Blockchain in the Food Supply Chain
Use cases, capabilities, challenges, costs
In IT since 1989, ScienceSoft offers full-cycle blockchain development services to help companies create innovative blockchain solutions for the food supply chain.
Blockchain in the Food Supply Chain: The Essence
Blockchain for the food supply chain provides 100% traceability of the food-related data and multi-party transactions, enables backtracking the food provenance in seconds rather than days, facilitates food safety and quality compliance verification, enhances protection of supply chain data.
Blockchain in the Food Supply Chain: Market Info
The global blockchain market for the food supply chain was estimated at $840 million in 2025. It is expected to reach $4.04 billion by 2029 at a CAGR of 48.3%. The solid growth is mainly driven by the demand across the food industry for supply chain transparency and facilitated traceability of food provenance to assure product authenticity, safety and high quality. The need to prove sustainable food manufacturing practices and ethical sourcing are also among the important factors contributing to the growing popularity of the blockchain-based food supply chain solutions.
How Blockchain in the Food Supply Chain Works
Architecture
Blockchain for the food supply chain is built around a distributed ledger that contains data on all food supply chain transactions and events. The ledger is formed by timestamped and encrypted data blocks linked in chronological order. Each block holds a batch of transactions validated based on the pre-defined consensus protocol. Food supply chain participants interact with the blockchain ledger using the role-specific web and/or mobile applications.
Main user groups:
- Raw food suppliers transact data on the food origin and movement across the supply chain.
- Food manufacturers provide information on the food product ingredients and manufacturing processes.
- Food inspectors and certification entities verify documents on the product origin and quality.
- Transportation and logistics providers upload details on the location and storage conditions of food products in transit.
- Food product distributors trace food supply chain activities to assure responsible sourcing practices, food product quality and safety.
- End consumers access details on food products’ provenance to verify their authenticity.
Explore a sample architecture of blockchain for the food supply chain by ScienceSoft
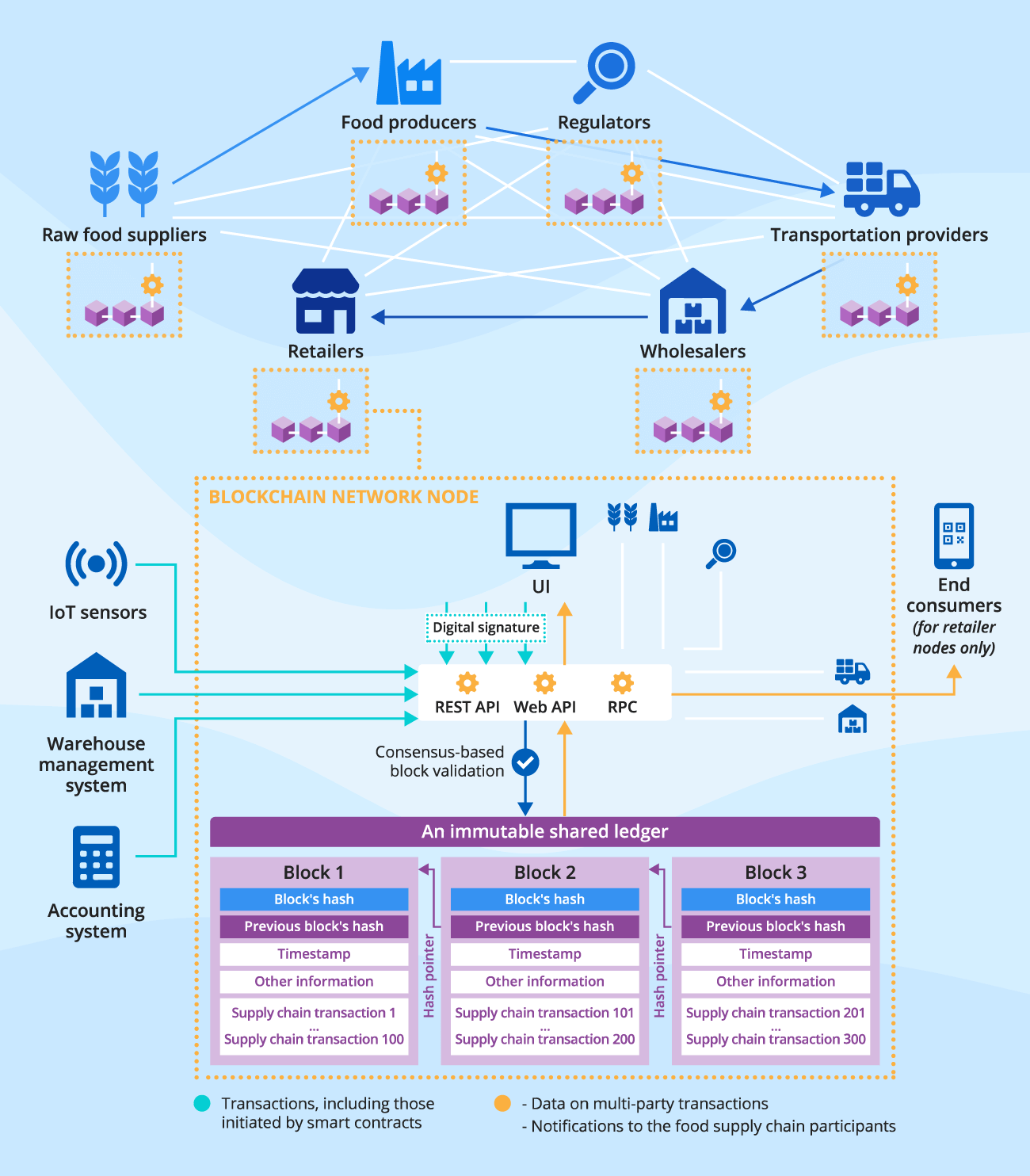
Hide
Main use cases
Food supply chain control
End-to-end traceability of multi-party transactions across all food supply chain levels for streamlined food supply chain control with reduced disruption risks.
Food fraud prevention
Tracing and storing data on the food origin and chain of custody to easily verify food authenticity and prevent fraud and counterfeiting.
Food safety control
Recording and monitoring data on farming practices, food product ingredients and their expiration dates, food storage and transportation conditions to timely identify potential points of food spoilage and contamination and prevent the distribution of unsafe food.
Food quality control
Recording and monitoring data on the food quality control procedures across food processing, manufacturing, distribution, and other stages, automated compliance checks to assure high food quality in accordance with global and internal standards.
Food selling and purchasing
Providing a blockchain-based marketplace for secure trading of food commodities and ready-to-use food products and full traceability of ordering, payment, and fulfillment transactions.
Food claim management
Providing the proof of food provenance and a complete history of food supply chain transactions to resolve claim disputes (e.g., on food quality or authenticity) and prevent recalls.
Food supplier selection
Recording data on food supplier pre-qualification, essential documents, performance indicators in a decentralized ledger for multi-tier supplier data monitoring, transparent supplier scoring and selection.
Food labeling
Recording a full history of food products’ origin, movement, and transformation to assure accurate product labeling and maintain compliance with the necessary food labeling regulations.
Key features
Automated recordkeeping
All transactions between the food supply chain participants and relevant product data from the connected systems (e.g., data on food manufacturing processes and product ingredients from ERP) are automatically validated, timestamped and recorded in blockchain.
A distributed ledger available to all food supply chain participants provides an immutable record and real-time view of all transactions between the involved parties, including food purchase orders, transfer of ownership, transfer of responsibility, payments, recalls, and more.
Food provenance tracking
Blockchain for food stores a complete history of data on a product journey from its origin through manufacturing, storage, transportation, and quality control processes to end consumers. Once recorded, food provenance data becomes immutable and can be accessed at any point.
QR code-enabled access to the blockchain data
End consumers can easily access food provenance data, certificates of origin and testing documentation stored in blockchain with their smartphones by scanning a QR code on the product package.
Real-time monitoring of food location, transportation and storage conditions
Combined with IoT technology, blockchain allows the food chain participants to monitor real-time location, transportation and storage conditions (temperature, humidity, vibration, etc.) for food products in transit and in the warehouse. The involved parties are instantly notified about non-compliant food logistics or conditions.
A full audit trail for the food supply chain documents
Blockchain records and stores data on all manipulations across the food supply chain documents, including those assuring the supplier qualification (e.g., accreditations, licenses), food origin and quality (e.g., certificates of origin, certificates of analysis), product ownership transfer (e.g., bills of lading, receipts), and more.
Blockchain enables automated processing of domestic and cross-border payments between the food supply chain participants in a secure, near-instant manner. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, which helps significantly reduce processing costs.
Regulatory reporting
Blockchain for the food industry allows supply chain stakeholders automatically generate regulatory reports in compliance with the relevant legal requirements. Regulators can access reports in the blockchain network to verify the report accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Self-executing protocols (smart contracts) automatically enforce fixed actions, pre-agreed by the food supply chain participants, upon the pre-defined events (e.g., making a payment to the supplier upon product delivery, checking food safety compliance against required safety standards during food farming, processing, manufacturing).
Hashing
The food supply chain data integrity is achieved via hashing. Each blockchain data block has a unique cryptographic identifier (a hash value) and contains the hash value of the previous block. If data stored in one block is modified, the hash value in this and all subsequent blocks changes, which makes the data tamper-evident.
Configurable user access rules
The food supply chains mainly rely on permissioned blockchains, where the rights to transact, view or share particular data can be configured for various food supply chain participants (e.g., suppliers, manufacturers, retailers).
Consensus-based data validation
In permissioned blockchains, consensus on transactions validation and their storage in a particular order is achieved via selective endorsement, where only known and trusted food supply chain members with special rights can validate the transactions.
Blockchain in the Food Supply Chain Consulting and Development by ScienceSoft
In supply chain software development since 2012 and in blockchain development since 2020, ScienceSoft creates powerful blockchain solutions for the food supply chain.
Technology Stack for Blockchain Implementation
To deliver reliable blockchain-based food supply chain solutions, ScienceSoft relies on a range of mature technologies, including:
The Challenges of Blockchain in the Food Supply Chain
Challenge #1: Analysis of the food supply chain data
Blockchain technology cannot provide the advanced analytics required for effective food supply chain management.
Check out the solution
Challenge #2: Protection of the food supply chain information
Although the permissioned blockchain for the food supply chain provides advanced data security, it can be susceptible to certain types of cyberthreats, such as routing attacks, phishing attacks, and code exploitation.
Check out the solution
Why It's High Time to Step into the Food Blockchain Market: A Startup's Success Story
A French startup has developed Connecting Food, a blockchain-based platform for real-time monitoring of the food supply chain activities and compliance. The platform facilitates food provenance traceability, offers QR code-based access to the food product information, indicates points of the food supply chain non-compliance, prevents recalls, and reduces food wastage.
The startup raised $5.5+ million in funding from 2016 to 2020. In 2021, Connecting Food was used by 30+ large food manufacturing and selling businesses, including the global snack food producer Mondelez, the multi-national bakery giant Europastry, and the Italian retailer Coop Italia.
Costs of Blockchain-Based Software for the Food Supply Chain
The cost of blockchain development varies greatly depending on:
- Blockchain network type (private, consortium, hybrid).
- The scope and complexity of a solution’s functional modules, including smart contracts.
- The number and complexity of role-specific web and/or mobile applications to interact with the blockchain.
- The number and complexity of integrations, which influences API development.
- Blockchain solution availability, performance, security, interoperability, and compliance requirements.

From ScienceSoft’s experience, the development cost for an MVP of blockchain-based food supply chain software will be around $80,000–$150,000. A full-featured blockchain food supply chain solution that comprises a private network and smart contracts requires $400,000–$1,500,000+ in investments.
Want to know the cost of your blockchain solution?

About ScienceSoft
ScienceSoft is a global blockchain development company headquartered in McKinney, Texas. We design and build blockchain solutions for improved traceability, safety, and transparency of the food supply chain data. In our blockchain projects, we employ robust quality management and data security management systems backed up by ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certificates.




