EHR for General Surgery
Specialized Capabilities, Development Roadmap, and Costs
In medical software engineering since 2005, ScienceSoft designs EHR solutions tailored for general surgery to streamline perioperative workflows with minimal administrative overhead. We align with HIPAA/GDPR and support organizational programs for HITRUST certification and Cures Act information-sharing compliance.
A Brief Look at EHR in General Surgery
Electronic health records for general surgery provide a single environment for managing surgical patient data across the perioperative cycle. They store structured surgical information and support core workflows, including order entry, scheduling, consent management, medication prescribing, and outcome tracking.
Custom EHR development makes sense for ambulatory surgery centers that need lean, specialty-specific workflows without replacing their enterprise EHR, for service lines aiming to orchestrate ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery) adherence and integrate registry or SSI reporting, and for academic medical centers with complex surgical workflows involving residents, fellows, and research registries. A tailored general surgery EHR module lets compliance and quality activities run seamlessly inside the everyday workflow rather than as a separate administrative process.
Useful integrations for general surgery EHR software: ORIS, AIMS, RIS, LIS, PACS, pharmacy networks, HIE, RPM, ERP, patient portal/app, surgical quality and infection surveillance registries.
Implementation time: 8–10 months for an MVP (e.g., one service line, core integrations); 12–18+ months for enterprise-wide deployments.
Costs: $200,000–$2,000,000+. You’re welcome to use our free calculator to estimate the cost of your initiative.
Specialized EHR Capabilities for General Surgery
Each surgical facility has its own mix of clinical priorities, reporting obligations, and integration environments, so the exact functional scope is defined individually for each project. The list below shows the features most commonly requested by ScienceSoft’s clients in general surgery.
How AI Can Assist in Surgical Workflows
Artificial intelligence in EHR systems can reduce workload and speed up clinical processes. Below is a list of the most feasible AI applications for general surgery.
Administrative support
- Ambient documentation (speech processing) during pre-op and post-op encounters.
- Surgical data extraction and structurization from free-text documentation.
- Context-aware information retrieval and summarization.
- Patient self-service chatbots (scheduling, instructions, FAQs, etc.).
Clinical decision support (may require regulatory clearance)
- Patient record analysis (across lab results, imaging assessments, surgical history, etc.) to detect patterns, trends, and abnormalities, identify high-risk patients, and catch deterioration early.
- Predictive analytics to forecast post-op complications, infection risk, etc.
- SSI signal detection in notes, messages, or PROs.
- Medical image analysis.
Valuable Integrations for a General Surgery EHR System
To enhance surgical automation, ScienceSoft’s consultants suggest integrating the EHR with the following standard systems. The actual integration map would be closely bound to your IT ecosystem and operational specifics.
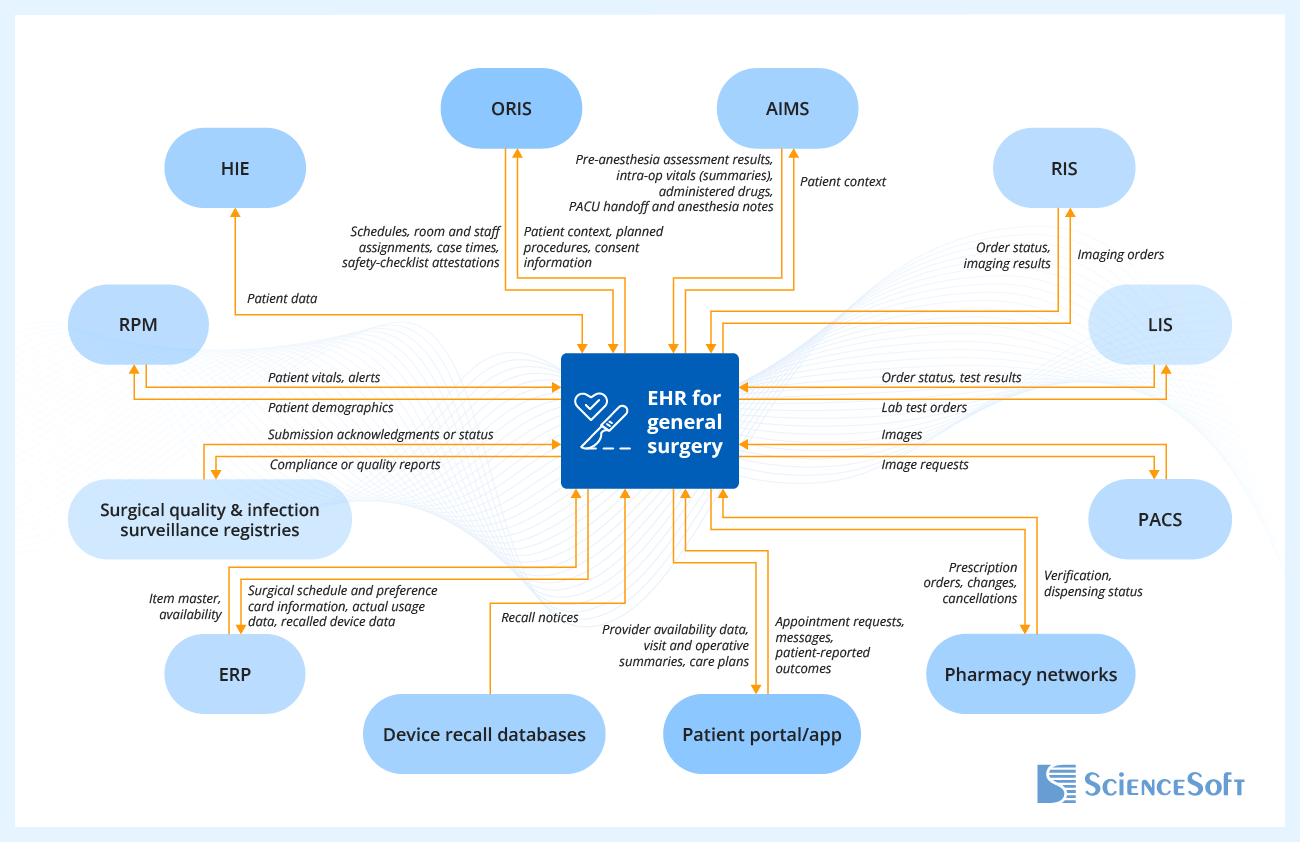
- Health information exchange (HIE) to securely exchange surgical encounter data, lab results, operative notes, and discharge summaries across hospitals, ASCs, and primary care providers.
- Operating room information system (ORIS) to book operating rooms and schedule patients for surgical procedures; to capture operational surgery data (case times, staff assignments, supply usage) for full traceability.
- Anesthesia information management system (AIMS) to document the entire anesthesia workflow in the EHR (pre-anesthesia assessments, ASA class, intra-operative vitals streamed from monitors, etc.).
- Radiology information system (RIS) to manage imaging orders, schedule patients for X-rays, CT, or ultrasound scans, and view results directly in electronic health records.
- Laboratory information system (LIS) to feed pathology and microbiology results into the patient’s chart and to monitor intra-op specimen management and post-op SSI surveillance data.
- Picture archiving and communication system (PACS) for in-chart access to radiology and intraoperative images.
- Pharmacy networks to send electronic prescriptions directly to the pharmacy and track verification and dispensing status.
- Patient portal or app for patients to schedule post-op follow-ups, view operative notes, complete PRO forms, and communicate with their surgical care team.
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software to connect surgical supply chain data to the implant log and operative documentation.
- Device recall databases to flag impacted implants, generate patient lists, and trigger clinician and patient notifications.
- Surgical quality and infection surveillance registries to speed up compliance and quality reporting.
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM) system to track post-operative vitals (e.g., temperature, heart rate, SpO₂) collected from connected devices in the EHR, with alerts for early detection of complications.
How to Build an EMR System for General Surgery
1.
Discovery and project planning
The process begins with an in-depth review of current surgical workflows. Business analysts and healthcare consultants work closely with surgeons, anesthesiologists, perioperative nurses, infection prevention specialists, and administrators to identify where existing systems fall short. Their input shapes the functional and non-functional requirements that describe what the new system must deliver: from structured surgical records and ERAS order sets to integration with lab, imaging, and pharmacy networks.
Compliance specialists examine regulatory obligations such as HIPAA, ONC certification criteria, DEA requirements for EPCS, and quality reporting standards like NHSN OPC and ACS NSQIP. In parallel, data migration specialists plan strategies for moving surgical notes, implant logs, preference card templates, and scheduling data from legacy systems to the new environment. The project team then creates a roadmap that outlines development milestones, integration priorities, budget estimates, and KPIs such as ERAS adherence and completeness of surveillance data.
Learn how ScienceSoft incorporates compliance into every stage of healthcare software development.
2.
Architecture design
Architects translate requirements into an overall system structure. At this stage, the team decides which quality attributes to prioritize. For a surgical EHR, scalability to handle high data volumes, reliability during peak usage, and cost-efficient cloud deployment are common focal points. The next step is to decompose the EHR into logical and functional modules. Architects define how these modules interact with each other and with external systems and prepare data flow diagrams that specify APIs, data formats, and communication protocols. In parallel, engineers compare frameworks and databases for performance and maintainability, assess licensing costs, and consider future scalability. The final choices are documented, along with a deployment strategy and a failover plan.
Learn how ScienceSoft ensures standards-based interoperability in healthcare software.
3.
UX/UI design
UX and UI designers define role-specific user journeys: how a surgeon documents an operative note, how a nurse verifies consent forms, or how an infection preventionist extracts OPC data. This helps them connect software functions with real surgical tasks. Next, they create wireframes and UI prototypes, which are validated in real surgical scenarios to ensure usability in high-pressure settings.
Designers focus on making administrative processes clear, fast, and foolproof. For example, operative note headers can pre-fill with the planned procedure, side, and mapped NHSN category, while ASA and wound class appear as suggested values from linked assessments. ERAS order sets can load with contextual defaults (multimodal analgesia, antiemetics, and VTE prophylaxis aligned to the procedure type), so clinicians start from a safe baseline instead of an empty form.
Learn how ScienceSoft builds user convenience into healthcare UX design.
4.
Development and testing
EHR development typically follows a different rhythm than consumer or enterprise software. Because regulatory requirements and clinical workflows are clearly defined, the scope of features stabilizes early. Instead of delivering minor updates every few weeks, engineering teams focus on producing a validated MVP and then evolving the system through less frequent, carefully planned releases. Any changes that touch order management, data integrity, or reporting workflows formal change control review led by technical, clinical, and compliance stakeholders to preserve regulatory alignment and prevent disruption to established surgical processes.
For a surgical EHR, the MVP typically includes the patient record module with structured surgical data, core charting and note templates, ERAS-based order sets, implant log with UDI capture, and basic integrations with LIS, RIS, PACS, and pharmacy networks. Once the core is stable, engineers extend functionality through clinically meaningful increments. Later releases may add compliance and quality reporting templates (SOR, C-CDA, OPC forms), operational analytics and outcome dashboards, device recall response, and patient engagement modules (portal, telemedicine, mobile adherence tools). Each increment is validated against measurable acceptance criteria (e.g., verifying that device recall alerts appear in implant logs within defined timeframes).
5.
Pre-launch activities
Right before deployment, compliance specialists conduct internal audits to verify adherence to HIPAA or GDPR, and other necessary regulations. They also review and update relevant documentation to ensure all regulatory deliverables (e.g., validation evidence for ONC or FDA-relevant modules) are up to date and aligned with the latest guidelines. Data migration specialists extract, transform, and load surgical data from legacy systems into the new EHR.
To ensure users adopt the system smoothly, the development team prepares a full set of knowledge-transfer materials. This typically includes a user guide, system administration manual, maintenance and support guide, and integration handbook that explains interfaces with LIS, RIS, PACS, ERP, and registries. Training sessions are conducted for each role group: surgeons rehearse operative note completion, nurses practice consent and safety checklist workflows, infection preventionists walk through data extraction for NHSN, and administrators learn to configure templates. At ScienceSoft, we typically split training into two groups. The early adopters help us uncover and fix hidden issues and refine user manuals. Later, they can coach their peers to speed up the large-scale adoption.
Learn how ScienceSoft treats knowledge transfer and user training in healthcare IT projects.
6.
Deployment and monitoring
Deployment can also go in waves rather than all at once. It may start with one hospital service line, such as general abdominal surgery, then expand once the core workflows prove stable. Implementation teams provide round-the-clock support during go-live, monitoring adoption, and collecting user feedback. Post-deployment, outcome dashboards, quality reporting feeds, and integration flows are closely observed to ensure data accuracy. Continuous monitoring extends to regulatory changes and evolving standards, allowing the system to stay aligned with updates in NHSN mapping, ONC certification rules, or device recall processes.
ScienceSoft’s EHR/EMR Tech Stack
Low-code development
Device connectivity
Machine learning platforms and services
AWS





Azure
Blockchain frameworks
Telehealth
Video streaming
Messaging and conferencing
Payment gates

EHR for General Surgery Development Costs
The cost of building an EHR system for general surgery can vary from $150,000 to $2,000,000+, depending largely on functional scope and required integrations.
$200,000–$300,000
For a surgery-specific module integrated into an existing enterprise EHR. This option adds structured surgical documentation, ERAS order sets, or operative note templates, while reusing the organization’s existing infrastructure and data model.
$400,000–$800,000
For a standalone system that covers core surgical workflows (structured charts and notes, ERAS order sets, digital safety checklist, e-prescribing) and basic integrations (e.g., ORIS, LIS, RIS/PACS).
$800,000–$1,400,000
For software that extends into compliance and operational support (UDI capture, device recall response, post-discharge surveillance data capture, compliance and quality reporting templates) with broader integrations (e.g., ERP, registries, RPM).
$1,500,000–2,000,000+
For an enterprise-level platform that adds telemedicine, patient engagement, and advanced analytics, plus AI-powered modules (ambient documentation, complication risk prediction).
Get to Know the Cost of Your EHR Development Project
Please answer a few quick questions about your EHR requirements to help our healthcare IT consultants calculate your solution cost faster.
Thank you for your request!
We will analyze your case and get back to you within a business day to share a ballpark estimate.
In the meantime, would you like to learn more about ScienceSoft?
- Project success no matter what: learn how we make good on our mission.
- Since 2005 in healthcare IT services: check what we do.
- 4,200+ successful projects: explore our portfolio.
- 1,400+ incredible clients: read what they say.

ScienceSoft as a Trusted Partner in EHR Development
- Since 2005 in medical software engineering.
- 150+ successful healthcare IT projects.
- Principal architects with 15+ years of experience engineering highly integrated, enterprise-scale software solutions that stand the test of time.
- 550+ developers, 50% of whom are seniors or leads.
- In-house consultants with Medical Doctor degrees and up to 20 years of experience in the sector.
- Proficiency in healthcare-specific regulations (incl. HIPAA, HITECH, ONC requirements, 21st Century Cures Act, GDPR, and more).
- Hands-on experience with healthcare interoperability standards (HL7, FHIR, CCDA, X12 837/835, XDS/XDS-I, NCPDP SCRIPT, and more), uniform datasets (e.g., USCDI), and clinical coding vocabularies (e.g., ICD-10, CPT, SNOMED CT, LOINC, RxNorm).
Our awards, recognitions, and certifications
Featured among Healthcare IT Services Leaders in the 2022 and 2024 SPARK Matrix
Recognized for Healthcare Technology Leadership by Frost & Sullivan in 2023 and 2025
Named among America’s Fastest-Growing Companies by Financial Times, 4 years in a row

Top Healthcare IT Developer and Advisor by Black Book™ survey 2023
Four-time finalist across HTN Awards programs

Named to The Healthcare Technology Report’s Top 25 Healthcare Software Companies of 2025

HIMSS Gold member advancing digital healthcare
ISO 13485-certified quality management system
ISO 27001-certified security management system









