Smart Medical Devices
Software Architecture, Features, Tech Stack
Since 2005 in healthcare software development and since 2011 in IoT, ScienceSoft is fully equipped to advise on and implement IoT-based medical device software.
The Essence of Smart Medical Devices
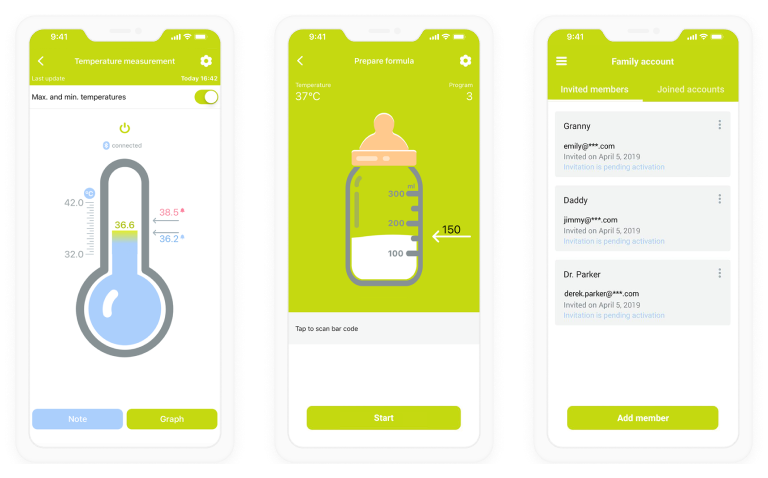
Smart medical devices are those that integrate advanced technology and computational capabilities to enhance medical diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring. They utilize sensors, AI, machine learning, and connectivity features to collect, analyze, and interpret patients' health data, aiming to facilitate personalized and proactive care, improve healthcare outcomes, and empower both patients and medical professionals with actionable insights and decision support. Examples of such devices include ECG monitors, spirometers, insulin pens, inhalers, and many more.
Smart Medical Devices Market Overview
The global smart medical devices market is expected to amount to $168 billion by 2034 at a CAGR of 12.3%. The popularity of smart medical devices is based on the need to closely check such chronic diseases as diabetes, asthma, COPD, etc., and limited access to on-site medical monitoring due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
How Software for Smart Medical Devices Works
Architecture
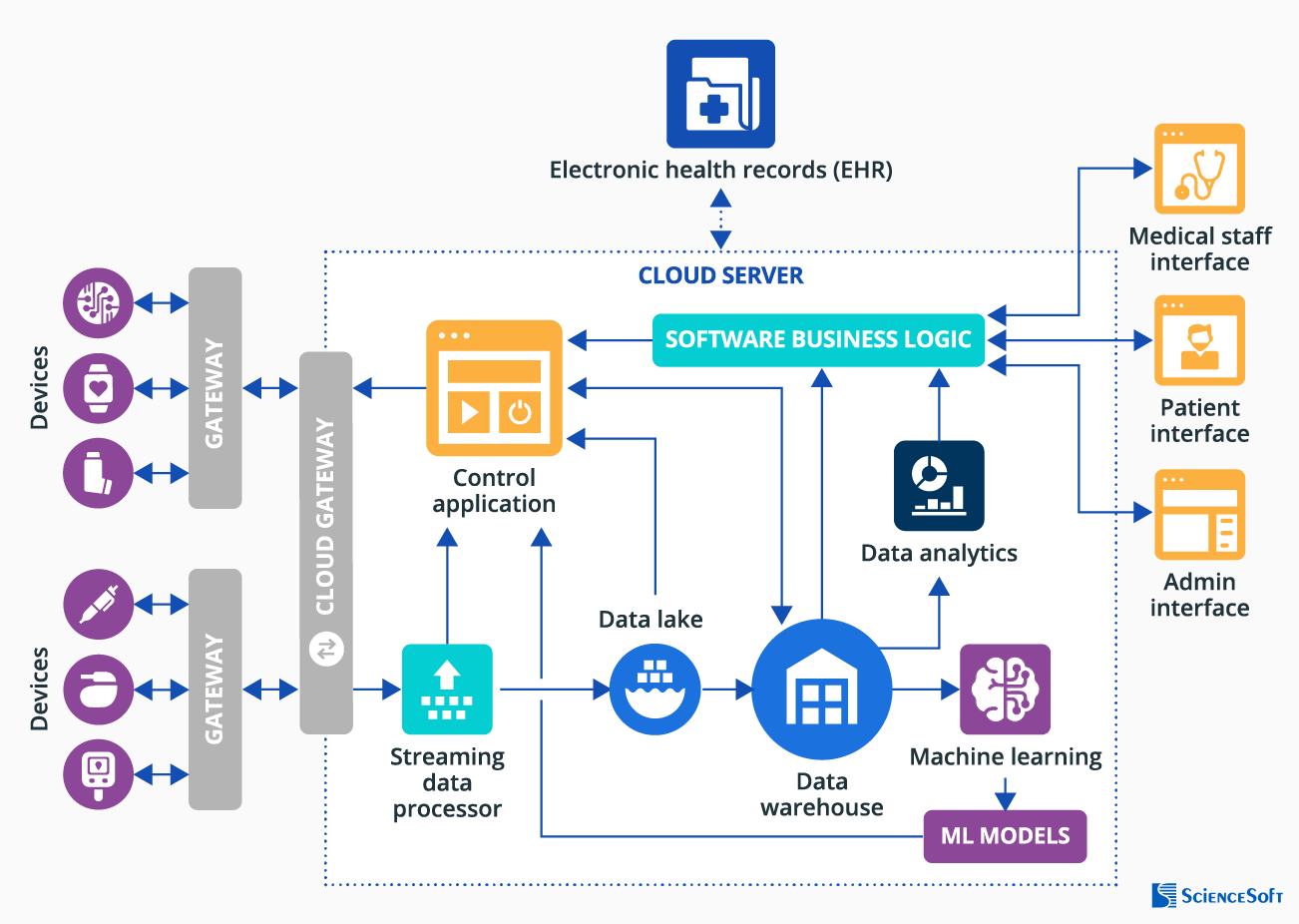
- Smart medical devices – to collect patient data or deliver therapy; equipped with connectivity capabilities (e.g., via Wi-Fi, NFC) and actuators to trigger a set of pre-programmed actions (e.g., for insulin pumps to adjust insulin dosage).
- Gateways – to filter, preprocess, and transfer data from the patients’ devices to the cloud, transmit control commands to the smart medical devices, etc.
- Cloud gateway – to compress data from smart medical devices and transmit it from gateways and the cloud IoT server in a secure and efficient way.
- Streaming data processor – to transmit the input data from smart medical devices to the data lake and control apps.
- Data lake – to store PHI data collected by smart medical devices in its natural format.
- Big data warehouse – to store structured data for further analysis of patient progress, symptoms, etc.
- Data analytics – in-depth analysis of collected patient health parameters or therapy device use patterns to spot trends and produce insights for further diagnosing, treatment or lifestyle adjustments, etc.
- Machine learning module and ML models – to recognize certain patterns in patient symptoms or vitals and create a model for a control application to improve patient care precision and efficiency (e.g., to improve heart failure therapy delivered by implantable cardiac defibrillator).
- Control application – to send commands to actuators installed in smart medical devices to trigger device actions.
- Software business logic – to provide medical device monitoring data to patients and doctors, record new device configurations, etc.
- Medical staff interface – to enable nurses, doctors, etc., to access the patient health monitoring data, get alerts on critical changes in it, configure threshold vitals parameters for alerts, adjust dosages of medications, view the insights on patient health state based on smart device data analysis, etc.
- Patient interface – to allow patients to view their health parameters (e.g., heart rate, glucose levels) and the state of a connected device via a mobile app, get alerts on suspicious health parameters, etc.
- Admin interface – to view the list of current software users (patients and medical staff), manage access to the system, etc.
- EHR integration – for an integrated view of patients’ medical history (chronic conditions, allergies, etc.), etc.
Use cases
Medical staff can monitor the vitals of patients with chronic medical conditions (e.g., COPD, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases) provided by smart medical devices to spot slow or abrupt changes in the health state and adjust treatment routines.
Remote care delivery
Patients can get therapy using smart therapeutic devices (e.g., insulin pens, smart inhalers, smart gloves for motor functions rehabilitation). The medical staff gets data on therapeutic device use (e.g., asthma treatment delivery, insulin injection), metrics on patient performance during physical therapy sessions, the patient recovery process, etc.
Patient diagnostics
Based on the analysis of continuously collected patient health data (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure), doctors can make informed decisions on patient diagnosis and further treatment, assess risks of disease progression, etc.
Medication plan adherence monitoring
With data from devices like smart pill bottles or smart insulin pens, doctors can remotely track patients’ medication intake (the dosage, the missed medications, etc.), check the medication adherence and efficiency, tune recommended dosage. Patients can also get automated notifications to take medications in time.
Paramedics patient monitoring
When the ambulance is delivering a patient to the hospital, wireless patient monitoring solutions allow doctors in the hospital to track a patient’s condition in real time and plan the patient care (including emergency surgeries).
Sports medicine
During the training, athletes can use wearable medical devices (e.g., heart monitors) for sports physicians to get a real-time health state and health risks assessment, an athlete’s performance data, and issue recommendations on the training plan.
Essential functionality
Technology Elements
Device connectivity
Cloud services
Real-time data streaming

Data lakes
Challenges for Smart Medical Devices Software and Ways to Overcome Them
Challenge #1
There is a risk of legal penalties if the personal health information (PHI) collected and transmitted by smart medical devices gets compromised.
Check out the solution
Challenge #2
Improper usage of smart medical devices can affect the accuracy of remote patient monitoring data.
Check out the solution
Investments and Key Cost Drivers
General investment size factors
- Scope and complexity of medical device software features.
- A number of smart device types connected to IoT software.
- Device connectivity technologies used (e.g., NFC, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth).
- The number of software user roles (e.g., patient, doctor, nurse).
Additional investment size factors
- Costs of smart medical devices.
Operational costs
- Cloud services usage (e.g., cloud data storage and analytics).

From ScienceSoft’s experience, an average cost of healthcare software connected with smart medical devices starts from $200,000 to $250,000+ (for a solution comprising a cloud and user application for one type of medical devices).
Need a tailored cost estimation for your software for medical devices?
Estimate the Cost of Your Medical Device Software
Please answer a few questions to help our healthcare IT consultants accurately assess your needs and calculate a personalized quote quicker.
Thank you for your request!
We will analyze your case and get back to you within a business day to share a ballpark estimate.
In the meantime, would you like to learn more about ScienceSoft?
- Project success no matter what: learn how we make good on our mission.
- Since 2005 in healthcare IT services: check what we do.
- 4,200+ successful projects: explore our portfolio.
- 1,400+ incredible clients: read what they say.

Software for Smart Medical Devices by ScienceSoft
Being ISO 13485 certified, ScienceSoft is well-equipped to power up smart medical devices with robust medical IoT software in line with the requirements of the FDA and the Council of the European Union. You set goals, we drive the project to fulfill them in spite of time and budget constraints, as well as changing requirements.
Consulting
What we do:
- Outline the functionality of future IoT software for smart medical devices based on your business needs.
- Create a high-level architecture design (featuring standardized HL7 or FHIR APIs for the required integrations with medical systems) and detail integrations with chosen smart medical devices (e.g., via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth).
- Define applicable interoperability and terminology standards (e.g., USCDI, CCDA, SNOMED CT, LOINC, RxNorm) to ensure data consistency throughout the ecosystem.
- Estimate the cost, ROI, and software delivery timelines.
- Provide an action plan for compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, MDR, and FDA regulatory requirements.
Development
What we do:
- Conceptualize IoT software for smart medical devices based on your high-level or detailed requirements.
- Create a comprehensive software feature list.
- Plan a flexible and scalable software architecture and integration with medical devices.
- Develop the MVP with priority features in 3-6 months and roll out other functionality upon the agreed schedule.
- Ensure IoT software compliance with required regulations (HIPAA, GDPR, the Cures Act, etc.).
- Maintain software and work on its evolution (if required).
About ScienceSoft
ScienceSoft is a US-headquartered international IT consulting and software development company with 14 years of experience in IoT and 20 years in healthcare software development. Holding ISO 13485 certification, we create software for smart medical devices according to the requirements of the FDA and the Council of the European Union.