requirements of a standard or a regulation.
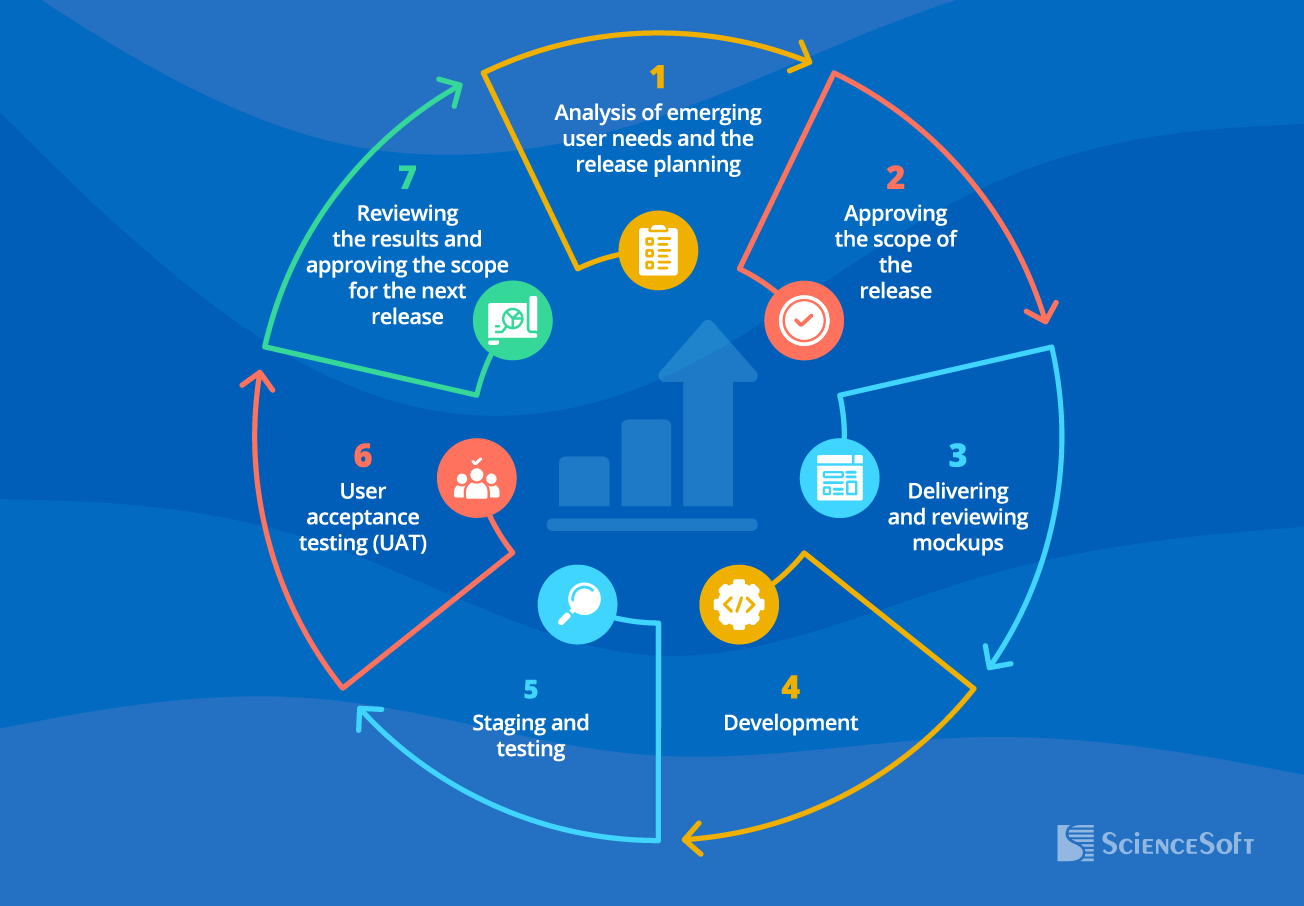
Step 8. Evolve EAS in iterations
Duration of releases: 1–3–6 months (depends on a development and deployment strategy).
The development and delivery of new working software modules continue iteratively according to the following scheme:
Enterprise Software Development Services by ScienceSoft
Enterprise software development consulting
Our consultants:
- Elicit and structure software requirements.
- Assess tech and economic feasibility of the project.
- Plan application security and compliance.
- Develop a business case.
- Deliver PoC.
- Design architecture, choose a tech stack.
- Deliver a detailed development roadmap.
- Plan a DevOps strategy.
End-to-end enterprise software development
Our team takes over:
- Needs analysis, requirements specification, app architecture design.
- UX and UI design.
- MVP development.
- Enterprise-level software development, integration with other business software, testing and QA.
- After-launch support.
- Continuous app management and evolution (on demand).
Why Outsource Enterprise System Development to ScienceSoft
In enterprise software projects, we drive project success for our clients no matter what, ensuring that the agreed cost and timelines are met, the development flow is predictable, and uncertainties are handled agilely.
- Since 1989 in software development.
- Since 2012 in cloud consulting and development of complex applications.
- Since 2005 in business intelligence and data warehouse services.
- Since 2003 in cybersecurity. All-level security configuration and monitoring (infrastructure, application logic, security testing, compliance).
- Proficiency in advanced techs like AI/ML (since 1989), big data (since 2013), IoT (since 2011), AR, VR, blockchain, etc.; Industry 4.0, Supply Chain 4.0, digital health, smart cities.
- ISO 9001- and ISO 27001-certified company to guarantee excellent service quality and customer data security.
Our awards, certifications, and partnerships
Benefits of Enterprise App Development with ScienceSoft
To help our clients prevent risks, ScienceSoft as a reliable tech partner offers an opportunity to start our cooperation with a PoC. We prepare a feasibility study with business outcomes bound to each project stage and provide our clients with free estimates for their custom enterprise software solutions.
We tailor collaboration frequency and forms to meet our clients’ individual expectations and maintain transparent customer communication. Our teams continuously improve collaboration throughout all levels of engagement and never stay silent about potential project risks.
We sign an NDA (already at the initial negotiation stage if needed) to guarantee the confidentiality of your information. As the project unfolds, your product stays protected due to our secure IT infrastructure (with IDS/IPS, DLP, SIEM), data security practices approved by the ISO 27001 certificate, and adherence to the industry-specific standards (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR).
Partnerships with the leading technology market players – Microsoft, AWS, Oracle, etc. – grant ScienceSoft direct access to their advisory services and additional discounts. It helps ensure top-notch quality of enterprise apps and optimize development and maintenance costs.
ScienceSoft as a Reliable Enterprise Software Development Partner
The client needed complex trade promotion management software to serve as a trade marketing planning system. The solution needed to be easily customizable, as the client operates in over 180 countries and needs to adjust the software to the local requirements.
However, the challenge was not only to provide quality development services but to collaborate with two international teams engaged in the project implementation. ScienceSoft accomplished this task in a highly productive and efficient way. The communication ran seamlessly.
The solution developed by ScienceSoft fully met the client's requirements and expectations.
Mikhail Anfimau, Senior Solution Architect, Leo Burnett
Typical Roles in Our Enterprise Software Development Teams
Below we describe the common roles involved in complex enterprise software development projects. Additional talents may be required, depending on the nature of the project, for example, you may need the skills of data scientists, 3D designers, etc.
Project Manager
- Keeping the project on schedule and within the scope and budget.
- Controlling project milestones and deliverables
- Facilitating and coordinating communication between all team members.
- Managing project risks.
Business Analyst
- Uncovering the underlying business issues that need to be addressed.
- Translating business needs into enterprise application capabilities.
- Organizing, specifying, and documenting requirements to the new enterprise software system from all stakeholders.
- Representing business interests during system design and software configuration planning.
System Architect
- Designing software architecture.
- Designing integrations with other in-house and third-party software systems.
Note: A system architect should have a good knowledge of advanced software architecture approaches, including ESB-driven service-oriented architectures and microservices.
UX Designer
- Performing UX research.
- Designing user interactions with the application.
- Designing the information architecture.
- Conducting usability testing.
UI Designer
- Deciding on the colors, icons, and screen layouts of the application’s GUI.
- Creating a UI kit for quick development of user interfaces.
Database Developer
- Developing and implementing databases, building data models.
- Optimizing resource consumption and storage space.
- Developing and supporting ETL/ELT processes.
Software Developer
Back-end Developer
- Writing back-end code and APIs.
- Performing unit tests.
Front-end Developer
- Creating functional components of the user interface.
QA Engineer
- Designing a test strategy.
- Selecting test tools.
- Designing, developing, and maintaining tests.
- Documenting, implementing, monitoring, and improving the testing process.
- Tracking test results, finding and reporting bugs.
DevOps Engineer
- Planning, configuring, and optimizing software infrastructure.
- Incorporating an infrastructure-as-code approach.
- Optimizing orchestration.
- Designing and creating CI/CD pipelines for automated deployment.
- Selecting and configuring tools to execute daily monitoring of the enterprise application system.
- Performing root cause analysis of EAS performance faults.
Sourcing Models for Enterprise Software Development
An entire EAS development process is in-house
- Direct supervision over the enterprise custom software development process and team productivity.
- High costs.
- Lack of experience and resources can lead to the project delay, setup, and management risks.
- All hiring and managerial efforts are on your side.
A mix of an in-house team and outsourced consultancy
- In-house team understands internal processes and software environment and has direct access to all assets.
- Outsourced consultancy helps close the gaps in specific tech skills.
- Risks related to vendor selection.
- Coordination of disparate project teams and risk management are partially/fully on your side.
Full EAS development process is outsourcing
- Established EAS design and development processes.
- A vendor assumes full responsibility for the team arrangement and management, quality of the project deliverables, and related risk management.
- High vendor risks.
Techs and Tools ScienceSoft Uses for Enterprise Software Development
Clouds
Low-code development
DevOps
Containerization
Automation
CI/CD tools
Monitoring
Machine learning
Programming languages
Frameworks and libraries
Cloud services


Platform engines
IoT
AWS
Azure
Enterprise Software Development Costs
Major factors that impact the cost of enterprise software development are:
- Application type (web, mobile, desktop); number of platforms and OS versions supported (for mobile).
- Number and complexity of app features.
- Number of business areas (finance, production, SCM, HR, CRM, etc.) and business processes (e.g., for CRM: email marketing, lead nurturing, case escalation) covered.
- The number of user roles.
- The complexity of the app logic and workflows.
- The number and complexity of integrations.
- Application availability, performance, security, latent capacity, and scalability requirements.
- The necessity to maintain existing data (in case of migration).
- Frequency of the application updates and improvements.
- Regulatory compliance requirements.
- Special features required (machine learning capabilities, etc.).
- Uniqueness and complexity of UI design.

From ScienceSoft's experience, building custom enterprise software that automates a particular area (e.g., operations management, HR, finance) costs around $50,000–$500,000, while developing an all-in-one enterprise system may require $1,500,000+ in investments.
Want to understand how much your enterprise solution may cost?
Get to Know the Cost of Your Enterprise Solution
Simply answer a few questions about your business needs. This will help our consultants estimate the cost of your unique enterprise solution faster.
Thank you for your request!
We will analyze your case and get back to you within a business day to share a ballpark estimate.
In the meantime, would you like to learn more about ScienceSoft?
- Project success no matter what: learn how we make good on our mission.
- 4,200+ successful projects: explore our portfolio.
- 1,400+ incredible clients: read what they say.

About ScienceSoft
ScienceSoft is a global IT consulting and software development company with 36 years in the market. We employ extensive technical expertise, practical knowledge of 30+ industries, professional business analysis, and KPI-based development to help our clients re-engineer, build, and integrate enterprise software. Being an ISO 9001- and ISO 27001-certified company, we rely on mature quality management and guarantee the cooperation doesn't pose any risks to the customers' data security.