Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare
Use Cases and Value
With 20 years of experience in healthcare IT, ScienceSoft develops robotic process automation (RPA) solutions that help free healthcare providers' staff from repetitive, monotonous tasks while reducing errors and costs in processes such as billing and patient records management. Healthcare process automation with RPA can deliver significant cost savings compared to building automation from scratch, as it minimizes the need for custom code.
RPA in the Healthcare Industry: Essence
Robotic process automation in healthcare is used to automate high-volume rule-based tasks such as updating patient records, scheduling appointments, or verifying insurance eligibility. RPA solutions offer low-code or no-code tools, with the help of which the hospital staff or the IT team can configure task automation rules. They can be implemented faster and more cost-effectively than traditional automation because they do not require complex integrations or changes to existing systems and IT infrastructure. Instead, they use software robots (bots or scripts) that can complete the same actions as human users (e.g., a patient registration specialist logging into the insurance verification portal and checking a patient's eligibility) but faster and with more precision. For example, according to Deloitte, RPA and cognitive automation (CA) can execute high-volume transactional processes approximately 15 times faster than a human and help reduce errors and time spent on rework and review by 70% to 99%.
RPA in healthcare is increasingly being combined with AI to achieve a broader automation scale or add advanced analytics capabilities. For instance, a regular RPA solution for patient records management can extract data from structured texts (online forms). When it's powered by AI, it can also extract data from unstructured texts (e.g., emails or discharge summaries).
RPA Market Trends and Adoption in the Healthcare Industry
The global robotic process automation market size was estimated at $3.79 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 43.9% from 2025 to 2030. The growth of the market can be attributed to the increasing demand for operational efficiency and cost reduction. The segment of RPA in the healthcare industry is expected to grow at 48.2% during the forecast period.
Healthcare Staff Tasks That RPA Can Automate
- Open emails and attachments (e.g., automatically open emails from diagnostic labs containing patient test results).
- Log into a web or a desktop application (e.g., launch a payer portal in a browser and log into it with credentials).
- Download/upload files (for claims submission, prior authorizations, etc.)
- Move files and folders (e.g., automatically move radiology reports from a shared folder to the appropriate patient folder).
- Extract structured data from documents or systems (e.g., extract adverse drug events entries from the EHR system for reporting purposes).
- Compile documents using data from different systems (e.g., EHR or document repository).
- Copy/paste text from different applications into structured fields on a template (e.g., auto-populate insurance eligibility requests, prior-authorization forms).
- Read and write to databases (e.g., retrieve patient demographic information from a hospital database).
- Scrape data from the web (e.g., monitor FDA or CDC websites for updates on drug recalls or new vaccination guidelines and notify relevant staff).
- Make basic calculations (e.g., calculate total cost based on billing codes, copays, and insurance coverage prior to generating a patient invoice).
- Follow 'if/then' decisions/rules (e.g., if a patient has not confirmed their appointment 24 hours in advance, then send a reminder SMS or escalate to front desk staff).
- Deliver files to third parties (e.g., auto-submit compliance reports to regulatory authorities, send invoices to patients).
- Send email/SMS notifications (e.g., appointment confirmations/reminders to patients).
RPA is perfect for straightforward, rule-based routines, but it struggles with more complex operations that require processing unstructured data, understanding context, or making independent decisions. To overcome these constraints, consider reinforcing RPA with AI. Such a combination can work well, for example, for the intelligent triage of GP referrals. RPA bots can pull patient records from the EHR, while NLP (Natural Language Processing) models can read free-text referral letters to predict urgency and the appropriate clinical pathway (e.g., a regular visit to a gastroenterologist or a colonoscopy procedure). Complex cases can still be routed to human clinicians for review.
RPA Applications in Healthcare
System Architecture for Appointment Workflow Automation
While RPA-powered software can be built from scratch, deploying it on the Microsoft Power Automate platform can reduce both development time and overall costs. It can also easily be integrated into the workflows of healthcare organizations already operating within the Microsoft ecosystem. Besides, Power Automate has built-in copilots and native integration with Power BI and AI Builder services, which makes it easier to combine RPA, BI, and AI capabilities for enhanced process optimization and data-driven decision-making.
Below, ScienceSoft's consultants share a reference architecture for the automation of the appointment management workflow based on the Microsoft Power Automate platform. This high-level, generalized overview serves as a conceptual guide; the actual architecture will depend on the specific requirements of the chosen solution.
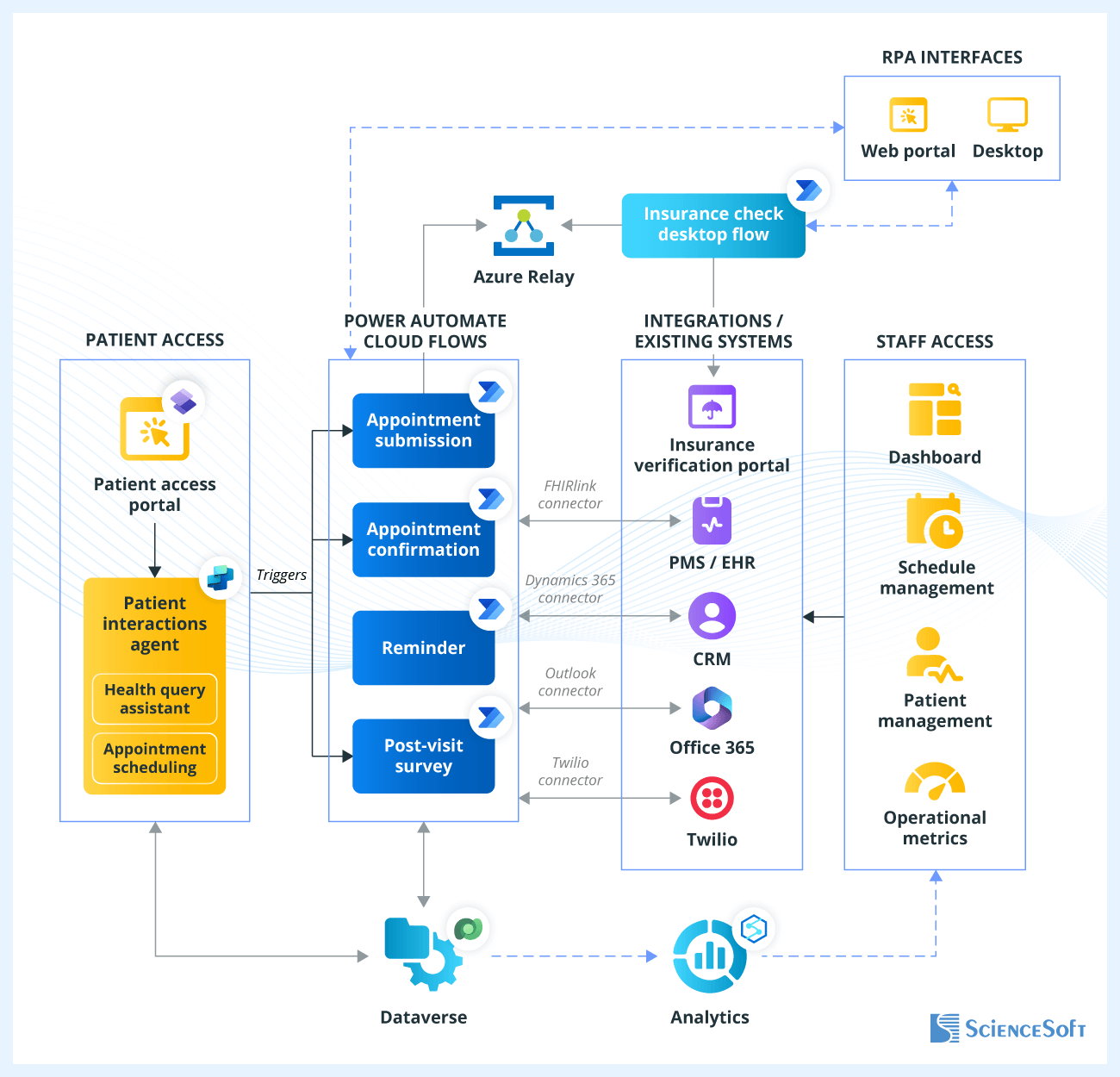
RPA bots, called flows in Microsoft Power Automate, manage the end-to-end automation process. Cloud flows use Microsoft Power Automate connectors to interact with internal systems (like EHR, PMS, and CRM) and external services (such as email or SMS). Desktop flows automate tasks in systems without modern APIs, such as legacy platforms, by mimicking human actions like logging into these systems. These flows are triggered by cloud flows and run in either attended (with user supervision) or unattended (fully automated) mode.
Automation flows in Power Automate can be built even by non-technical users like hospital administrators. They can ask Microsoft Copilot in natural language, for example, to create a flow that schedules appointments and sends confirmation emails. Copilot then generates a draft workflow, suggesting triggers and actions, which administrators can refine, adding conditions or customizing messages.
Once created, automation logic is stored in Microsoft Dataverse, which houses structured data and activity logs.
An example of an automation flow can be the following:
- A patient submits an appointment request through the patient portal. This triggers an automated cloud flow via an HTTP request.
- The cloud flow captures the requested physician's specialty, date, time, and patient ID, and stores the request in Dataverse.
- The cloud flow connects to the calendar system in the EHR via the FHIR R4 connector and searches the provider's calendar for availability in alignment with the 21st Century Cures Act and USCDI.
- If no slots are found, the cloud flow executes fallback logic (e.g., adjusting the date or time). If no alternative is confirmed by the patient, the flow routes the request to administrative staff (e.g., via Microsoft Teams or email) for manual handling.
- If a suitable slot is found, the cloud flow triggers a desktop flow to perform insurance eligibility verification. The desktop flow logs into the insurance portal and checks the patient's coverage, copay, and deductible information.
- Once availability and insurance are confirmed, the cloud flow sends a tentative appointment notification to the patient. It uses either the Office 365 Outlook connector (for email) or the Twilio connector (for SMS). The message includes confirmation and cancellation links, and the flow logs the communication event.
- When the patient confirms the appointment, a cloud flow is triggered via an HTTP webhook. It generates an appointment ID, creates the record in the EHR calendar system, and updates the CRM and Dataverse.
- One day before the appointment, a scheduled cloud flow runs to retrieve upcoming appointments from Dataverse and sends an email or SMS reminder that includes visit details, pre-visit instructions, and a check-in link for virtual visits.
- After the appointment, another cloud flow is triggered (e.g., based on a status update in the system). It sends a feedback form via email and may analyze responses using AI Builder. Based on the input, the system can suggest follow-up appointments, update the CRM, or flag the patient for care management.
Technologies We Use
Machine learning platforms and services




DevOps
Containerization
Automation
CI/CD tools
Monitoring
Costs of Implementing RPA in Healthcare
Based on ScienceSoft’s experience, the cost of implementing RPA in healthcare ranges from $25,000 to $250,000+. Pricing depends on factors such as:
- The number, type, and complexity of workflows being automated
- The scope of system integrations required.
- Security and compliance requirements to be taken into account (e.g., HIPAA).
- AI capabilities (e.g., agentic AI).
Below are sample cost scenarios using Microsoft Power Automate:
$25,000–$90,000
For automating a specific administrative task, such as appointment scheduling, patient records management, or insurance eligibility checks.
Operational costs: $15 per user/month for Power Automate platform usage.
$150,000–$250,000+
For a comprehensive solution combining RPA and AI to automate complex workflows, such as prior-authorization or triage of general practitioner (GP) referrals.
Operational costs: $15 per user/month for Power Automate platform usage + $500/month for AI Builder capacity (for AI-driven features like NLP, document recognition, or risk scoring).
Why ScienceSoft?
- 20 years in healthcare IT.
- ISO 13485, ISO 9001, and ISO 27001 certifications.
- Experience in achieving compliance with the requirements of HIPAA, GDPR, and the 21st Century Cures Act.
- Principal architects with experience building complex and secure solutions for the healthcare industry.
- In-house PMO with 40+ project managers holding PMP, PSM I, PSPO I, ICP-APM, and other certifications.
Our awards, recognitions, and certifications
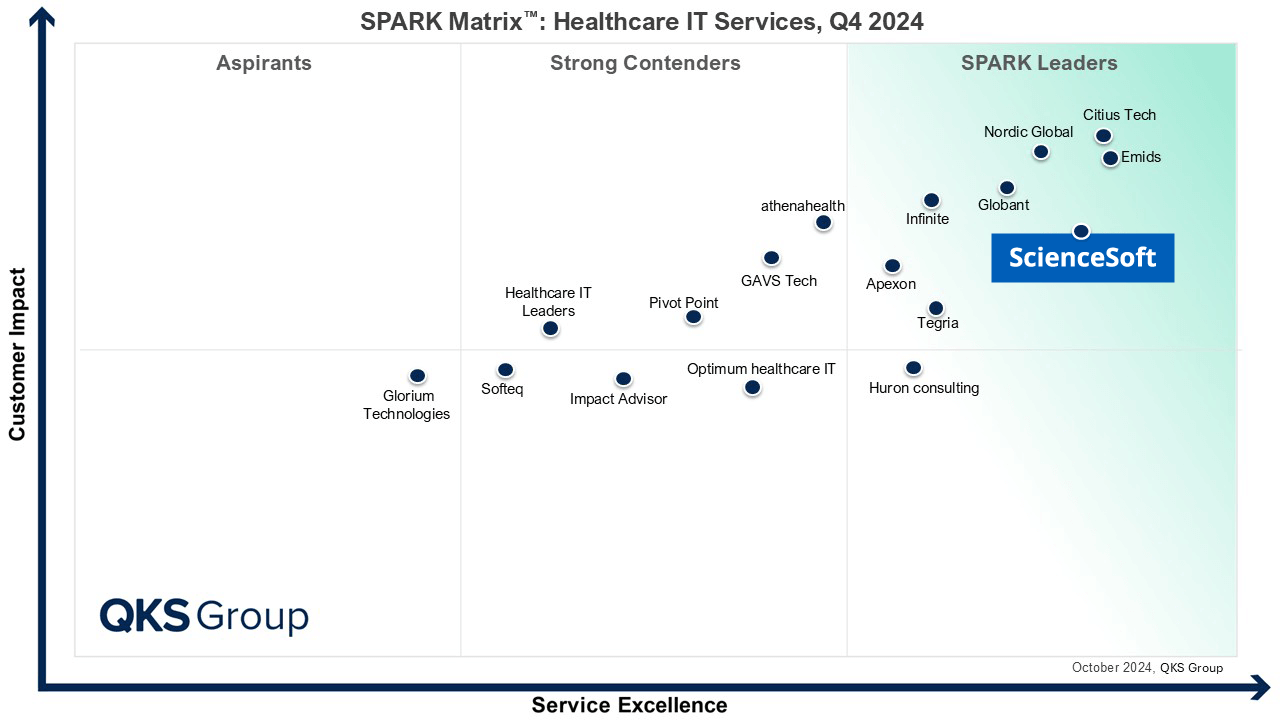
Featured among Healthcare IT Services Leaders in the 2022 and 2024 SPARK Matrix
Recognized for Healthcare Technology Leadership by Frost & Sullivan in 2023 and 2025
Named among America’s Fastest-Growing Companies by Financial Times, 4 years in a row

Top Healthcare IT Developer and Advisor by Black Book™ survey 2023
Four-time finalist across HTN Awards programs

Named to The Healthcare Technology Report’s Top 25 Healthcare Software Companies of 2025

HIMSS Gold member advancing digital healthcare
ISO 13485-certified quality management system
ISO 27001-certified security management system







