Healthcare Quality Management System
Capabilities, Integrations, and Costs
With ISO 9001 and ISO 13485-certified quality management systems and 20+ years of experience in healthcare IT, ScienceSoft develops healthcare QMS software to streamline SOP control, training, and audits for providers and regulated healthcare products.
Healthcare Quality Management Systems: Summary
A 2025 review by HHS-OIG found that hospitals failed to capture about half of patient harm events identified in medical record review. At the same time, the US FDA says it receives over two million medical device reports each year related to suspected device-associated deaths, serious injuries, and malfunctions. Together, these figures show the scale of quality and safety data that providers and medical product companies are required to centrally manage and report.
Healthcare QMS software helps healthcare providers and regulated healthcare product teams run quality management and reporting work in one place, with clear ownership and audit-ready evidence. For providers, a quality management system supports patient safety and accreditation routines. For regulated products, a medical QMS supports consistent handling of deviations, complaints, and supplier actions without losing traceability.
The initial cost of implementing a centralized QMS solution usually falls between $120,000 and $700,000+ for midsize organizations, depending on the complexity of quality management processes and the existing QM tool stack. Use our free online calculator to get a cost estimate for your case.
Organizations That Can Benefit From Tailored QMS Software
Ambulatory networks
Post-acute care providers and SNFs
Contract manufacturers and critical suppliers for regulated products
Imaging networks
Core Capabilities of Quality Management Software in Healthcare
Below is a curated selection of capabilities often requested by ScienceSoft’s clients who implement proprietary healthcare QMS software. In practice, each system is tailored to the organization’s quality processes, regulatory scope, and reporting needs, so the final set of modules and workflows may differ.
Controlled policies and SOP lifecycle
A secure library stores clinical policies, standard operating procedures (SOPs), work instructions, and standard forms, tracking them from draft to retirement. Versioning, ownership, review dates, and filters keep the current approved document easy to find. Old versions remain available as audit evidence and investigation context.
Role-based training
The role-based training module helps training coordinators assign training plans by job role and unit and link each course to a specific SOP or policy version. When a policy or SOP changes, the updated training item can be quickly reassigned to the affected roles. The system then records results and highlights overdue staff for department or quality managers.
Quality event intake and structured triage
Structured intake forms allow staff to report quality events with tags, attachments, and immediate actions. Quality specialists review and route issue reports and set containment steps. Required fields and due dates prevent incomplete reports and unattended follow-ups.
Investigations and RCA workspaces
Investigation workflows help document safety event reviews using RCA templates such as timelines, contributing factors, and 5 Whys. In product quality teams, QA specialists use the same evidence-led approach for deviations, complaints, and audit findings. Standardized investigation records keep conclusions, attachments, and approvals linked to the actions they trigger.
Change control and impact assessment
The change control record inside the system centralizes approvals for procedure, equipment, supplier, labeling, or software updates. It collects impact questions, routes reviews to their owners, and captures approvals with electronic signatures. A built-in checklist tracks the required follow-ups (updated procedures, staff retraining, validation or testing evidence) so the change can’t be closed or escalated with incomplete steps.
CAPA and effectiveness checks
When issues or trends require a systemic fix, the quality team can open a corrective and preventive action record to document the root cause, assign tasks, and collect completion evidence and approvals. Effectiveness checks define what will be measured and when, and keep the record open until results confirm the issue is reduced, not just closed.
Audit readiness hub
One workspace lets auditors schedule reviews, reuse checklist templates, and link each checklist item to a specific SOP version. Evidence such as files, photos, and record links can be attached to checklist answers and findings. Those findings are routed to follow-up tasks or a CAPA record, and an exportable report includes the full history.
Provider-specific modules
Safety event reporting
Patient safety forms are tailored to clinical events such as falls, medication errors, and near misses. Clinical staff can record details and attach evidence. Risk managers review the report, escalate high-severity events, and route it to the right unit owner and patient safety lead. The event record links to investigation notes and action status.
Clinical practice audits
Clinical practice audits can help run observational audits such as hygiene, isolation precautions, medication administration, and documentation completeness. Configurable checklists capture notes, photos, and context by unit and shift. Results can roll up into dashboards for quick review.
Provider risk register
Inside the QMS, the risk register helps risk managers and safety specialists track high-priority clinical, operational, and technological risks based on trends from incidents, audits, and complaints. Each risk record can include different categories (e.g., owner, likelihood, current controls, review dates) and linked evidence. Mitigation actions become tasks in the assigned owner’s inbox.
Accreditation evidence hub
The hub lets an accreditation or compliance coordinator work through requirements one by one. Each requirement can be conveniently linked to the exact policy version and related proof. Missing proof becomes a task, with due dates and reminders. Before inspections, the hub can be used to compile all linked proof into one evidence pack.
QAPI project portfolio
Project workspace helps quality improvement leaders run QAPI initiatives. For each project, the project owner records goals, units, and metrics, then tracks actions and due dates. Simple charts will show whether the metric is improving after each intervention.
Regulated medical product modules
Complaint investigations
QMS can provide a structured complaint record with fields for product identifiers, event details, and supporting evidence. The record goes through a review flow and stores the investigation result and failure category, so complaints can be grouped and compared over time. Based on set rules, it can open linked CAPAs, supplier corrective actions, or a field action record.
Field action coordination
Field action (recall, correction, or safety notice) record links the action to affected lots or serial numbers, related complaints, and investigation results. Built-in lists help to track which customers were notified, who responded, and which corrections were completed. An effectiveness check and full history remain attached for inspections.
Design controls
The design control workspace governs how requirements, risks, verification, and validation are defined, reviewed, and approved throughout the product lifecycle. It maintains traceability between design inputs, test results, defects, and changes so teams can assess impact before release and when post-market signals require design updates. Linked evidence supports DHF reviews and regulatory inspections.
Supplier quality workflows
Supplier records store qualification status, audit results, and key documents in one place. When a defect occurs, a supplier corrective action (SCAR) record tracks the request, the supplier’s response, supporting files, and closure approval, linked to the related internal issue. For organizations with complex vendor collaboration and approvals, a QMS can complement a supply chain management portal.
Batch and DHR review
Release review records support checklist-based verification of required tests, completed issues, and approved changes before release. Missing signatures, out-of-spec results, or open investigations can block or flag the release status. The final record provides a consistent release decision trail and a complete evidence package for audits and customer reviews.
AI Capabilities to Streamline QMS Workflows
AI-assisted event reporting
When incident reports are submitted, AI can help turn free text into a structured draft by suggesting likely event type, harm level, unit, or any other required fields. Users can review and adjust the draft before finalizing the record, so investigations start with clearer, more complete information.
Duplicate detection
When new complaints or deviations are logged, AI can flag likely duplicates by matching text and key fields like product, lot, symptom, and failure category. It surfaces the closest past records and their outcomes, so teams don’t open a second investigation for the same issue.
Audit evidence copilot
During survey or inspection preparation, AI can assist with assembling evidence packs by pulling the relevant policies, approval history, training records, corrective action closures, and follow-ups. It can flag gaps such as missing effectiveness checks or overdue actions, giving teams time to address them before evidence is reviewed.
Important Integrations for a QMS
In order to function correctly, a centralized QMS will need access to internal systems that store QM-relevant data. Your integration map may vary based on your systems and workflows; many organizations start with a few key connections and expand as needs evolve. These patterns reflect what we’ve seen across healthcare providers and regulated product companies.
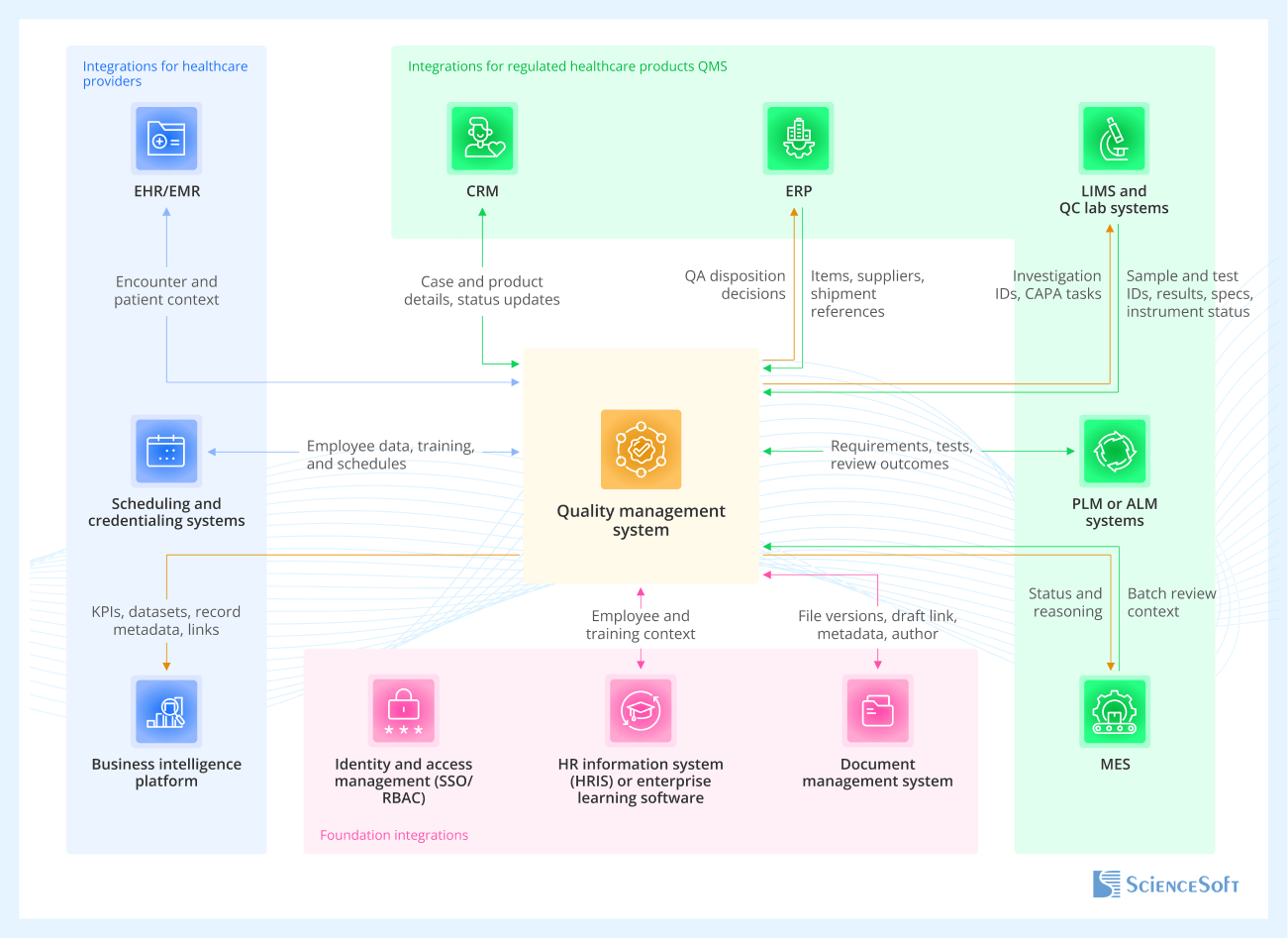
Foundation integrations
Apply to nearly all healthcare QMS implementations, across providers and product companies.
- Identity and access management (SSO/RBAC) ensures only authorized users can create, approve, and sign records like SOPs and CAPAs, with role-based controls that hold up in audits and prevent approval errors.
- HR information system (HRIS) or enterprise learning software automates training assignments and routing based on employee attributes, so QA teams don’t have to manually maintain training assignments.
- Document management system supports drafting SOPs, policies, work instructions, and forms while the QMS controls approval, versioning, and effective dates.
Integrations for healthcare providers
-
EHR/EMR links safety events and investigations to encounter context so patient safety specialists and risk managers can review unit, service line, and timing without copying full clinical data.
- Scheduling and credentialing systems support dynamic training triggers and auditability tied to clinical roles and privileges.
- Business intelligence platform supports quality reporting and cross-system KPI analysis.
Integrations for regulated healthcare products QMS
-
CRM keeps complaint cases consistent by syncing customer and product context between CRM and regulated complaint handling in QMS.
- ERP ties deviations, NCRs, batch release, and field actions to item masters, suppliers, lots, serial numbers, and shipment history for QA release and supplier quality teams.
- LIMS and QC lab systems bring lab context (sample IDs, test results, OOS flags) into QA workflows, which helps investigators see exactly what failed and under what conditions.
- PLM or ALM systems support design control and DHF traceability by connecting design inputs, revisions, test evidence, and defect logs.
- MES data can be linked to support batch review and release workflows in the QMS in high-volume production.
Integrate read-only first, then allow write-back selectively
Integrations can slow down QMS projects when teams try to keep multiple systems fully synced in both directions. A safer approach is to connect the QMS so it can pull reference data for users to view, such as employees, roles, items, suppliers, and lots. After the process is running, add write-back only for a few actions with clear business value, such as pushing QMS hold and release decisions to ERP.
Development Tips for QMS Implementation
Reduce cost by reusing configurable workflow components
ScienceSoft’s architects suggest designing a custom QMS around reusable workflow components instead of hard-coding each module anew. For example, the same form engine, routing rules, notifications, approvals, and dashboard templates can be reused across CAPA, audits, and change control, then adjusted per site by changing fields, roles, and thresholds. It also helps to define a few “non-negotiables” up front, like standard statuses, audit trails for key fields, and electronic signatures, then apply them across all workflows. This typically reduces build and change costs while keeping traceability consistent as the solution scales.
Standardize templates and definitions to avoid rework and reporting issues
To avoid inconsistent reporting across sites, it’s a good idea to standardize a small set of core records before teams start configuring workflows locally. Otherwise, the same type of record (for example, a deviation or CAPA) gets captured with different fields, categories, and statuses, and cross-site reporting stops lining up. In practice, this means defining about 10 to 15 core templates (CAPA, RCA, audit checklist, change impact assessment) and locking key field definitions such as severity scale, root cause categories, required fields, and status criteria. This reduces rework later and simplifies the user experience by keeping forms, fields, and terminology consistent across sites and workflows.
Add AI with retrieval-augmented generation
If you decide to add AI to your QMS, it’s a good idea to start with a read-only assistant that retrieves and summarizes approved content, such as policies, SOPs, and past CAPAs, rather than generating answers from memory. Retrieval-augmented generation is often the simplest way to ground responses with citations, compared to fine-tuning which can be rather expensive. In healthcare, this works best when retrieval follows QMS role-based access, applies redaction and minimum-necessary rules, and logs prompts, sources, and outputs for auditability. Start with draft responses that require human approval, then expand only if usage proves consistent and safe.
Healthcare QMS Software: Cost Estimation
Healthcare QMS software cost typically ranges from $120,000 to $600,000+, depending on scope needs.
$120,000–$250,000+
Extending and integrating existing quality tools
Best for organizations that already use DMS, LMS, and incident reporting tools, or an off-the-shelf eQMS but need custom workflows, data connections, and stronger audit trails. It covers targeted automation of CAPA, change control, training reassignment, and reporting without replacing existing systems.
$250,000–$600,000+
Basic QMS platform from scratch
Best when you need a strong foundation to scale later. The MVP typically includes controlled policy and SOP workflows, CAPA with effectiveness checks, change control, and an audit readiness hub, plus role-based access and dashboards.
$700,000+
Enterprise QMS
For a tailored, enterprise-grade QMS program when you need automation across sites and complex governance, or when regulated quality and validation expectations are high. The scope often includes a wider module set, complex approval chains, advanced reporting, and multiple integrations.
Why Build Your QMS With ScienceSoft
-
Since 2005 in healthcare IT, with a Doctor of Medicine consultant on board.
- 150+ completed healthcare projects across clinical and administrative workflows.
- A dedicated architecture practice with 9 principal architects to establish data governance and interoperability in complex enterprise environments.
- Practical experience with HIPAA/GDPR requirements, healthcare data exchange standards (HL7, FHIR), 21 CFR Part 11, and data integrity controls supporting audit-ready QMS workflows.
- ISO 13485 -certified quality management system to support medical device and SaMD software development under regulatory expectations.
- Quality-first approach based on a mature ISO 9001-certified quality management system.
Our awards, recognitions, and certifications
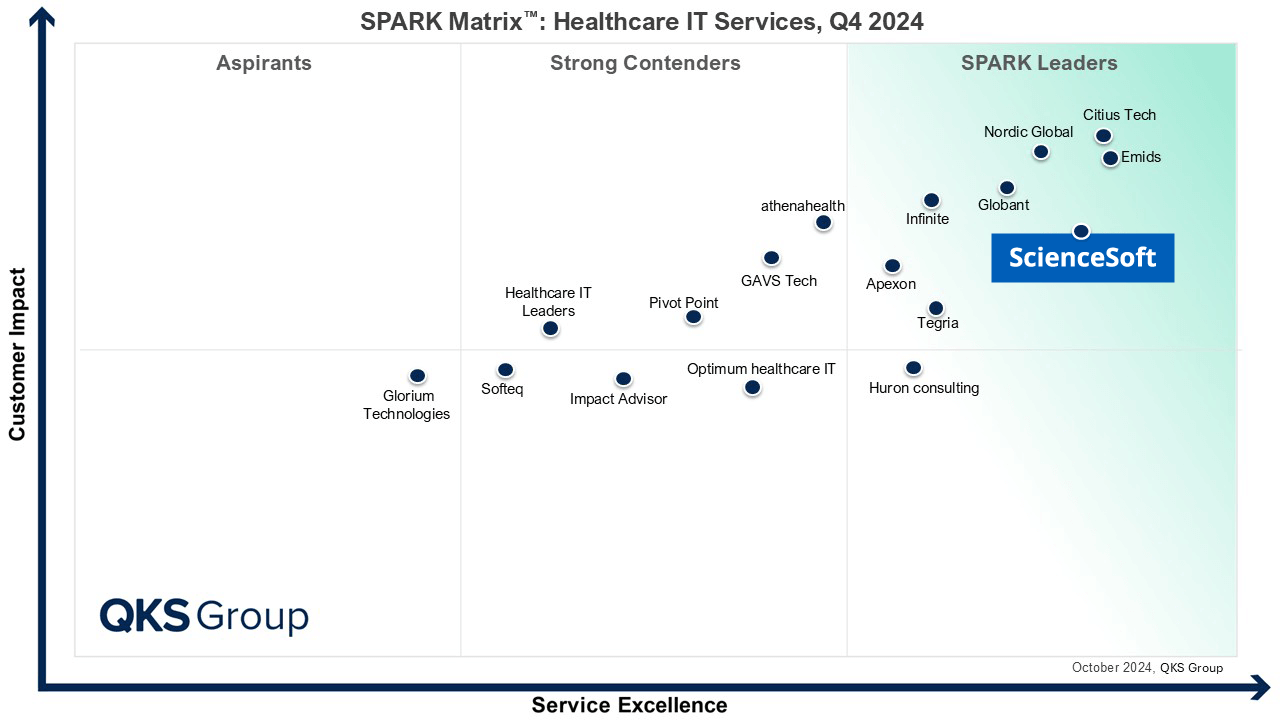
Featured among Healthcare IT Services Leaders in the 2022 and 2024 SPARK Matrix
Recognized for Healthcare Technology Leadership by Frost & Sullivan in 2023 and 2025
Named among America’s Fastest-Growing Companies by Financial Times, 4 years in a row

Top Healthcare IT Developer and Advisor by Black Book™ survey 2023
Four-time finalist across HTN Awards programs

Named to The Healthcare Technology Report’s Top 25 Healthcare Software Companies of 2025

HIMSS Gold member advancing digital healthcare
ISO 13485-certified quality management system
ISO 27001-certified security management system






