Ultimate Guide to Profound IoT Application Testing
In IoT since 2011, ScienceSoft has been providing outsourced QA services for 23 years and software testing services for 36 years.
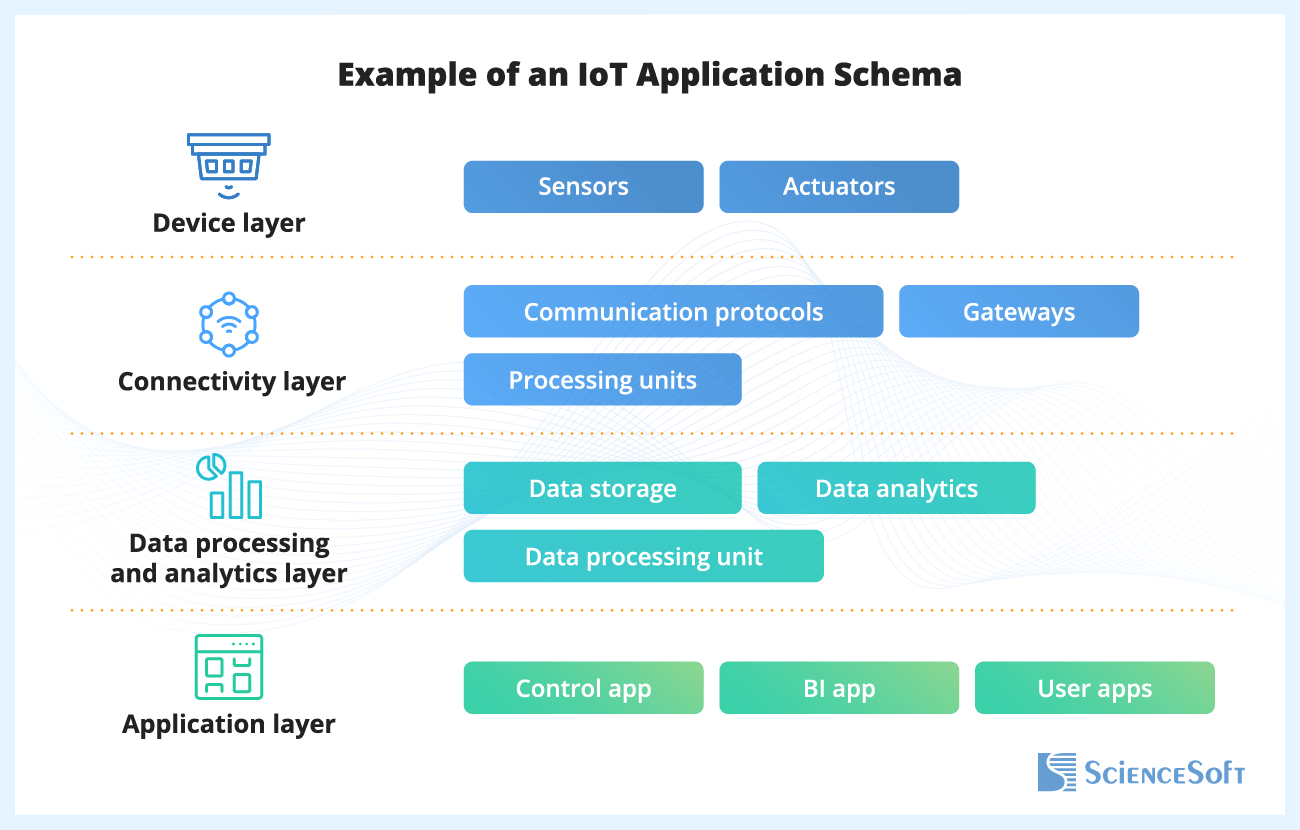
IoT App Testing: the Summary
IoT testing aims to check an IoT system’s performance, efficiency, and safety. It covers performance testing to learn how the system handles high-volume streaming data, security testing of the app, gateway, and IoT devices, functional and integration testing specific to distributed architectures.
Sample lineup of an IoT testing team: a test lead and test automation lead, manual and test automation engineers, a cybersecurity expert.
With 14 years of experience in IoT solutions delivery, ScienceSoft knows all subtle aspects of IoT solutions and offers customers high-quality and comprehensive IoT testing services.
IoT App Testing Plan
The actual IoT testing setup plan will vary depending on the IoT solution’s requirements, the chosen development model, the current SDLC stage of your IoT project.
However, ScienceSoft’s testing experts have outlined some common stages to go through.
1. Designing IoT application testing process
A QA manager should be assigned as early as requirements specification development to ensure IoT functional requirements are designed in a testable way. Typically, the requirements are drawn up in a form of user stories.
The QA manager should decide how often a future QA team and the IoT development team need to collaborate to ensure relevant test cases’ prioritization, efficient defects’ management and regression testing.
Then, the QA manager should carefully consider possible IoT testing risks and design an all-around risk mitigation plan for your project. Possible risks include:
- Non-scalable, incomplete, improperly configured IoT test environment not fully reflecting the actual hardware configurations, lacking simulators or virtualization tools.
- Improper test automation frameworks’ choice and configuration.
- Lack of IoT testing talents to promptly create and execute test cases addressing potential IoT-specific quality issues.
2. Preparing for IoT app testing
Preparation for the IoT application testing process differs based on the sourcing model you opt for: in-house testing or outsourced testing.
2.1 Preparing for in-house IoT app testing
The assigned QA manager designs an overall IoT test strategy and plan, including effort estimation. As an IoT system’s architecture is prone to changes, the QA manager needs to regularly revise and update the test artifacts accordingly.
Then, the manager assembles an IoT testing team or teams.
| Expert tip: ScienceSoft’s IoT consultants note that you may require several testing teams to cater to different IoT application modules. The actual number of testing teams will depend on the application’s architectural complexity. |
Besides, to avoid time- and data-intensive repetitive test cases execution, an IoT testing project requires a balanced combination of manual and automated testing. A separate team should be assembled to take over automated testing.
| Best practice: ScienceSoft’s testing experts usually automate integration and regression testing as well as critical functional test cases, while performance testing is inherently automated. Still, IoT security, usability, and the majority of functional test cases should be performed manually. |
Testing types that our experts consider relevant for any IoT application test plan
Test engineers validate the functionality of:
- Each IoT app component in isolation, sending test input events to each component to validate its output and behavior against requirements.
- End-to-end workflows of the entire IoT application.
- IoT app’s UI components, as soon as the UI is ready.
- Entire IoT system under specific network configurations and compelling real-life environments, during IoT field testing.
Test engineers validate:
- Flawless communication between different IoT app components and their tech stack compatibility.
- End-to-end enterprise workflows, as IoT solutions are often integrated with enterprise solutions (e.g., asset tracking and monitoring, field service applications, ERP, CRM, a data warehouse).
- Quality data transfer between the IoT app and its third-party integrations to ensure that the data changed in one system is altered accordingly in all the connected systems, and the relevant change history is available.
To ensure an IoT application’s resilience to hacker attacks, a cybersecurity engineer reviews the security of the system architecture, performs the vulnerability assessment and penetration testing.
To safeguard the entire IoT system’s cyber-security, you can also opt for the security testing of:
- IoT field gateways (validating the communication channel security and proper data encryption).
- IoT devices (examining the devices’ firmware and its upgrade process for vulnerabilities, reviewing the boot process from security perspective).
Additionally, your IoT test plan may include performance testing to:
- Measure the IoT app’s performance metrics (e.g., latency, throughput, response time, CPU utilization).
- Validate the stability of the entire application’s functioning and graceful degradation under stress load, changing operational and network conditions (like intermittent failures or the loss of network connectivity).
- Consider the effects of thousands of devices continuously sending and receiving data.
| Expert tip: Not all popular performance testing tools support IoT-specific communication protocol standards (e.g., MQTT, XMPP, CoAP, SOAP), so ScienceSoft’s performance test engineers recommend carefully considering the compatibility of your IoT app’s tech stack with the capabilities of the preferred performance testing tool. |
2.2. Vendor selection for outsourced IoT testing
If you realize your in-house resources are insufficient for overarching IoT app testing, you can consider its outsourcing, as it proves to be more cost-effective than hiring and training the additional test engineers on payroll.
To select a fitting vendor, you should:
- Design a comprehensive request for proposal (RFP) in line with your IoT solution’s specific requirements and architecture.
- Look for QA vendors with successful IoT testing projects in your domain.
- Consider the testing vendors’ tech stack and availability of human resources to meet your needs.
- Shortlist 3-5 vendors with eligible experience and resources.
- Share your IoT testing RFP with shortlisted vendors to get their cost estimations and an IoT testing presentation. This way, you can understand the vendors’ approach to an IoT testing strategy, testing teams’ lineup, testing toolkit, the planned test automation involvement.
- Negotiate an SLA and IoT testing cost with the matching vendor.
3. IoT testing launch
To get IoT testing started, testing teams design test cases and develop test scripts. Then, to check the end-to-end entire system’s functioning, an IoT test lab is created with the help of chosen service virtualization tools and simulators.
| Best practice: ScienceSoft’s IoT testers use real IoT devices during IoT field testing. |
Consider Professional IoT Testing Services
With 36 years in software testing services and 14 years in IoT solutions delivery, ScienceSoft’s QA experts can promptly get into your IoT solution’s specifics (within 3 weeks) and ensure its high quality.
IoT testing consulting
ScienceSoft’s consultants will:
- Design a general test strategy and plan for the entire IoT application and test plans for each module.
- Create a test automation architecture for IoT system components.
- Help select optimal IoT testing frameworks and tools.
- Provide estimation and costs breakdown for IoT testing efforts.
- Advise on an optimal sourcing model for your IoT testing project.
- Perform analysis and mitigation of potential IoT application testing issues, in case of an ongoing project.
IoT testing outsourcing
ScienceSoft’s testing experts will:
- Design the IoT testing process: a test strategy and plan for the entire IoT app and for specific modules; a test automation architecture with regard to the specifics of each IoT app component; a tailored testing toolkit.
- Set up and maintain the IoT test lab, generate and manage IoT test data.
- Develop, execute, and maintain IoT test cases and scripts.
- Create a reusable automated regression test suite for your IoT system.
About ScienceSoft
- 14 years in IoT testing services.
- 24 years in test automation.
- ISTQB-certified testing professionals.
- ISO 27001-certified to ensure security of customers’ sensitive information.
- Strong QA management, able to coordinate and control project-wide/enterprise-wide QA and testing.
ScienceSoft conducted penetration testing on our iOS and Android IoT apps as well as 2 IoT smart devices (indoor and outdoor security cameras), which are powered by Tuya. The apps and the devices alike were tested thoroughly and rigorously. Throughout the testing process, ScienceSoft’s team was always very responsive and very helpful. We were much satisfied with the professional performances of ScienceSoft and we are more confident of our system, as it was rated in the high security level, software and hardware, by ScienceSoft. We do appreciate the professionalism of ScienceSoft people.
Jemma SHI, Security and Compliance Department, Tuya
Typical Roles in Our IoT App Testing Teams
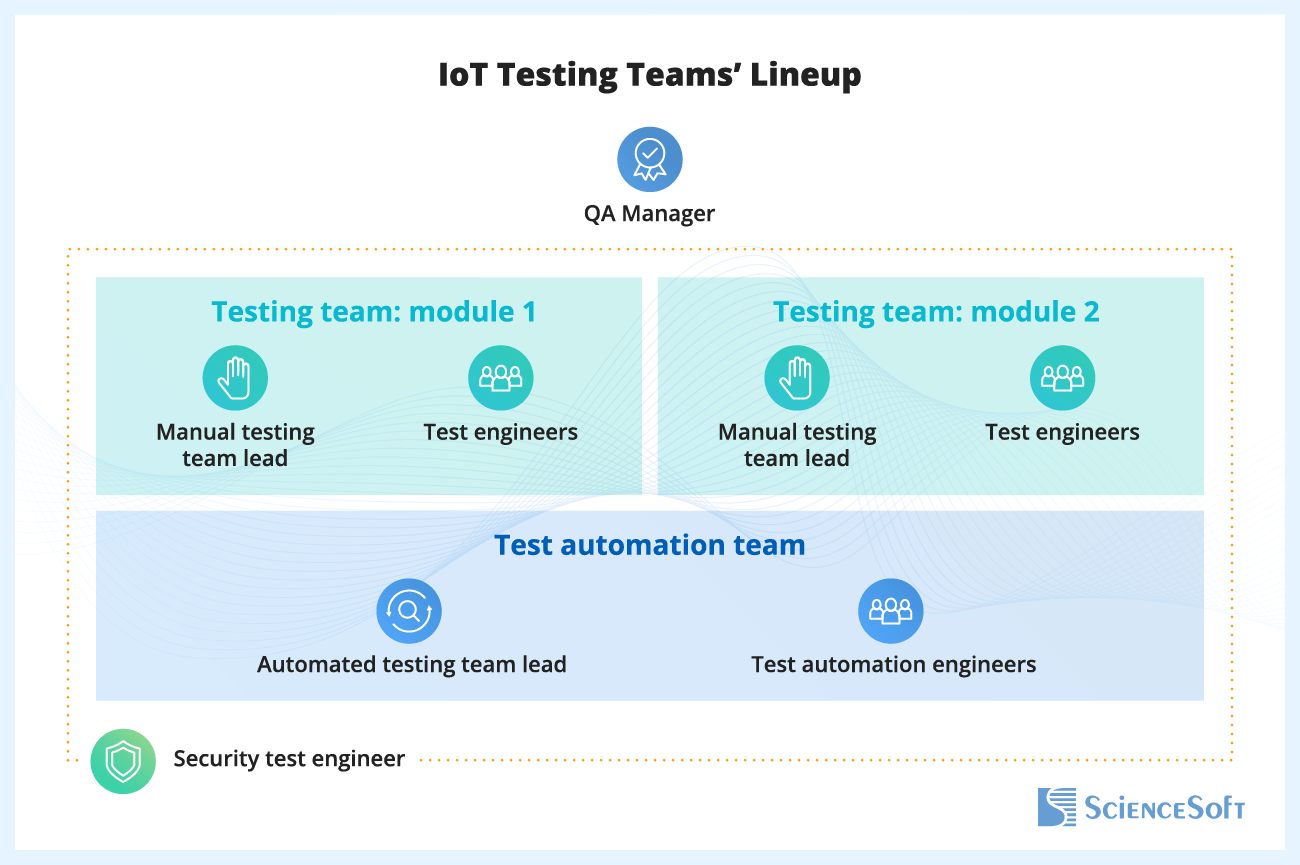
ScienceSoft’s IoT testing experience shows that testing a complex IoT system may require several testing teams, each responsible for a system’s specific module. Below we describe basic testing project roles.
QA manager (for projects involving several testing teams)
- Helps design IoT requirements in a testable way.
- Develops a robust IoT test strategy and plan with regard to the solution’s requirements and architecture.
- Gathers IoT testing teams.
- Decides on IoT test management software.
- Guides the IoT test lab setup process and acquisition of its components.
Test lead (one per each testing team)
- Designs a test plan for the corresponding IoT app’s component.
- Guides test engineers, measures and analyzes their performance.
- Solves testing process issues and comes up with relevant testing process improvements.
Note: the actual number of test engineers within each testing team will be subject to the IoT module’s functional and tech complexity.
Test engineer
- Designs and maintains IoT app’s test cases.
- Executes manual testing.
- Reports defects via prescribed tools.
Test automation lead
- Decides which IoT integration and functional test scenarios suit test automation and will comprise an automated regression test suite to be run after each change of an IoT system.
- Designs test automation architecture for the IoT application.
- Chooses test automation tools and frameworks relevant for the IoT solution under test.
- Collaborates with the IoT architect and developers to ensure test scripts’ maintainability and granularity.
Test automation engineer
- Configures relevant test automation tools.
- Develops, executes, and maintains IoT automated integration and regression test scripts.
- Reports defects after analyzing test results.
Cybersecurity engineer (for the entire project)
- Develops a threat model for the IoT system to proactively outline potential security issues.
- Carries out code audit and vulnerability assessment of the IoT solution.
- Evaluates IoT devices’ access security and firmware configuration, provides instructions on how to mitigate the revealed issues.
- Performs penetration testing of the IoT solution in line with OWASP’s top 10 security risks check list for IoT systems.
IoT Testing Sourcing Models
QA management and testing teams are in-house
- Full control over the IoT testing processes.
- Potential shortage of in-house testing professionals.
- Possible lack of competence in certain IoT testing specifics or testing types (e.g., integration, security, performance testing, data quality checks).
QA management is in-house; testing teams are completely or partially external
- Possibility to balance IoT testing costs by timely scaling up and down the number of testing team members proficient in IoT testing specifics.
- A skilled QA manager is mandatory (to design and plan the IoT testing process, guide and regularly evaluate the IoT testing advance and the efficiency of external testing teams).
QA management and testing teams are outsourced
- Experienced QA management and IoT testing talents.
- Full responsibility for IoT testing project management and delivery lies on vendor.
- Possible vendor risks.
- Potential communication issues between the outsourced QA teams and in-house IoT development team and test engineers, if any.
Benefits of IoT App Testing with ScienceSoft
Quick start
ScienceSoft’s testing specialists will get into your IoT testing needs within 1-3 days; set up the test environment, write test scenarios and test scripts and start automated testing activities within 3 weeks.
Testing transparency
Through IoT apps testing process, ScienceSoft provides regular tailored reports based on a predefined set of KPIs.
Complete security
Being ISO 27001-certified, we guarantee the safety of your data. ScienceSoft uses VPNs, SSLS, and encryption protocols combined with our internal security measures to protect your sensitive information.
Tools ScienceSoft Uses for IoT Application Testing
Automated UI testing tools
API testing tools
Performance testing tools
Security testing tools
CI/CD tools
IoT Testing Costs
ScienceSoft’s IoT consultants state that each IoT solution is unique and requires a tailored testing process, so IoT testing costs vary dramatically. Among the main factors determining IoT application testing cost they name:
- Number and complexity of IoT app functions.
- Required number of intended users.
- IoT system’s performance requirements (including scalability, reliability, average response time, the number of transactions per unit time, etc.).
- Technologies used in the IoT solution (e.g., real-time monitoring, big data analytics, AI and machine learning, etc.).
- Number and complexity of IoT system components.
- Number of required third-party integrations.
- Specific security and compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, GLBA, SOX, GDPR).
Additionally, there are cost calculation factors specific for different sourcing models:
For an in-house option
- Number of IoT testing teams and test engineers within each one.
- IoT testing and QA professionals’ hiring costs and fully loaded salary.
- Additional training for testing teams’ members.
- Cost of employed tools (e.g., IoT testing frameworks’ licenses, simulators, virtual machines and storage, etc.)
For an outsourced option
- Number of IoT testing teams and test engineers within each one.
- IoT testing professionals’ rates (based on their experience and competence).
- IoT testing time based on:
- Total number of test cases.
- Design and maintenance efforts per test case.
- For testing outsourcing going in parallel with the app’s development:
- Percentage of test automation.
- Regression test coverage.
As an example, we can take a testing project for a company manufacturing automotive engines having 4 factories across a country. Each smart factory has 6 departments with 5-10 machines equipped with IoT sensors. The sensors measure the machines’ temperature, vibration, run time, operating speed, and product output. The IoT cloud-based event-driven application enables near real-time monitoring of the factories’, departments’, and machines’ performance; OEE and other KPIs’ visualization in reports and dashboards. The company requires a single-round acceptance testing.
|
The rough estimate for this testing project, including functional, integration, performance, security testing types will be about $70,000. Note: The system’s field testing costs aren’t included in this cost calculation and should be counted additionally. |

About ScienceSoft
ScienceSoft is a global IT consulting, software development, and QA company headquartered in McKinney, TX, US. We deliver outsourced QA services for IoT testing projects to help our clients ensure smooth functioning, robust integrations, scalability, and security of their IoT solutions. Being ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certified, we rely on a mature quality management system and guarantee that cooperation with us does not pose any risks to our clients’ data security.

