Wearable Device App Development Services
We develop custom wearable software that enables medical device manufacturers, healthcare and wellness software product companies to deliver personalized remote care, real-time health and lifestyle insights, and seamless user experiences. Experienced solution architects ensure every wearable-based system achieves the optimal balance between scalability, cost-efficiency, and performance.
Wearable device app development services allow medical device manufacturers, healthcare and wellness software product companies to accelerate time to market, avoid vendor lock-in, and gain full visibility into solution documentation. Compared to off-the-shelf solutions, custom systems are designed specifically to avoid the typical limitations of ready-made tools:
- Adapt to any (even niche) use cases. For example, in one of our projects, ScienceSoft’s wearable apps developers introduced custom motion capture algorithms for joint ROM measurement, which significantly improved the accuracy and stability of the sensors.
- Support a wider range of medical devices and sensors, including both FDA‑cleared and consumer wearables, with custom adapters that standardize data formats to ensure interoperability.
- Ready to easily plug into both internal systems and partner platforms (including older, legacy software).
- Offer configurable notification logic that reduces alert fatigue and enhances provider adoption.
ScienceSoft as a Trusted Wearable Device App Development Company
- Since 2005 in healthcare IT.
- Since 2011 in IoT.
- Leveraging cloud technologies since 2012.
- 550+ developers, with 50% being seniors or leads with 9–20 years of experience.
- Proficiency in ensuring compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, Cures Act, GCC, FDA, and MDR requirements.
- Experience with uniform interoperability standards (e.g., HL7, FHIR, XDS/XDS-I, and DICOM), datasets (e.g., USCDI), and clinical terminologies (e.g., SNOMED CT, LOINC, RxNorm).
- An official partner of Microsoft and AWS.
Our awards, recognitions, and certifications
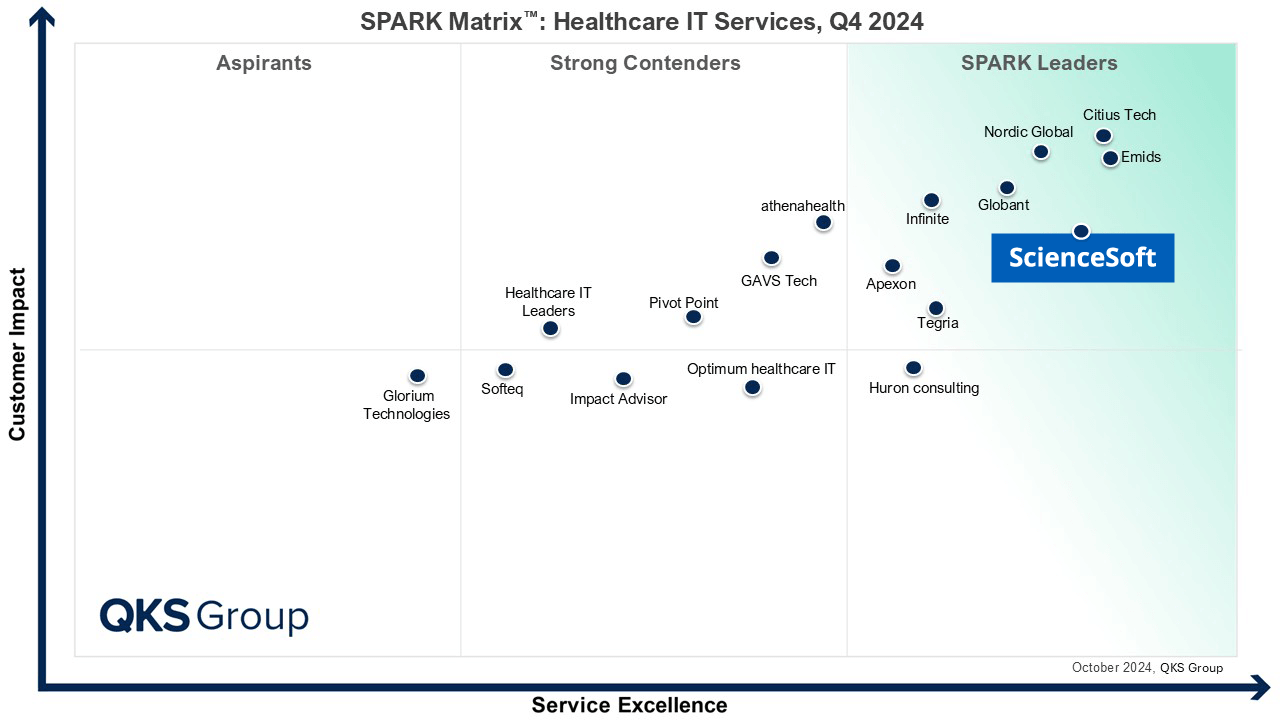
Featured among Healthcare IT Services Leaders in the 2022 and 2024 SPARK Matrix
Recognized for Healthcare Technology Leadership by Frost & Sullivan in 2023 and 2025
Named among America’s Fastest-Growing Companies by Financial Times, 4 years in a row

Top Healthcare IT Developer and Advisor by Black Book™ survey 2023
Four-time finalist across HTN Awards programs

Named to The Healthcare Technology Report’s Top 25 Healthcare Software Companies of 2025

HIMSS Gold member advancing digital healthcare
ISO 13485-certified quality management system
ISO 27001-certified security management system
Software Our Wearable Technology Developers Create
How AI Enhances Wearable Software Workflows
Patient assistants
In wellness and chronic disease management applications, AI is often used to support adherence and long-term engagement. For example, it can analyze patient habits, behavioral tendencies, and even speech patterns from the messaging history. These insights can then be used to generate personalized reminders, lifestyle advice, or educational content suggestions.
Remote patient monitoring systems (especially for geriatric patients) can use machine learning to predict adverse health events like heart attacks. ScienceSoft’s research suggests that, in the next 5 to 10 years, 50% of senior patients will use intelligent wearables to catch such risks early on.
Clinician assistants
In remote patient monitoring systems, AI helps clinicians efficiently manage large volumes of patients. Machine learning models can establish individualized baselines for each patient using historical wearable data. This allows the system to detect subtle, patient-specific deviations that might otherwise go under the clinician’s radar. ML can also predict health deteriorations before they occur, identify high-risk patients, and even suggest a prioritized list of potential interventions. At the same time, generative AI can save clinicians’ time by transforming analytics results into concise, natural-language insights that highlight the most important changes.
Documentation management
In clinical settings, natural language processing can reduce administrative burden by extracting and structuring information from patient symptom diaries, self-assessment surveys, or messages to doctors. Then, large language models (LLMs) can create clinical notes based on the extracted information and wearable data. Finally, AI can automatically populate patient records with the collected data and notify a clinician to approve its modifications.
Device maintenance and security
AI helps ensure consistent device performance and reliable data capture in remote care, long-term monitoring, and wellness programs. Predictive analytics can detect early signs of device or connectivity issues and alert support teams before system performance is affected. For large-scale clinical deployments, machine learning can optimize logistics by forecasting inventory needs and scheduling shipments and maintenance tasks automatically. At the same time, AI adds an extra layer of software security by monitoring audit logs and data access patterns in real time. Upon spotting suspicious behavior, the system immediately alerts administrators and can even trigger automated safeguards (like temporarily locking a questionable account).
Sample Architecture for Healthcare Wearable App Development
The diagram below illustrates a typical cloud-first architecture used in remote patient monitoring (RPM) solutions.
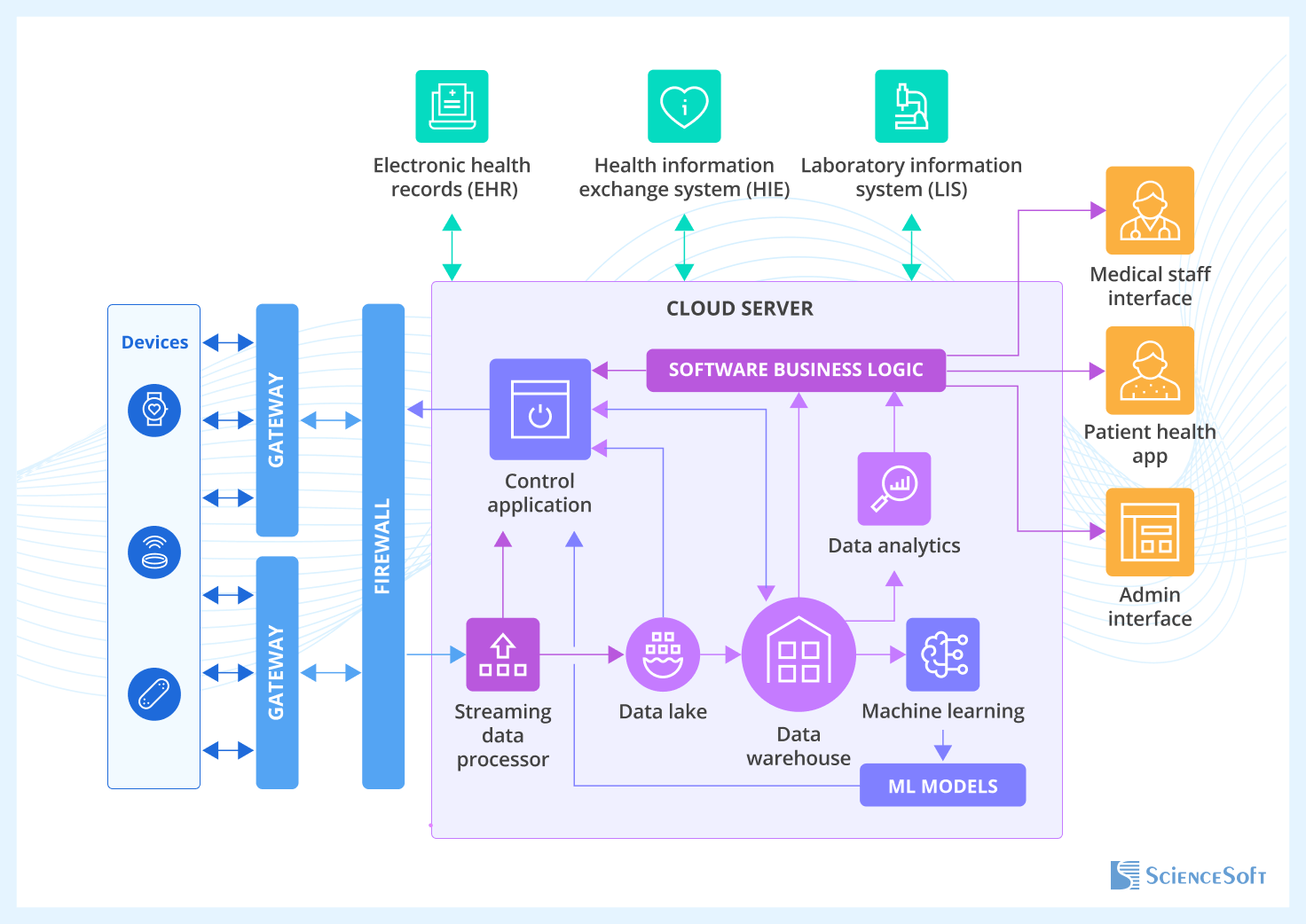
Connected wearable devices transmit captured patient health information to the cloud back end via gateways and a firewall. The gateways filter and preprocess the data before sending it to the cloud, while also transmitting control commands back to the devices.
In the cloud, the stream processing module analyzes real-time data to enable quick reactions such as alerts for abnormal health parameters. This raw and semi-structured data goes to the data lake, where it’s stored in its original format. Meanwhile, the clean, structured data is sent further to the data warehouse, where it’s available for fast querying, analytics, and reporting. The AI/ML engine uses raw data for model training and powers the analytics module to enable advanced insights (e.g., disease progression forecasting). Relying on this data, the engine can suggest monitoring or therapy delivery setting adjustments. Software business logic routes relevant data and allows user access to that data (e.g., shows analytics results on the clinician’s dashboard). Meanwhile, the control applications help transmit user commands, for instance, by triggering the necessary setting adjustments in the devices.
At the user interaction layer, role-specific interfaces enable clinicians and administrators to view relevant data and control device settings. Patients can also use dedicated apps to get limited insights into their health state and communicate with providers. The integrated systems contribute contextual patient data, such as diagnoses, lab results, or medication history, to the cloud backend for more accurate analytics and decision-making.
In an RPM scenario, a fully cloud-based setup has major advantages, especially when it comes to scalability and centralized intelligence. It allows all data to be funneled into one place, making it easier to run advanced analytics, apply machine learning, and continuously update algorithms without touching the devices. This approach simplifies device-side logic, reduces hardware complexity, and enables powerful cross-device insights through aggregated data processing. However, in certain scenarios, it can be useful to introduce a hybrid approach. Shifting some responsibilities (e.g., threshold-based alerts) to the edge helps reduce bandwidth consumption, lowers response latency for immediate actions, and improves resilience during network interruptions, all while keeping the cloud available for complex computations. It’s a way for wearable app developers to get the best of both worlds: the flexibility and power of the cloud, with the responsiveness and efficiency of edge computing.
Service Options ScienceSoft Offers to Wearable App Development Companies
Consulting on wearable software development or implementation
We support medical device manufacturers and health software product companies in planning wearable software initiatives that are clinically adoptable, financially justifiable, and technically viable. We design future-ready architectures (cloud, hybrid, or edge) with a clear view of cost-performance trade-offs and AI readiness. Our consultants identify applicable regulatory requirements and registration pathways, align core functionality with CPT reimbursement rules (e.g., 99453/99454, and map out data flows to ensure seamless interoperability with required devices and systems. Each engagement results in a detailed roadmap with phased budgeting, regulatory risk mitigation plans, and practical guidance on avoiding alert fatigue, connectivity issues, and fleet governance failures.
From-scratch wearable software development
We carry out end-to-end development of wearable platforms that support both generic and niche care delivery models and demonstrate clear business value from day one. Our engineers help you define a viable architecture that supports compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., HIPAA, Cures Act), integrates seamlessly with preferred wearable devices and systems (including legacy software), incorporates AI-readiness and OTA fleet control. The result is an application that reduces care delivery friction and delivers measurable ROI under real-world bandwidth, workflow, and device management constraints. If your solution includes SaMD functionality, such as clinical decision support, we also assist with FDA registration and prepare the required technical documentation in the appropriate format.
Low-code development for reduced wearable software costs
With low-code platforms like Power Apps, we deliver wearable solutions that meet compliance, integration, and scalability demands, with faster delivery and lower upfront investment. This approach is especially effective for pilot RPM programs or workflow augmentation apps where speed and budget control are critical. We help clients architect secure, HIPAA-compliant solutions that support FHIR-based data transformation, OTA update logic, and transparent AI modules. To avoid governance risks, we also implement CI/CD automation, role-based controls, and audit tracking from the start. Throughout the project, we focus on ensuring stable performance, mitigating vendor lock-in, and maximizing ROI beyond the licensing curve.
Wearable software support, monitoring, and troubleshooting
We provide 24/7 support for wearable-based platforms, ensuring service continuity, regulatory compliance, and minimal disruption to clinical workflows. Our support stack includes real-time observability, automated anomaly detection, and end-to-end data validation across device, network, and cloud layers. For fielded devices, our OTA patching and rollback tools help teams quickly respond to firmware issues or security vulnerabilities. Every engagement is backed by service-level objectives for mean-time-to-detect and restore, helping healthcare organizations minimize unplanned downtime and stay within mandated reporting windows (such as HIPAA’s 60-day and CIRCIA’s 72-hour breach clocks). Over time, we help clients benchmark and reduce detection and recovery times through structured root-cause analysis, metrics reviews, and toolchain optimization.
Wearable software modernization and evolution
We modernize legacy wearable platforms to eliminate accumulated technical debt, meet updated regulatory requirements, and unlock long-term scalability. Each project begins by assessing whether refactoring, re-platforming, or full rebuild delivers the best ROI with minimal service disruption. We upgrade core modules, ensuring that continuous wearable streams are reliably processed at scale and converted into structured FHIR Observations for downstream systems. To improve software delivery velocity, we embed CI/CD pipelines, test automation, and rollback controls. During the transition, we safeguard data integrity and clinical continuity with validated migration workflows. The result is a compliant, resilient, and future-ready system that supports real-time analytics, AI integration, and ongoing innovation.
Technologies We Use to Build Software for Medical Devices
Device connectivity
Cloud services
Real-time data streaming

Data lakes
How ScienceSoft Addresses the Challenges of Wearable Software Development
Device ecosystem fragmentation
Developing remote monitoring or chronic condition management platforms, device diversity is a major technical hurdle. These platforms often need to ingest and process data from a wide range of devices. Each wearable comes with its own set of APIs, data formats, authentication methods, and update cycles. Without a clear strategy, developers often find themselves with code that's tightly coupled to individual devices, creating fragile systems that are hard to maintain or scale as new devices are introduced.
Solution
Connectivity and data synchronization
Wearable devices often experience connection instability due to the mobile nature of users, frequent offline periods, or poor Bluetooth connections. These issues can lead to data inconsistencies, lost patient information, and incomplete dashboards, which can cause frustration and impact the quality of care.