AI in Long-Term Care
Overview
In AI consulting and development since 1989 and in healthcare IT since 2005, ScienceSoft helps healthcare software product companies and long-term care providers design scalable and user-friendly AI systems. We deliver applications of different complexity, from AI chatbots for streamlining administrative tasks and personalizing long-term care to AI-powered remote monitoring and fall detection systems. We can launch an MVP in 1–4 months and develop a full-fledged solution with major releases every 2–4 weeks.
AI for Long-Term Care: Essence
Artificial intelligence (AI) in long-term care (LTC) can enhance care quality with personalized care plans, improve the safety of senior residents with fall detection and wander alerts, and reduce the administrative burden on care staff with voice-based charting through virtual assistants.
Market Overview and AI Adoption in Long-Term Care
According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 142 million older people are unable to meet their basic needs independently, and two out of three older people are likely to need care and support at some point during their lives. At the same time, the WHO estimates a shortage of 4.5 million nurses by 2030. This combination of growing demand for long-term care and a shortage of healthcare professionals drives senior living facilities and hospitals to implement AI-powered solutions. In fact, a 2024 survey of 100 US senior living facilities by LifeLoop revealed that AI was the technology that senior living leaders planned to use the most.
Use Cases of AI for Long-Term Care
Below, our healthcare consultants summarized the most common applications of AI in long-term care.
Records management and care planning
Long-term care facilities manage extensive resident documentation that must stay current, e.g., ADL assistance levels. AI-supported solutions can save hours of staff effort each day. GenAI agents and multi-agent systems in an LTC EHR can turn dictated notes into structured entries, generate summaries for care handoffs, and flag missing documentation. They can also propose personalized care plans based on the resident record and facility templates and submit them for staff review. Such drafts can then automatically feed daily task lists for the staff that reflect the residents’ current status, required assistance, and cognitive training goals.
You can find a sample Azure-based architecture for the EHR orchestration layer that supports GenAI agent workflows on the AI-native EHR page.
Assistants for people receiving long-term care
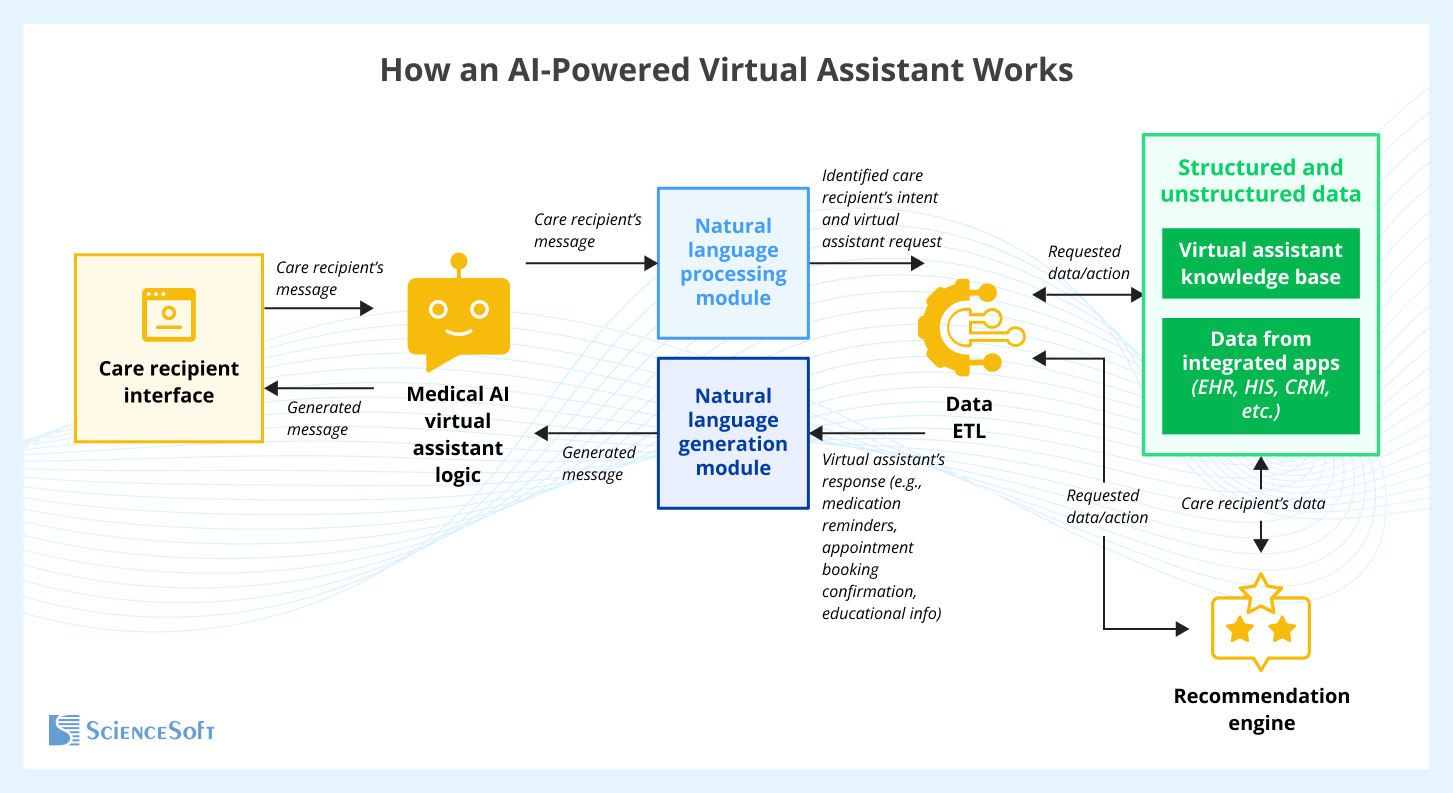
GenAI-powered virtual assistants help people receiving long-term care handle daily tasks through natural voice or chat conversations. They can set medication reminders based on schedules entered by a care recipient, a family caregiver, or care staff, schedule home visits or appointments, and send routine updates to designated family contacts and the care team. For education, assistants can answer questions using approved facility materials and care protocols, so guidance stays consistent for chronic conditions such as diabetes or Alzheimer’s disease.
Voice and chat conversations can provide companionship, prompt cognitive activities, and suggest music, videos, and audiobooks that match preferences and cognitive ability. With GenAI-guided check-ins, residents can answer prompts about mood and symptoms, and the assistant summarizes what changed since the last check and flags responses that may need follow-up by care staff. Verified check-in summaries can be added to the resident care plan, so the care team and the resident or family can spot changes earlier.
Below, ScienceSoft's architects share a sample architecture of an AI-powered virtual assistant for people receiving long-term care.
AI can enhance remote patient monitoring systems used in home care and eldercare settings. AI algorithms can process the data received from the connected medical devices and smart wearables to model individual baselines for each care recipient, detect anomalies (e.g., HR spikes, gradual glucose increases), and assign individualized risk scores (of hospitalization, cognitive deterioration, etc.). When anomalies are detected, the AI system can trigger real-time alerts to caregivers, suggest diagnostic tests, and recommend care plan modifications (e.g., medication adjustments, referrals to cardiology, endocrinology, or neurology). AI-powered monitoring systems can also prioritize alerts based on severity (e.g., life-threatening vs. non-urgent) to prevent the alert fatigue of caregivers.
Fall detection and prediction
AI can enable fall detection systems by analyzing the real-time data received from smart wearables and wireless sensors embedded in the long-term care or home environment. The AI engine can detect critical events, such as falls or sudden immobility, and determine the need for intervention. When abnormal patterns are identified, the AI system can autonomously trigger alerts to staff or the emergency services (in case of home care). The AI engine can also analyze an individual's fall history (e.g., frequency, timing, context of falls), medical history (e.g., medications, mobility impairments, chronic conditions such as Parkinson's or diabetes), and current vitals (e.g., heart rate, gait patterns, and blood pressure) to predict the likelihood of future falls. Fall detection systems can include caregiver validation loops and real-time model retraining, improving accuracy over time and ensuring reliable alerts. AI-powered solutions can also identify potential causes or trends and offer preventive recommendations, for example, modifying the environment (removing tripping hazards, ensuring adequate lighting, or installing grab bars) or adjusting the treatment (e.g., if a fall was a side effect of a recently administered med).
The AI engine can analyze a resident's past wandering behaviors, real-time behavioral changes (e.g., increased pacing), and cognitive status (e.g., dementia stage) to predict the likelihood of wandering before it occurs. For example, if a senior resident tends to wander in the early morning when confused or agitated, AI can detect the pattern and trigger actions (e.g., alert a nurse, verbally redirect or calm a resident in case the wander management system is integrated with a virtual assistant). The AI engine can also be used to identify potential triggers of wandering incidents, such as noise or medication, assign risk scores to residents, and recommend preventive strategies like distraction, engagement, or hydration. Additionally, ML algorithms can analyze staff response time trends to support workflow improvements and enhance resident safety.
Staff scheduling
AI-powered systems can provide long-term care facilities with recommendations on optimal shift scheduling and staff allocation by considering factors like historic data on care demand (identifying high-demand periods), care recipient condition, upcoming appointments, planned family visits, employees' working hours and skills.
Social engagement
AI-powered community engagement platforms can connect senior residents with similar interests and become their convenient collaboration space. For example, powered by an ML-based matching engine, such platforms can help residents with similar interests find each other and make friends.
Assistants for family members
AI-powered chatbots for family engagement can automatically answer questions of family members about the health status of their senior relatives and provide the necessary information instantly, freeing up time for nurses and other caregivers.
Insights from ScienceSoft's Healthcare IT Experts
Techs We Use to Build AI Solutions for Long-Term Care
Considerations of Using AI for Long-Term Care
Below, our healthcare consultants outlined some of the key considerations to take into account when developing an AI-supported solution for long-term care.
Consideration #1
AI-powered long-term care solutions must ensure high algorithm accuracy to generate trustworthy insights (e.g., predicting wander events) and drive effective care outcomes (e.g., timely interventions that prevent resident injuries and reduce emergency hospital visits).
Solution
To further improve the model's accuracy, we use a human-in-the-loop approach where caregivers validate AI outputs (e.g., false fall alerts). This feedback is captured in a dashboard and fed back into the model to improve future predictions, creating a continuous learning loop.
Maintaining model accuracy is not only a technical challenge but a business-critical one: high false-negative rates in fall detection can lead to resident harm and legal action; high false-positive rates contribute to alert fatigue and staff disengagement. Accuracy metrics like precision, recall, and F1 score should be monitored as operational KPIs.
Consideration #2
Advanced AI solutions may incur high development and maintenance costs.
Solution
Costs of AI Solutions for Long-Term Care
The cost of AI solutions for long-term care typically ranges from $30,000 to $800,000. Pricing depends on several factors, including the scope and complexity of the solution, whether it’s built from scratch or integrated into existing software, and whether it leverages pre-trained models or requires the development of a proprietary AI model.
Key cost factors that influence the cost of an AI-powered app include:
- The scope of AI functionality. For example, a basic chatbot that can communicate via text messages and handle simple tasks like appointment scheduling will require much less investment than a virtual assistant that can understand voice commands, provide brain games, detect distress from voice tone, and learn preferences over time.
- Algorithm complexity. For example, developing a solution based on low-complexity decision tree algorithms for fall detection will require fewer efforts than developing a solution based on a neural network that can detect motion patterns, identify potential falls, and learn to improve performance over time.
- The number of data sources and the volume of data for processing (e.g., medical histories, real-time health monitoring data).
- The number and complexity of integrations with other solutions. For example, a fall detection system may need to be integrated with the EHR to automatically input fall-related data (e.g., date, time, location of a fall), eMAR software to help caregivers determine if a recent medication change may have contributed to the fall, remote patient monitoring system to check the care recipient's vitals after a fall, nurse call system to automatically alert nurses or emergency personnel after a fall is detected.
Below are sample costs for some AI-powered solutions in high demand:
AI for records management
From $30,000
AI module that enables a single data management process, e.g., summarizing residents' medical histories or recognizing handwritten notes from caregivers.
From $150,000
A virtual assistant that can transcribe conversations of care recipients with the long-term care facility staff.
From $800,000
A custom AI-powered EHR system for long-term care with features like auditory input of care notes, scheduling recommendations to optimize staff-resident interactions, and smart billing tools that automatically capture services provided and align them with long-term care reimbursement codes.
AI for care personalization
From $30,000 to $200,000
A single-purpose AI tool, such as a virtual assistant that can provide voice or visual reminders for senior residents to take their medications.
From $70,000 to $250,000
A senior resident app with an AI chatbot providing appointment scheduling assistance and informational support (e.g., on medication side effects and regimen, on managing conditions like arthritis, diabetes, or high blood pressure).
From $300,000 to $800,000+
An EHR-integrated digital therapeutics solution with AI-powered care planning and real-time remote patient monitoring features.
What Makes ScienceSoft a Reliable Partner for Delivering AI Solutions for Long-Term Care
- Since 2005 in healthcare IT.
- Since 1989 in AI software development.
- AI consultants and developers with 7–20 years of relevant experience and competencies in major ML technologies, frameworks, and libraries.
- ISO 13485, ISO 9001, and ISO 27001 certifications.
- Expertise in HIPAA, GDPR, NCPDP, FDA, ONC, MDR, and other regulatory requirements.
- Proficiency in healthcare standards (e.g., HL7, FHIR, USCDI, ICD-10, SNOMED CT, LOINC, CPT, XDS/XDS-I, CCDA).
Our awards, recognitions, and certifications
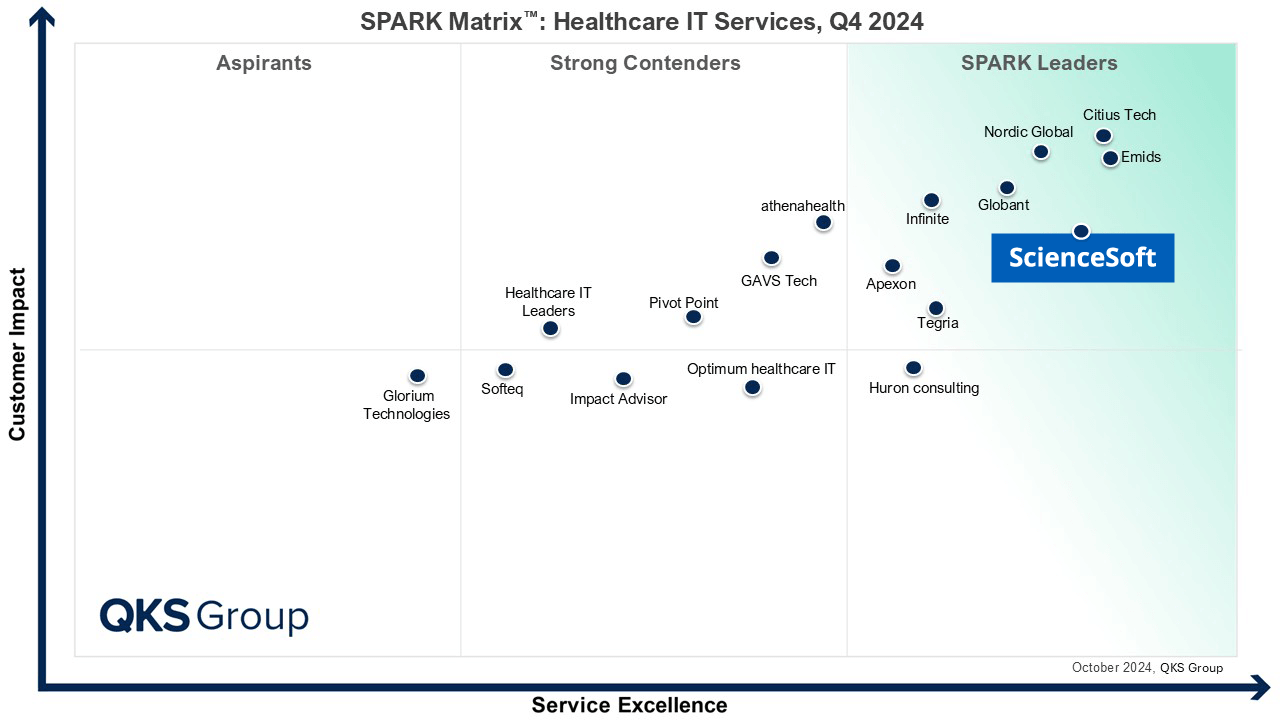
Featured among Healthcare IT Services Leaders in the 2022 and 2024 SPARK Matrix
Recognized for Healthcare Technology Leadership by Frost & Sullivan in 2023 and 2025
Named among America’s Fastest-Growing Companies by Financial Times, 4 years in a row

Top Healthcare IT Developer and Advisor by Black Book™ survey 2023
Four-time finalist across HTN Awards programs

Named to The Healthcare Technology Report’s Top 25 Healthcare Software Companies of 2025

HIMSS Gold member advancing digital healthcare
ISO 13485-certified quality management system
ISO 27001-certified security management system