Wearable App Development
Architecture, Steps, and Key Technologies
In healthcare IT since 2005 and in IoT development since 2011, ScienceSoft helps businesses in the healthcare domain design and develop apps for wearable medical devices.
Wearables in Healthcare: The Essence
In healthcare, wearable IoT is a network of patient-worn devices connected to the cloud. Wearable apps collect, transmit, and analyze health data in real time, enabling continuous patient monitoring and immediate healthcare interventions.
Based on ScienceSoft's hands-on implementation in live projects, wearable technology is highly efficient for chronic condition monitoring, therapy delivery, rehabilitation, diagnostics, and activity tracking.
An Overview of the Healthcare Wearables Market
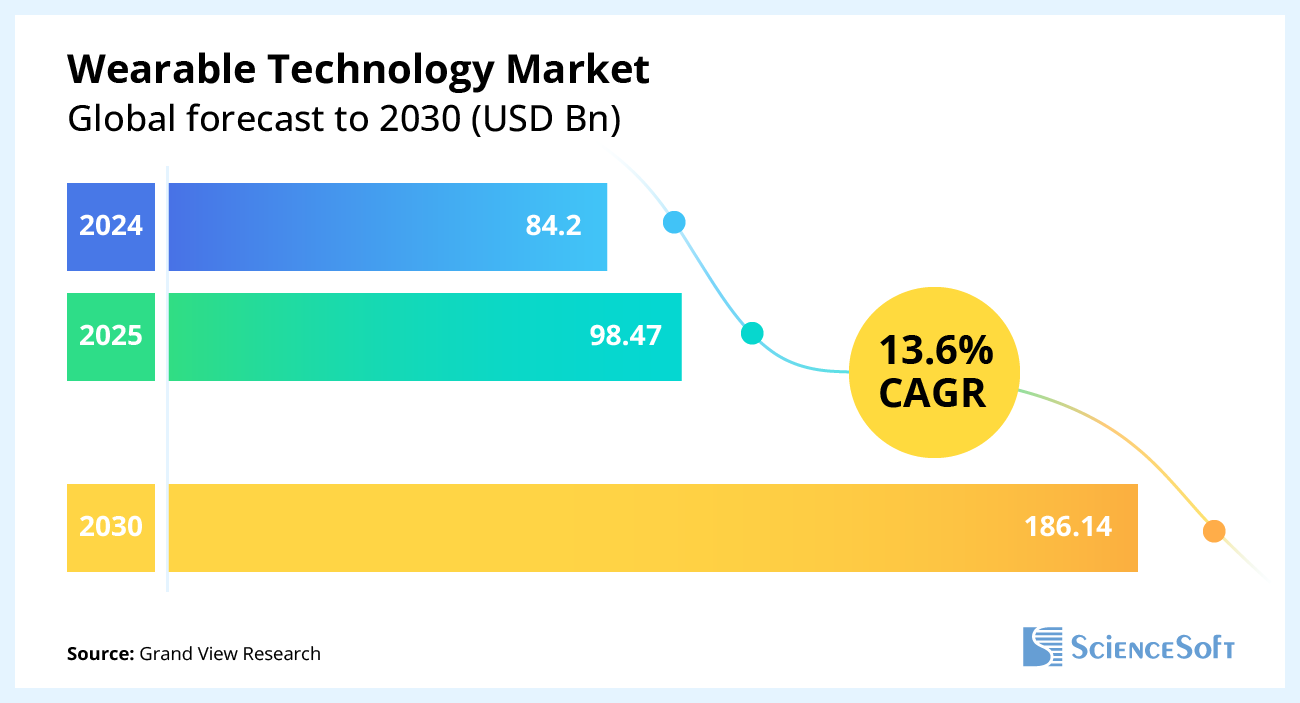
The global wearable technology market size was estimated at $84.2 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 13.6% from 2025 to 2030. The core market drivers are the growing consumer awareness of physical well-being, the rise of lifestyle-associated chronic diseases, the growing geriatric population, the increasing popularity of home healthcare and remote monitoring, and the focus on personalized patient care.
How the Healthcare Industry Adopts Wearable Technology
Wearable medical devices and complementary apps provide medical professionals with a holistic picture of the patients’ health state. They also enable patient self-monitoring and, therefore, help improve patient care outcomes. The adoption of the technology shows a steady increase:
Industry insights
- 113.1 million wearable devices were shipped worldwide in the first quarter of 2024, according to IDC. The number is projected to reach 612.5 million by 2028.
- North America held the major revenue share of over 34% of the wearable technology market in 2024.
The Architecture of Cloud-Based App for Wearable Devices
ScienceSoft's experts recommend the following cloud-based software architecture to power wearable devices in healthcare.
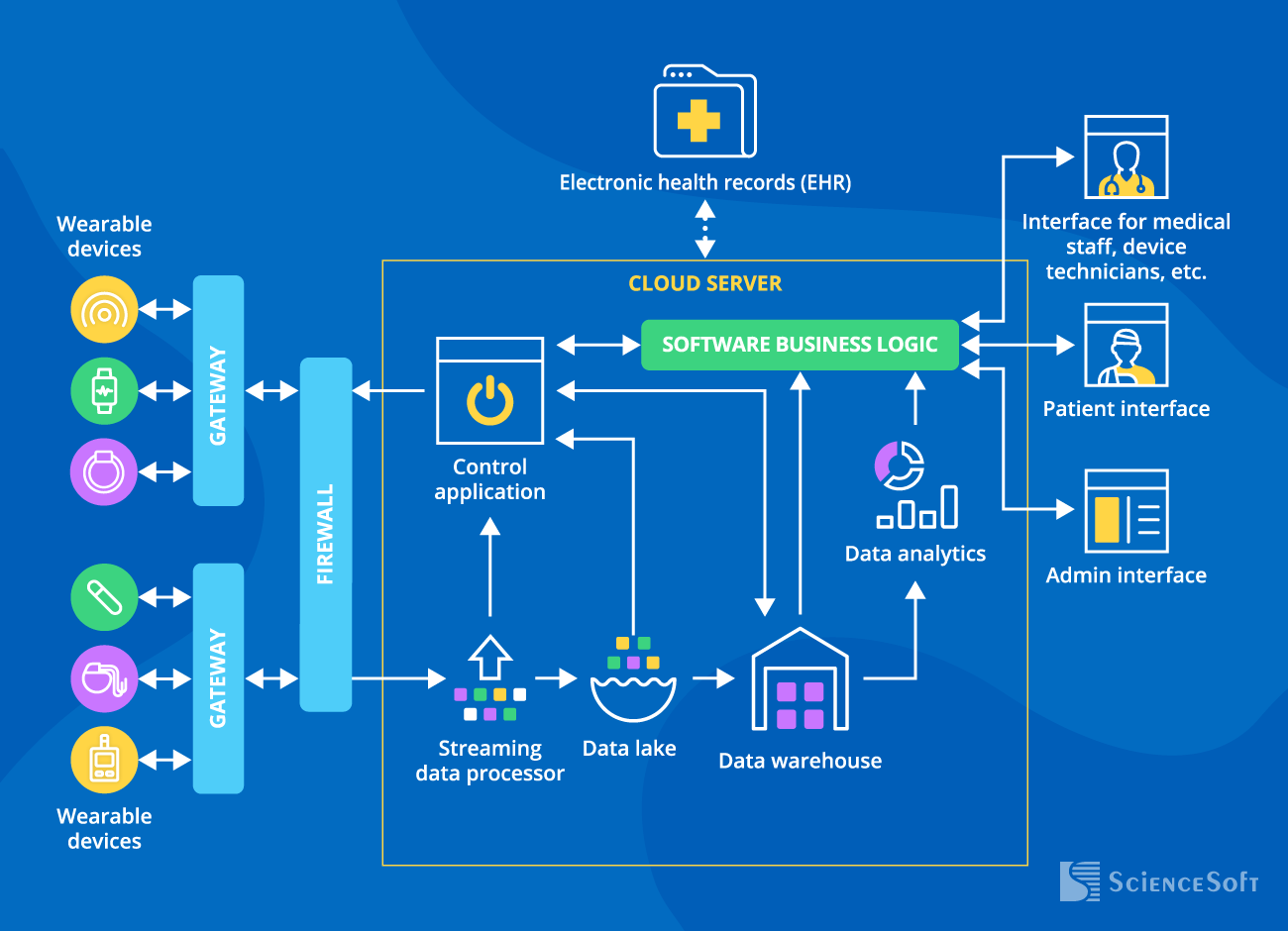
The solution includes a cloud server, which receives data from wearable devices via gateways and a firewall. The cloud server includes data storage, processing, and analytics modules and hosts the solution’s business logic and control applications. The solution also has user interfaces for patients, medical staff, medical device technicians, and admins, which help access the collected and analyzed data from wearables, send commands to the wearable devices (e.g., initiate pain management), and more.
In similar projects, ScienceSoft's healthcare IT team integrates the IoT solution with EHR to enable a comprehensive view of patients’ medical history (chronic conditions, allergies, etc.).
Wearable Medical Devices Used in Patient Care
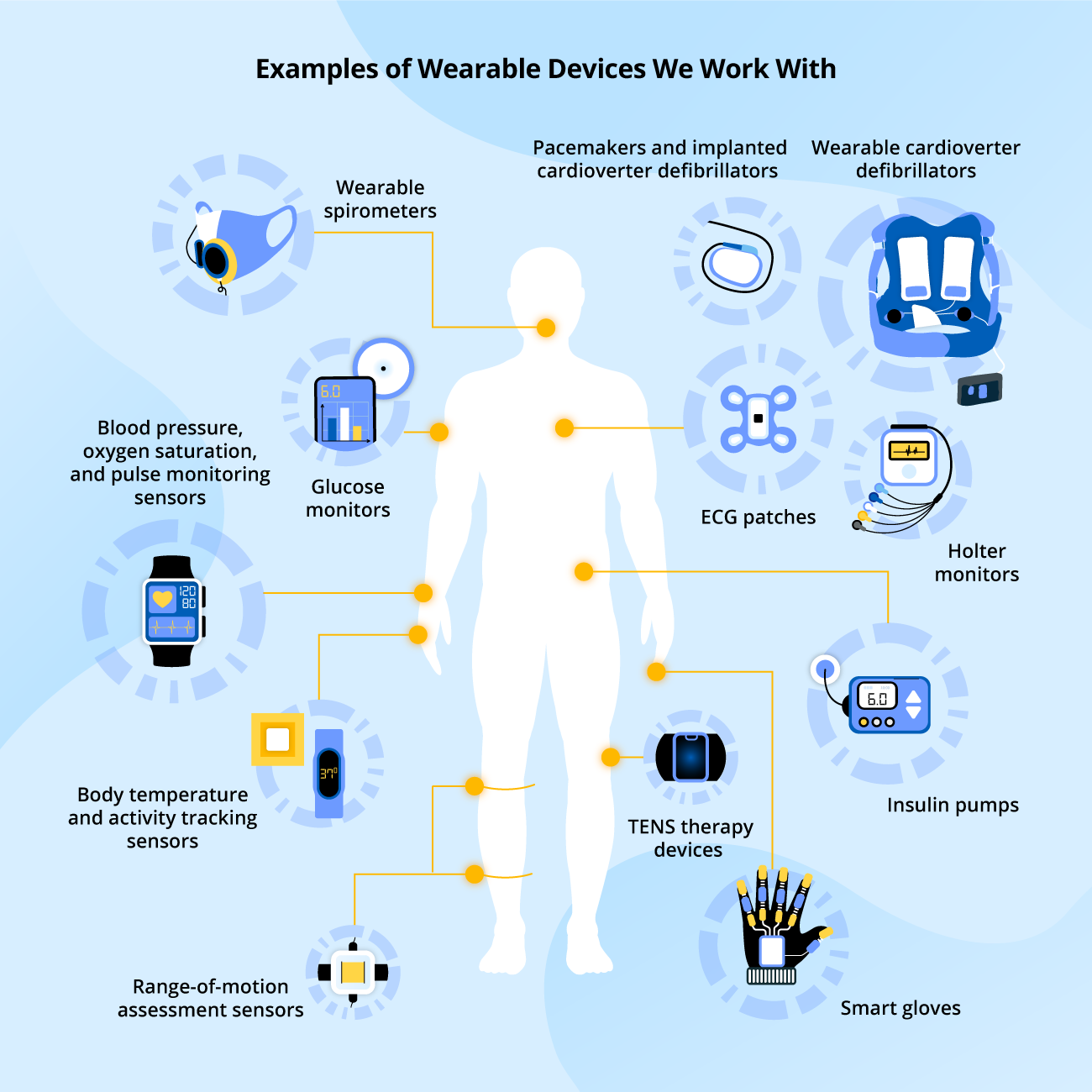
Use Cases of Wearable Health Technology
Health condition monitoring
Healthcare organizations’ staff can monitor patient health state in real time with personal health monitoring devices and use the gathered information to timely adjust the disease management plan. Patients can track their health parameters and request consultations if the solution indicates alarming patterns in vitals.
Device examples: wearable spirometer, hemodynamic/pressure monitoring devices, ECG patches, etc.
How it works: Wearable patient monitoring devices (e.g., glucose monitors) collect data related to a patient’s condition (e.g., a blood glucose level) and transfer it to the medical software cloud server. The anonymized patient data is processed and analyzed to identify patterns in it. The identified patterns accompanied by the source data are available to doctors and patients in respective user applications and help track patient health conditions, improve treatment, and promote disease self-management.
Use cases ScienceSoft suggests:
- Respiratory monitoring for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, etc.
- Monitoring of blood glucose for patients with diabetes type 1 and type 2.
- Monitoring of cardiac diseases.
- Fetal and neonatal monitoring.
- Monitoring of COVID-19 patients (e.g., using body temperature and blood oxygenation level monitoring devices combined with telehealth software).
- Patient monitoring during cancer treatment (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate).
- Home care for geriatric patients.
- Measurement and recording of dyskinetic symptoms and tremors by patients with neurological disorders.
Patient therapy delivery
Medical wearables help treat chronic disease symptoms (e.g., pain, hyperglycemia) and maintain patients’ health, while automatically accumulating data on wearable-enabled therapy delivery for a doctor’s review.
Device examples: implanted pacemakers, defibrillators, closed-loop pancreas systems, insulin pumps, etc.
How it works: Wearable patient therapy devices can be either implanted (e.g., implantable cardioverter-defibrillators) or attached to the skin (e.g., insulin pumps). Therapy delivery can be triggered by a patient via the user application or automatically by the solution (if, based on patient data analysis, it identifies the need for treatment). Reports with therapy data and insights on the device state are available in the medical staff app.
Use cases ScienceSoft suggests:
- Cardiac rhythm management.
- Insulin therapy for diabetes patients and insulin intake monitoring.
- IoT-based tracking of medical devices’ condition.
- Pain management via electrotherapy devices stimulating nerves or muscles (e.g., for migraine alleviation, muscle spasms).
- Posture correction using wearable devices that emit vibrations to help promote healthy behaviors.
Patient rehabilitation
Wearables for patient rehabilitation can enable physical therapy delivery and collect data on at-home or hospital-based rehabilitation progress. The key advantage is that the wearables allow the medical staff to precisely capture the way patients perform physiotherapy exercises, monitor rehabilitation efficiency and patients’ vitals during the exercises.
Device examples: smart gloves, range-of-motion assessment sensors, body temperature and respiration sensors, EMG sensors, etc.
How it works: The patient health state data is collected by devices’ sensors that read and quantify patients’ movements, assess vitals (e.g., heart rate) during a rehabilitation session. Cloud software stores and analyzes data transferred by rehabilitation wearables. The data interpreted by software is shown in the app for physical therapists to help them assess patients’ improvements, rehabilitation efficiency, and adjust the therapy.
Use cases ScienceSoft suggests:
- Stroke rehabilitation (e.g., using smart gloves to regain movement through repeated hand and arm movements).
- Monitoring of joint movement improvement (e.g., after bone fractures, joint surgeries).
- Cardiac monitoring for patients recovering after heart surgeries or acute conditions (e.g., a heart attack).
- Home care for patients with chronic diseases (e.g., neurological, cardiac diseases).
- Electromyography monitoring of nervous and muscle response during rehabilitation.
Early disease diagnostics
Wearable diagnostics devices can identify intermittent symptoms (e.g., heart palpitations) that could have been not present during doctor appointments. When a patient has such infrequent symptoms, a doctor prescribes continuous monitoring with wearables (often for 1-2 weeks). These devices enable fact-based disease diagnosing and help improve patient outcomes.
Device examples: skin temperature, perspiration sensors, heart rate monitors, glucose monitors, holter monitors, etc.
How it works: The cloud server gets patients' vitals from real-time monitoring devices. Based on pre-set parameters, the solution spots abrupt changes in patient vitals and displays a report on identified abnormalities in the doctor’s app. The comprehensive data allows doctors to timely confirm patients’ diagnoses and plan treatment.
Use cases ScienceSoft suggests:
- Diagnostics of cardiac conditions and developing pathologies like atrial fibrillation.
- Monitoring of patients with prediabetes.
- As a part of complex diagnostics of neurological conditions (e.g., Parkinson’s disease).
- Blood coagulation monitoring to prevent ischemic stroke.
Activity tracking
Physical activity tracking wearables aim to maintain patient health and improve the quality of life. Wearables enable a continuous analysis of the quantity and quality of physical activity and help patients introduce well-informed lifestyle change decisions.
Device examples: wearable activity trackers, smart watches, skin temperature sensors, perspiration sensors, etc.
How it works: Software collects data from wearable devices that track patients’ physical activity like steps, energy consumption, physical activity time, quality of physical activity (e.g., moderate or vigorous activity). The analyzed data is displayed to a patient for self-monitoring and is available for a doctor as an activity report (featuring average daily activity, number of days meeting a pre-set physical activity threshold, etc.). During appointments or health check-ups, the doctor uses the activity insights together with other health metrics (e.g., lab tests, medical device data) to offer recommendations on health state improvement.
Use cases ScienceSoft suggests:
- Physical activity tracking among populations (especially geriatric patients, people leading a sedentary lifestyle, etc.).
- Monitoring of physical activity for patients with cardiovascular diseases.
- Activity tracking for cancer patients (e.g., those receiving chemotherapy) to evaluate their health state and predict chemotherapy complications.
- Tracking of physical activity among patients with rheumatic diseases (e.g., juvenile idiopathic arthritis).
- Activity monitoring for patients who underwent bariatric surgery.
6 Key Steps to Build Wearable Application
Wearable app development is usually split into 6 steps: discovery; requirements engineering and architecture design; project planning; UX and UI design; development, testing, and launch; maintenance and evolution. Below, ScienceSoft’s consultants describe a generalized plan for wearable software development.
Note: In each unique project, the duration, stage order, and activities may vary to better reflect the client's needs.
1.
Discovery
- Defining the business goals and the high-level scope of the software for wearables.
- Investigating the target market segment, competitors and identifying the target audience.
- Identifying the target wearables (e.g., market-available products, proprietary wearable devices).
- For commercial software products: productizing wearable device software.
- Defining the compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, Cures Act, GDPR, FDA, or MDR requirements).
- Conducting a risk assessment and creating a risk mitigation plan.
- Creating a business case for the software (featuring the estimated development cost, the total cost of ownership, and the expected ROI).
When the software for wearables poses a medium or high risk to the patients (which corresponds to Class II and Class III medical devices according to FDA classification), it requires FDA 510(k) submission (for the US) or CE marking. You should consider this at the very beginning of the project to prepare all the necessary documentation. In our wearable-related projects, we follow the approach to documentation described in IEC 62304:2006 (Amendment 1:2015) and ISO 13485.
2.
Requirements engineering and architecture design
- Defining the functional and non-functional requirements for wearable device software.
- Planning the feature set, including the core and secondary functionality.
- Designing a secure and scalable software architecture.
- Planning integrations with the target wearables.
- Choosing the optimal technologies (e.g., for device connectivity, backend development).
- Identifying suitable interoperability standards (e.g., HL7, FHIR, CCDA), established datasets (e.g., USCDI), and clinical terminologies (e.g., LOINC, SNOMED CT, RxNorm).
- For software products: choosing a monetization strategy (in-app purchases, ads, subscription, etc.).
- Designing a detailed wearable device software requirements specification.
3.
Project planning
At ScienceSoft, we mainly use Agile methodologies for project management. They proved to be effective even for strictly regulated domains like healthcare. Using Agile – say, Scrum or Kanban – helps adjust the wearable device software requirements and functionality on the go. It allows for more flexibility during the development and helps our clients get exactly what they need even if regulatory requirements or user needs change midway into the project.
4.
UX and UI design
- Conducting UX research with the target users of wearable device software in mind.
- Outlining user interaction with the software, building user personas and scenarios.
- Designing UX wireframes to illustrate user interaction with the software.
- Creating visual identity and design elements for the software.
- Creating a UI prototype.
5.
Development, testing, and launch
Building the server side of the software and the APIs for wearable device integration.
- Developing the software UI based on the prototypes.
- Implementing security and compliance features (e.g., MFA, role-based access, end-to-end data encryption).
- Conducting end-to-end testing, including functional, integration, performance, security, and accessibility testing.
- Conducting a HIPAA compliance risk assessment (for the US).
- Launching the software or uploading the custom mobile application for wearables to the App Store (for iOS) or Google Play Market (for Android).
6.
Maintenance and evolution
- Supporting and maintaining the wearable device software (e.g., implementing new security measures, addressing user issues, optimizing cloud resource consumption).
- Introducing new software features and adjusting the UX/UI based on user feedback and the changing business needs.
Successful Implementation of Wearables by US Hospitals
- Desert Oasis Healthcare, California, introduced remote patient monitoring with wearables for patients with heart failure. 70% of remotely monitored patients reported that the program enabled them to better manage their condition. 90% said that RPM complements their offline appointments and makes them more valuable.
- After implementing wearable technology for at-risk patients, Augusta University Medical Center, Georgia, reported that patient deterioration into preventable cardiac or respiratory arrest reduced by 89%.
Wearable App Development Costs
Cost drivers to consider:
- Functional scope.
- Non-functional requirements (e.g., security, performance).
- Compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, FDA).
- Mobile development approach (native vs. cross-platform).
- Number and complexity of device integrations.
- Uniqueness of UX/UI design.
The costs of wearable app development may vary from $50,000 to $400,000+, depending on the software type and functional scope.
$50,000–$150,000
For a fitness app with basic functionality:
- Manual activity logging.
- GPS tracking.
- A premade collection of training and educational resources.
$200,000–$300,000
For a fitness app that also supports:
- Tailored workout plans based on each user’s physical condition, goals, preferences, etc.
- Progress tracking with gamification elements.
$200,000–$400,000+
For wearable medical device software that enables:
- Patient monitoring.
- Clinical decision support.
- Virtual appointments.
- EHR integration.
Services by ScienceSoft
ScienceSoft delivers software for wearable medical devices leveraging its 20 years in health IT and an ISO 13485-certified quality management system. Our top priority is driving project success no matter what while keeping to the agreed time and budget and responding to uncertainties agilely.
Consulting services
- Plan functionality of IoT software for wearables based on your business needs.
- Map user journeys to plan UX and UI.
- Design high-level architecture, APIs for integrations with medical systems.
- Plan integrations with wearables.
- Estimate the cost, ROI, and software delivery timelines.
- Guide to HIPAA, HITECH, FDA compliance.
Wearable app development
- Conceptualize software for wearables based on your business needs.
- Create feature lists for each user group.
- Plan software architecture and integrations with wearables.
- Develop the MVP and roll out secondary features based on the feedback.
- Ensure compliance with required regulations (HIPAA, the Cures Act, HITECH, etc.).
About ScienceSoft
In healthcare IT since 2005, ScienceSoft is an international wearable app development company with headquarters in Texas, US, and offices in Europe and the Gulf Cooperation Council. ScienceSoft has ISO 13485 certified quality management system for developing software for medical devices and SaMD and is ready to design and build remote patient monitoring software leveraging the medical Internet of Things.