Blockchain for Supply Chain
Use Cases, Features, Challenges, Costs
In supply chain software engineering since 2012 and in enterprise blockchain development since 2020, ScienceSoft introduces robust blockchain-based supply chain solutions to businesses.
Blockchain for Supply Chain: The Essence
Blockchain for supply chain is aimed to increase supply chain transparency, improve traceability of multi-party supply chain activities, eliminate manual efforts across invoking and recording supply chain transactions, enhance security of sensitive supply chain data.
Blockchain Supply Chain Market
The global market of blockchain for supply chain was estimated at $1.17 billion in 2024. It is expected to reach $33.25 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 39.7%. The main drivers for the popularity of blockchain-based solutions are increasing demand for supply chain transparency and traceability, security of supply chain transactions, and robust automation of supply chain finance processes with no middlemen.
How Blockchain for Supply Chain Works
Main use cases
Supply chain control
End-to-end visibility into all supply chain data and transactions for enhanced transparency and improved control over supply chain operations across multiple tiers of suppliers and quick collaborative issue resolution with the involved parties.
Supply chain finance management
A tamper-resistant record of all multi-party financial obligations, automated payment enforcement upon pre-agreed events.
Supplier risk management
Recording and monitoring supplier-related data, including supplier interaction history, supplier performance information, data on essential documents (accreditations, certificates, etc.) to assure responsible sourcing practices and prevent legal, commercial and reputational supplier-associated risks.
Logistics management
Immutable records on documents that serve as a proof of transfer of responsibility for goods, automated e-document filing and exchange, tracking and tracing location and storage conditions for goods in transit and in the warehouse (e.g., essential for cold chain management) to streamline the administrative procedure, reduce transportation timelines, and ensure compliant goods logistics.
Supply authenticity verification
Tracking and tracing provenance of raw materials and finished products, recording data on the documents that verify their origin and quality, ensure their authenticity and prevent losses from counterfeit and gray market.
Supply chain compliance management
An immutable audit trail of all supply chain data and transactions, automated compliance checks against internal, global, industry- and region-specific regulations to prevent compliance violations and meet regulatory demand for goods provenance information.
Inventory management
Recording and tracing data on inventory movement between different facilities and its utilization throughout various manufacturing stages, monitoring stock availability across locations for streamlined inventory control and timely replenishment.
Claim management
Full traceability of supply chain data and transactions to assure proof of goods origin and provenance, automated safety and quality recall processes for faster claim resolution and prevent further distribution of unsafe, low-quality products.
Sample architecture
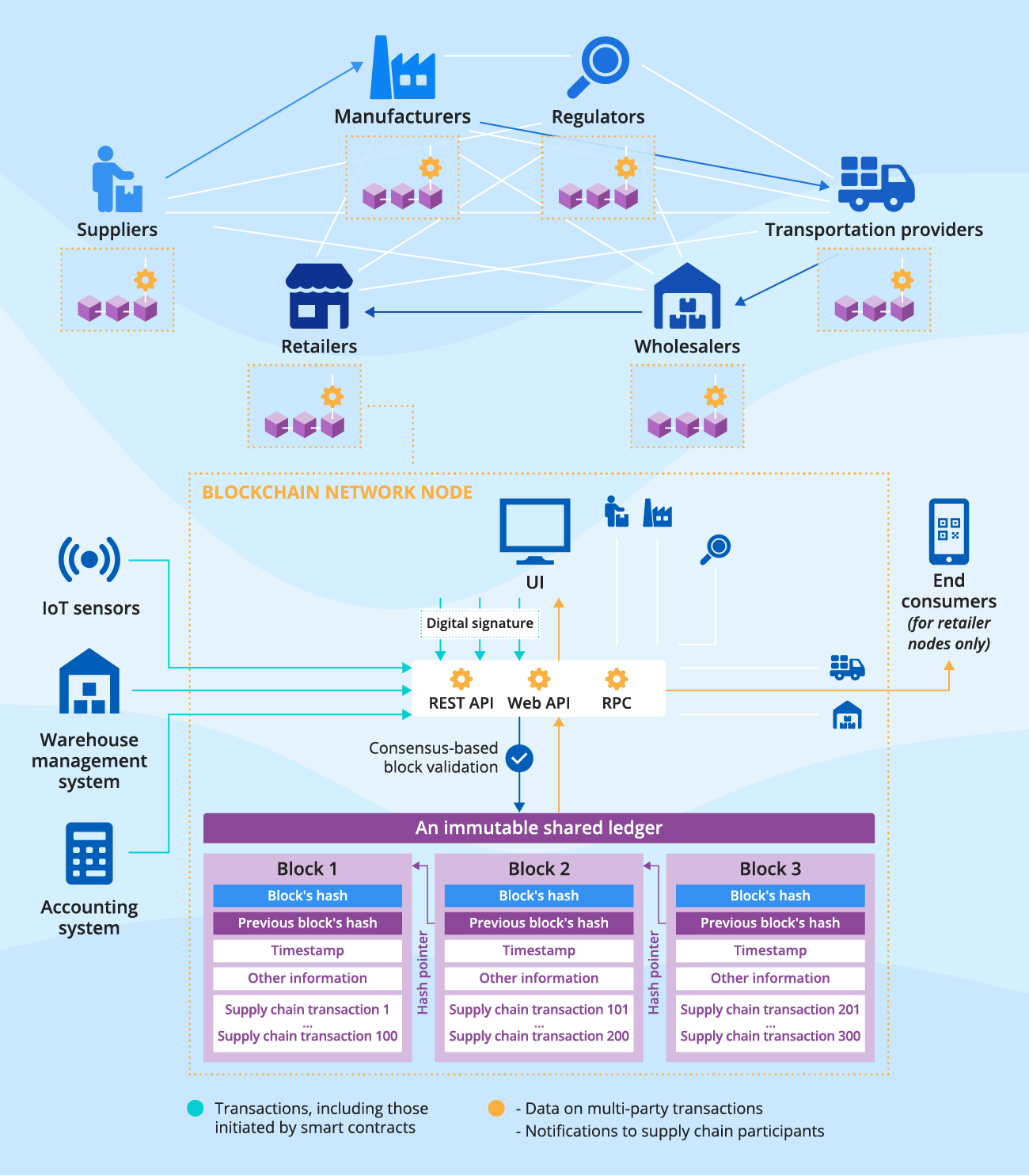
Supply chain transactions in the blockchain network are initiated by authorized supply chain participants or automatically enforced by smart contracts upon pre-defined events. To mitigate security risks, supply chains mainly rely on permissioned blockchains, so that data on supply chain events and transactions can be validated only by known and trusted supply chain members with special rights. Particular user groups, such as end consumers, are allowed to access the blockchain network only to view data.
Once validated and encrypted with a hash function, blockchain data is stored in timestamped blocks linked in chronological order. The blocks form a distributed ledger that serves as a single source of truth to trace supply chain activities and verify the provenance of assets and inventory. All authorized network members maintain their own copies of the shared ledger that get auto-updated as new data appears. The supply chain participants interact with the blockchain to transact and trace data using role-specific web and/or mobile applications (e.g., for suppliers, manufacturers, regulators, distributors).
Key features
Automated recordkeeping
All transactions between supply chain participants and relevant data from the connected systems (ERPs, IoT data management systems, etc.) are automatically validated, timestamped and recorded in the distributed ledger.
Supply chain tracking and tracing
The distributed ledger enables the supply chain participants to track all supply chain activities (orders, payments, goods transportation, manufacturing workflow, and more) in real time and trace their history end to end.
Smart contract-enabled automation
Smart contracts serve as rule-based instructions to automatically enforce particular supply chain transactions pre-agreed by the involved parties when certain conditions are met (e.g., checking goods transportation compliance at pre-defined regular intervals, making a payment to the supplier upon product delivery).
Supplier data verification
Blockchain offers supplier identity management capabilities, enables supplier data verification by trusted third-party validators (e.g., credit rating agencies), and provides an immutable audit trail for all supplier information updates.
Supply chain objects registration
Blockchain enables one-by-one and batch onboarding of products, locations and documents referenced in supply chain events and transactions, as well as their coding in accordance with GS1 standards to maintain a unified data record, streamline product tracking and information exchange with digital and physical systems.
A full audit trail for supply chain documents
Blockchain records and stores data on all manipulations across contracts, purchase orders and sales orders, invoices, bills of lading, product certificates, manufacturing specifications, quality control reports and other essential supply chain documents, including details on document creation, editing, viewing and sharing.
Supply chain data validation
Supply chain transactions are validated by trusted supply chain members with special rights. Consensus on transactions validity and their storage order is achieved via selective endorsement.
Hashing and timestamping
Blockchain automatically generates a hash value (a unique cryptographic identifier) for each data block in the network. If supply chain data in one block changes, hash values of all consequent blocks will change, which makes the data tamper-evident.
Transaction e-signing
Each blockchain participant has a unique digital signature to e-sign the submitted supply chain transactions and prove their ownership.
Supply chain data safety in blockchain is achieved with multi-factor authentication, data encryption, fraud detection algorithms, permission-based access control, and more.
Technology Stack for Blockchain Implementation
To deliver reliable blockchain-based supply chain solutions, ScienceSoft relies on a range of mature technologies and tools, including:
The Challenges of Blockchain for Supply Chain
Challenge #1: Seamless integration with numerous data sources
Blockchain needs to continuously collect supply chain data to maintain a complete history of purchase orders, supply chain finance transactions, goods provenance, location, and storage conditions and manufacturing processes. Thus, the solution has to seamlessly integrate with all relevant systems (including legacy ones) of multiple blockchain network members.
Check out the solution
Challenge #2: Formalization of business rules in smart contracts
Once specified in smart contracts, rules for the automated enforcement of supply chain transactions in the blockchain network become immutable. Inaccurate formalization of business rules can result in incorrect data and payment flow between supply chain participants.
Check out the solution
Challenge #3: Blockchain adoption
To prevent information gaps and enable end-to-end supply chain traceability, blockchain has to be adopted by all supply chain participants.
Check out the solution
Challenge #4: Non-transactional data storage
Non-transactional supply chain data, such as purchasing and transportation documents, media files, and supplier information, is too large to be stored in the blockchain efficiently. At the same time, it needs to remain transparent and easily accessible for all supply chain participants.
Check out the solution
Costs of Blockchain-Based Software for Supply Chain
The cost of blockchain supply chain management software development varies greatly depending on:
- Blockchain network type (private, consortium, hybrid).
- The number and complexity of a solution’s functional modules, including smart contracts.
- The number and complexity of web and/or mobile applications for various user groups (e.g., suppliers, manufacturers, retailers, consumers) to interact with the blockchain solution.
- The number and complexity of potential integrations with relevant software (e.g., ERP, accounting software, selling platforms), which influences integration API development.
- Blockchain solution performance, scalability and security requirements.
- Blockchain-to-blockchain interoperability capabilities.
- The required deliverable (PoC, MVP, a full-scale solution), which influences the duration of the development project.
On average, companies see the payoff of custom blockchain development in 12–18 months.

From ScienceSoft’s experience, the development cost for an MVP of blockchain-based supply chain software will be around $80,000–$150,000. A full-featured blockchain supply chain solution that comprises a private network and smart contracts requires $400,000–$1,500,000+ in investments.
Want to know the cost of your blockchain solution?
Blockchain for Supply Chain Consulting and Development by ScienceSoft
In software development since 1989, ScienceSoft offers end-to-end blockchain development services to build reliable blockchain inventory management and supply chain control solutions covering the needs of businesses in 30+ industries.
Blockchain for supply chain consulting
- Analyzing your business needs and eliciting requirements to a blockchain system for supply chain.
- Suggesting optimal blockchain network type (private, public, consortium, hybrid), architecture design, and tech stack.
- Providing a detailed feature set for the blockchain system for supply chain.
- Preparing an integration plan with required software (e.g., ERP, accounting software, selling platforms).
- Blockchain security consulting.
- Delivering a roadmap for blockchain system development, including a risk mitigation plan.
Blockchain for supply chain development
- Business needs analysis and requirements elicitation to a blockchain solution for the supply chain.
- Blockchain software conceptualization.
- Architecture design of blockchain for supply chain.
- Developing the blockchain solution.
- API development to expand the solution’s integration capabilities.
- Testing and quality assurance.
- Drawing up materials for end user training (optional).
- Blockchain software support and evolution (if required).
About ScienceSoft
ScienceSoft is a global IT consulting and software development company headquartered in McKinney, Texas. We provide blockchain consultancy and development services to help our clients design and build blockchain in supply chain. In our blockchain projects, we employ robust quality management and data security management systems backed up by ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certificates.


