AI Chatbots for Healthcare
Secure and Controlled AI to Lower Administrative Load and Increase Care Accessibility
In AI development since 1989 and healthcare IT since 2005, ScienceSoft engineers AI chatbots, virtual assistants, and agents for healthcare providers and software product companies. Our solutions help automate patient communication, administrative tasks, and routine operational workflows while remaining safe, compliant, and easy to integrate.
Medical Chatbots With AI in Brief
AI chatbots (conversational agents) for healthcare are intelligent digital assistants that can handle patient and staff interactions across both clinical and operational workflows, adapting their responses based on context, intent, and risk level rather than following fixed scripts. In practice, they can:
- Act as a 24/7 digital front door for patient self-service, including basic symptom checking and first-line triage (AI identifies high-risk cases early and hands them off to emergency services right away).
- Act as virtual care assistants, helping patients follow treatment plans or manage chronic diseases.
- Take over high-volume administrative work, such as appointment scheduling, reminders, pre-procedure instructions, and pre-visit data collection.
- Support clinical staff with quick chart lookup, coding, and documentation shortcuts.
- Switch between multiple languages and dialects in text and audio conversations, and document them in standardized, interoperable formats.
AI healthcare chatbots, virtual assistants, and agents can complement patient-facing solutions (telemedicine apps, patient portals, mobile health apps) and clinical software (EHRs, hospital apps, clinical decision support systems). They help increase access to care, improve patient engagement, and offload repetitive work from clinicians and admin staff.
Essential Market Insights
The global healthcare chatbot market was estimated at $1.2 billion in 2024. By 2030, it is forecasted to reach $4.3 billion, growing at a CAGR of 24%. The broader market for conversational AI in healthcare was already at $13.68 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $106.67 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 25%.
The growth is primarily driven by the need to improve patient engagement, increasing adoption of telehealth and remote care, and advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and AI technologies.
Medical Chatbots, Explained
Architecture
Below, ScienceSoft's solution architects share the architecture of a real AI voice agent engineered for one of our projects. The voice agent is built to handle inbound and outbound appointment scheduling calls and can be adapted to perform other tasks, such as providing pre-procedure instructions.
Since the agent is meant for voice conversations, this architecture includes components for real-time voice processing and generation, but a similar architecture with fewer components can be used for text-based AI agents as well. Additionally, the architecture in the example is built on AWS services, but the same pattern can be reused with other cloud platforms or in an on-premises setup.
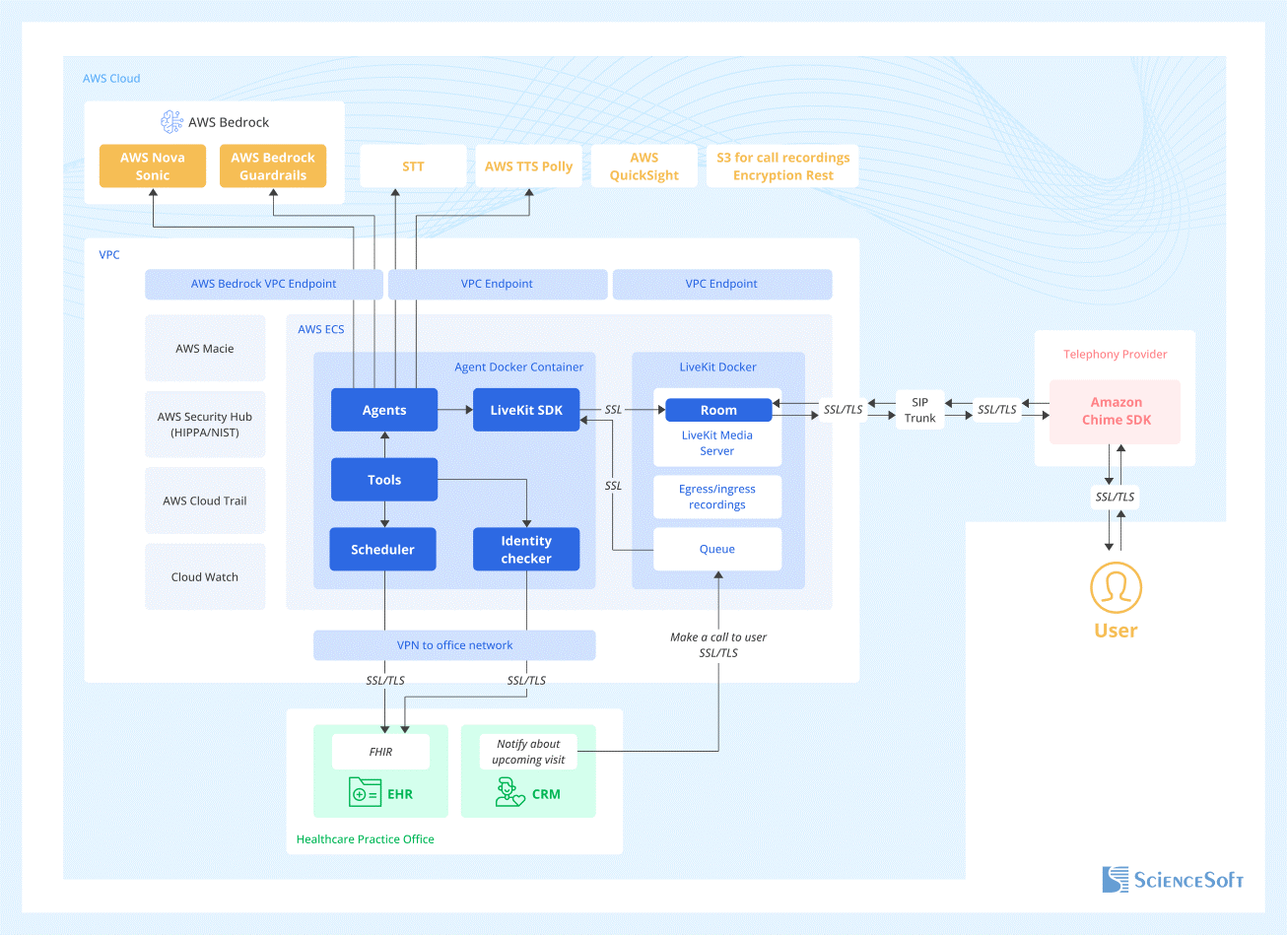
In this example, the voice agent is deployed in a segregated Amazon Virtual Private Cloud using HIPAA-eligible services under a BAA. The agent connects to hospital systems such as EHR, CRM, and practice management via FHIR-based APIs and relies on LiveKit to handle real-time audio calls.
For speech, the agent uses Amazon Nova Sonic. This speech-to-speech model supports bidirectional streaming via a single API, enabling it to listen and reply almost instantly without noticeable pauses. Patient calls come into a dedicated phone number managed by the Amazon Chime SDK, then are routed via SIP trunking to LiveKit.
LiveKit opens a separate “room” for every call, adds both the caller and the AI assistant as participants, and mixes their audio into a natural, live conversation. At the same time, it records the call and securely stores it in Amazon S3. These recordings are later used to generate transcripts, support compliance reviews, and power analytics on call quality and patient engagement.
Security and monitoring mechanisms are built in. Amazon Bedrock Guardrails acts as an AI firewall, continuously checking each conversation for unsafe content, scope violations, and potential PHI leaks. AWS CloudTrail logs every API call and action for full traceability. Amazon Macie scans S3 data for unencrypted or exposed buckets, while VPC Endpoints keep all traffic between the agent and AWS services on private networks instead of the public internet.
The platform is designed to scale as demand grows. One AI instance serves one call at a time, but the orchestration layer can spin up many instances in parallel to handle peak volumes.
During routine calls, each key operation (ID checks, scheduling, etc.) is performed by a dedicated tool that controls the assistant’s behavior. For example, one tool verifies a patient’s identity against the EHR, another checks available time slots, and another writes confirmed appointments back into the scheduling system. This design makes the solution safer and easier to govern: each operation has a clear purpose, limited permissions, and is fully logged for monitoring and audit. Clear tool separation also serves as a safeguard against the agent going “off script.”
See How It Works in Practice
Medical AI Voice Assistant for Appointment Scheduling
See how the agent built on the architecture presented above handles a real call by Vadim Belski, ScienceSoft’s Principal Architect and Head of AI.
How ScienceSoft’s Healthcare Clients Apply AI Chatbots
AI chatbots (conversational agents) deliver the fastest payback with minimal regulatory burden for providers when used for low-risk, high-volume administrative tasks such as patient self-service, scheduling, and document management.
Digital front door
A virtual assistant serves as the starting point for a patient journey on a hospital website, patient portal, or mobile app. The patient explains what they need, and the assistant asks a few clarifying questions before walking them through the next steps (e.g., scheduling, triage, or intake). The goal is to complete the request in a single interaction, without the patient having to guess which department to contact or where to click next. A similar AI agent can also be used in info kiosks to guide walk-in patients to the right department or service desk.
Routine administrative requests
A chatbot or voice agent handles routine administrative requests, such as FAQs about services, hours, locations, and basic insurance and coverage questions. It can also handle simple status checks that require ID verification (“Is my bloodwork ready?”). Whenever the assistant goes below a preset confidence threshold (e.g., in case of complex or unclear questions), it escalates the request to the human staff.
Appointment scheduling
A chatbot or voice agent helps patients book, reschedule, and cancel appointments via chat or inbound and outbound calls. It first verifies the patient’s identity, then selects the appropriate provider and time slot, and records the appointment in the EHR or practice management system. It can also send automated reminders to help reduce no-shows.
Pre-visit intake and registration
A virtual assistant interviews patients to collect structured pre-visit information, including demographics and contact details, insurance, medical history, allergies, and current medications. This way, the assistant can ensure all key fields are completed, reducing the time spent filling out forms at check-in. Collected data can be saved to the EHR or the patient portal for staff review.
Pre-procedure instructions
An agent contacts patients before a specific procedure (e.g., MRI, endoscopy, surgery). It verifies the patient’s identity before sharing any other details and explains preparation steps (fasting, medications, documents, and arrival time). The assistant also answers clarifying questions and escalates to human staff when needed.
First-line triage
A chatbot or voice agent asks patients structured questions about symptoms, highlights red flags like chest pain, suggests the level of care (emergency vs. urgent vs. routine), and routes patients according to your organization’s protocols and escalation criteria, without making any final clinical decisions. AI can also alert emergency services and reassure the patient if emergency care is needed.
Post-operative support and chronic disease management
A virtual assistant supports patients after surgery or in chronic disease management. It sends short scheduled messages that ask how the patient is doing and reminds them about medications, lab tests, and follow-up visits. It can also answer routine patient questions, collect symptom updates (including from wearables where relevant), and summarize important changes for clinicians.
Post-visit surveys
A chatbot runs short questionnaires after visits to capture patient-reported outcomes and satisfaction. It writes structured results back into the EHR or analytics tools. The assistant does not provide medical advice or change care plans.
Virtual assistant for doctors and nurses
A virtual assistant can be embedded into the apps for clinicians or nurses to speed up their routine work. It can quickly pull key facts from the chart (recent labs, meds, allergies, diagnoses), answer “where do I find…?” questions, and pre-fill documentation templates based on structured data or short dictation.
We help healthcare providers implement assistive AI tools that are intentionally designed not to qualify as Software as a Medical Device (SaMD). These solutions are explicitly restricted from offering medical advice such as diagnoses, treatment decisions, or clinical recommendations. As a result, providers can deploy custom AI agents for administrative and workflow support without triggering the regulatory obligations associated with SaMD or regulated clinical decision support (CDS), including FDA clearance, CE marking, and similar approval processes.
Technologies Powering Healthcare Chatbots
ScienceSoft's software engineers and data scientists prioritize the reliability and safety of medical chatbots and use the following technologies, tailoring the stack to your existing infrastructure and regulatory needs if needed.
The Challenges Ahead and Ways to Solve Them
Below are practical recommendations from ScienceSoft on how to mitigate key challenges when implementing AI in healthcare.
Challenge #1: Hallucinations
LLM-based systems can hallucinate, misinterpret ambiguous patient input, or sound overconfident about uncertain recommendations. In healthcare, this creates real risks: giving advice outside scope, failing to escalate urgent cases, or implying clinical decisions without proper review.
Solution by ScienceSoft:
- Pick the right use case where being wrong will not harm patients and where the conversation can be tightly structured (e.g., scheduling, FAQs, or intake forms). A clear scope (“do these X things only”) leaves less room to guess and helps avoid hallucinations.
- Give the agent the right data. The data should be available, clean, approved, up-to-date, and easy to retrieve.
- Use the right technology (models, agents, platforms) so the agent cannot go off-script. Choose a model that is reliable enough for the job, and configure it correctly. Make the agent use tools and structured steps. Tools act like guardrails: the agent can only perform approved actions and must follow a defined flow. Add platform guardrails, logging, monitoring, and access controls to block risky outputs, prevent the agent from seeing or using data it should not, and catch issues early.
- Apply the right governance: test with real scenarios before launch, monitor performance after release, and use review and change control for any model or content updates so quality does not drift and new hallucinations are not introduced.
Challenge #2: PHI security
Medical chatbots access large volumes of PHI and must comply with HIPAA, GDPR (the EU), PDPL (GCC), or other jurisdictional regulations.
Solution by ScienceSoft:
- Ensure PHI is processed only by vendors that have signed the required agreements (e.g., a BAA with cloud and AI model providers), and confirm that LLM vendors’ data-handling practices meet healthcare compliance requirements.
- Deploy AI in audited, encrypted, access-controlled infrastructure.
- Apply data minimization so the assistant receives only what it needs for the current task, and enforce RBAC so it can only perform approved actions.
- Use conversation guardrails: verify identity before sharing any patient-specific details, restrict responses to general information when the user is not verified, and block requests that could expose PHI to the wrong person.
- Log and monitor all PHI access and actions (e.g., using CloudTrail, CloudWatch, Security Hub, Macie, or equivalents) to support audits and incident investigations.
- Perform regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing, backed by incident response planning and ongoing compliance reviews.
We recommend taking a phased approach: start with clearly scoped, low-risk tasks that boost staff productivity and reduce administrative load, such as appointment scheduling or pre-procedure instructions, and then iteratively add more ‘agent-like’ capabilities as the assistant proves to be safe, accurate, and well-accepted by users.
How Much Will an AI Chatbot Cost You?
The cost of a medical AI chatbot (conversational agent) can range from $15,000 for a simple informational assistant to over $300,000 for an advanced AI agent that communicates with different systems and handles complex, multi-step workflows end-to-end. The investment depends heavily on how smart and integrated you want your chatbot to be, your compliance landscape, and whether you need to add voice conversations alongside text-based ones.
Major cost factors of AI chatbots in healthcare
Development costs
- Intended use and functionality of a chatbot.
- The number of data sources to process, data quality.
- ML algorithms' complexity and expected accuracy.
- Compliance-associated costs (e.g., implementation of HIPAA security measures, FDA registration for healthcare chatbots with SaMD functionality).
- UI requirements.
- Required integrations (e.g., with EHR, third-party telehealth solutions, scheduling modules).
Operational costs
- AI maintenance costs.
- Infrastructure costs.
Approximate cost ranges
$15,000–$60,000
For a basic informational healthcare chatbot that answers patient questions about a clinic’s services, doctors, locations, procedures, and pricing, using knowledge-based responses with safety guardrails. Typically, it has no integrations with hospital systems.
$80,000–$100,000+
For an operational agent (or a coordinated agent system) for front-desk and call-center tasks that can handle appointment scheduling and confirmations, share directions, send reminders, and deliver pre-visit instructions via chat or voice, escalating to staff when needed. Typically, it integrates with a PMS or scheduling system.
$150,000–$300,000+
For an advanced clinical & operational agent that runs longer, context-aware conversations and completes complex workflows end-to-end (for example, first-line triage combined with scheduling), with stronger orchestration and safety controls. Typically, it integrates with multiple systems, such as PMS + EHR.
Ready to Implement a Medical AI Chatbot?
With 36 years in AI and 20 years in healthcare IT, ScienceSoft builds HIPAA-compliant healthcare chatbots, virtual assistants, and voice agents that are safe, efficient, and deeply integrated into your workflows.
Featured Expert Talk
AI-Powered Intake & Triage | Presentation at WHX Tech 2025
Presentation by Hadeel Abu Baker, Senior Healthcare IT Consultant at ScienceSoft, from WHX Tech 2025 (formerly Arab Health) in Dubai. Hadeel shows how LLM-powered healthcare chatbots can enable self-serve patient intake and intelligent triage and scheduling.











