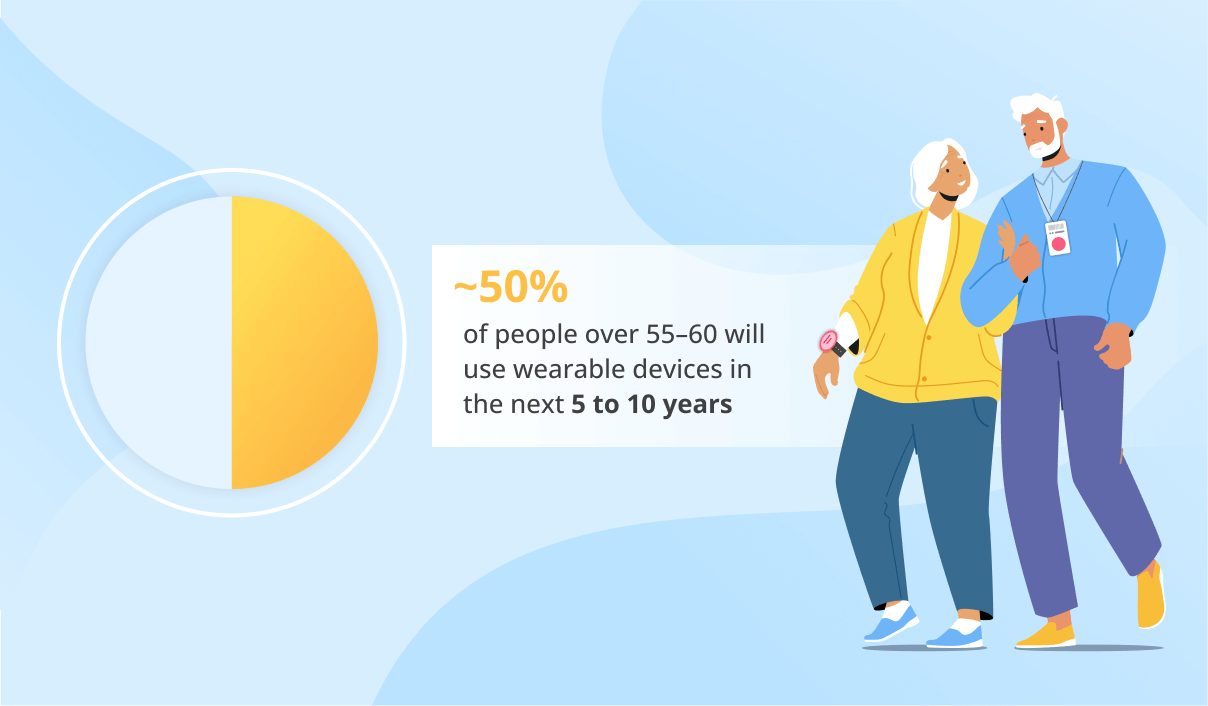
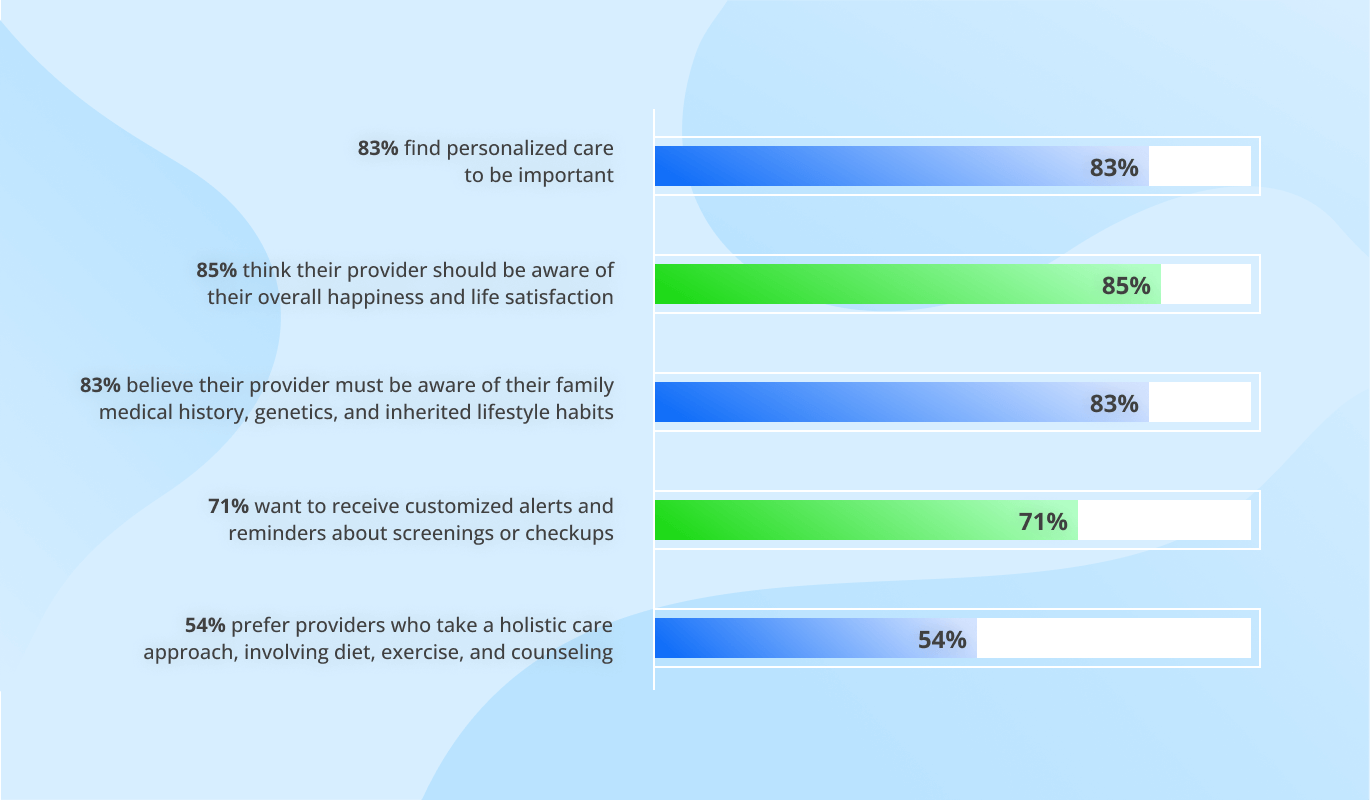
AI for Treatment Personalization
Use Cases, Architecture, Costs
Since 1989 in AI development and since 2005 in healthcare IT, ScienceSoft designs secure AI-powered solutions to help healthcare providers deliver more personalized and effective care.
AI-Driven Treatment Personalization in Brief
AI solutions for care personalization use machine learning and patient data analytics to adapt medical care to each patient's specific needs and characteristics. This process usually involves consolidating large amounts of patient data, such as medical history, demographic data, and real-time readings from wearable devices. Artificial intelligence analyzes that data to enhance care personalization on both the doctor’s and the patient's side. For instance, physicians can use AI suggestions for personalized health plans, while patients can navigate their rehabilitation process with the help of virtual assistants.
Healthcare AI Market Overview
In 2024, the healthcare AI market was valued at $20.9 billion worldwide. It is expected to reach $148.4 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 48.1%. There are a number of factors that drive the growth of AI in healthcare:
- Intense economic pressure on healthcare providers due to the aging population and an increasing number of patients with chronic diseases.
- The exponential growth of data in the healthcare domain that is still not being taken advantage of by providers.
- The rising demand for enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and better patient outcomes in the healthcare domain.
Use Cases of AI for Personalized Care
Personalized treatment plans
AI analyzes heterogeneous clinical data, such as the patient’s physiological characteristics and demographics, treatment history, medical images, and lab results. The data is then further analyzed by AI and used to generate customized care plans or recommend adjustments to the treatment programs offered by physicians.
Diagnostic support and predictive analytics
Diagnostic AI models can interpret medical images, detect patterns in symptom history, analyze lab test results, monitor real-time patient vitals, and more. Analyzing this data enables AI models to identify early signs of potential health issues and predict disease progression and patient outcomes. This allows for timely clinical interventions and proactive care plan changes.
Medication customization
By analyzing a patient’s health data (including allergies, chronic diseases, and already prescribed medicine), AI algorithms can predict how the patient would respond to certain drug components and identify the most suitable medications and optimal dosages, lowering the risk of adverse events and unwanted drug interactions. When integrated with smart medical devices (e.g., glucose monitors), AI models can also track medication efficiency during the intake period and suggest dosage adjustments or drug alternatives for a physician to consider.
With the help of AI, physicians can automatically set personalized thresholds for monitoring vitals, physical activity, location, environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, air quality), and more, depending on each patient’s needs. AI can then identify anomalies in health data in real time and promptly alert physicians. Lastly, AI-powered systems can also track patient progress during treatment or rehabilitation and suggest treatment plan adjustments that can then be sent to healthcare professionals for approval.
Patient sentiment analytics
Natural language processing (NLP) can be used to gauge patient sentiment and adjust communication strategies. By analyzing a patient’s tone and word choice, a patient-facing AI solution can tailor its communication style based on the patient’s emotional state and needs. AI can also advise healthcare professionals on adjusting their interactions with patients to make sure they feel heard and understood.
Therapy delivery
Although this field is not fully developed and regulated yet, a properly trained AI engine can serve as a legitimate therapeutic tool. For example, an AI chatbot can be used for cognitive-behavioral therapy, providing interactive conversations and tools for dealing with symptoms of anxiety and depression. However, such a tool will need to get FDA approval or CE marking before being released to the market.
Personal AI assistants
Basic patient-facing AI tools like chatbots can provide informational support to patients and perform simple tasks like appointment scheduling. More advanced AI assistants can guide patients through their treatment and rehabilitation process, answer patients’ questions about their condition, remind them to take their medications, do exercises, or log their symptoms, and help them deal with stress. When integrated with medical devices and wearables, this functionality can be especially useful for facilitating self-management in post-operative, chronic disease, and cancer patients.
Get AI-Driven Insights for Effective Treatment Planning
ScienceSoft is ready to build compliant and accurate AI-enabled software for streamlined care planning and improved patient outcomes.
How AI-Driven Treatment Personalization Works
Drawing on their experience in designing medical AI software, ScienceSoft's software engineers provide a sample architecture for an AI-driven solution for care personalization.
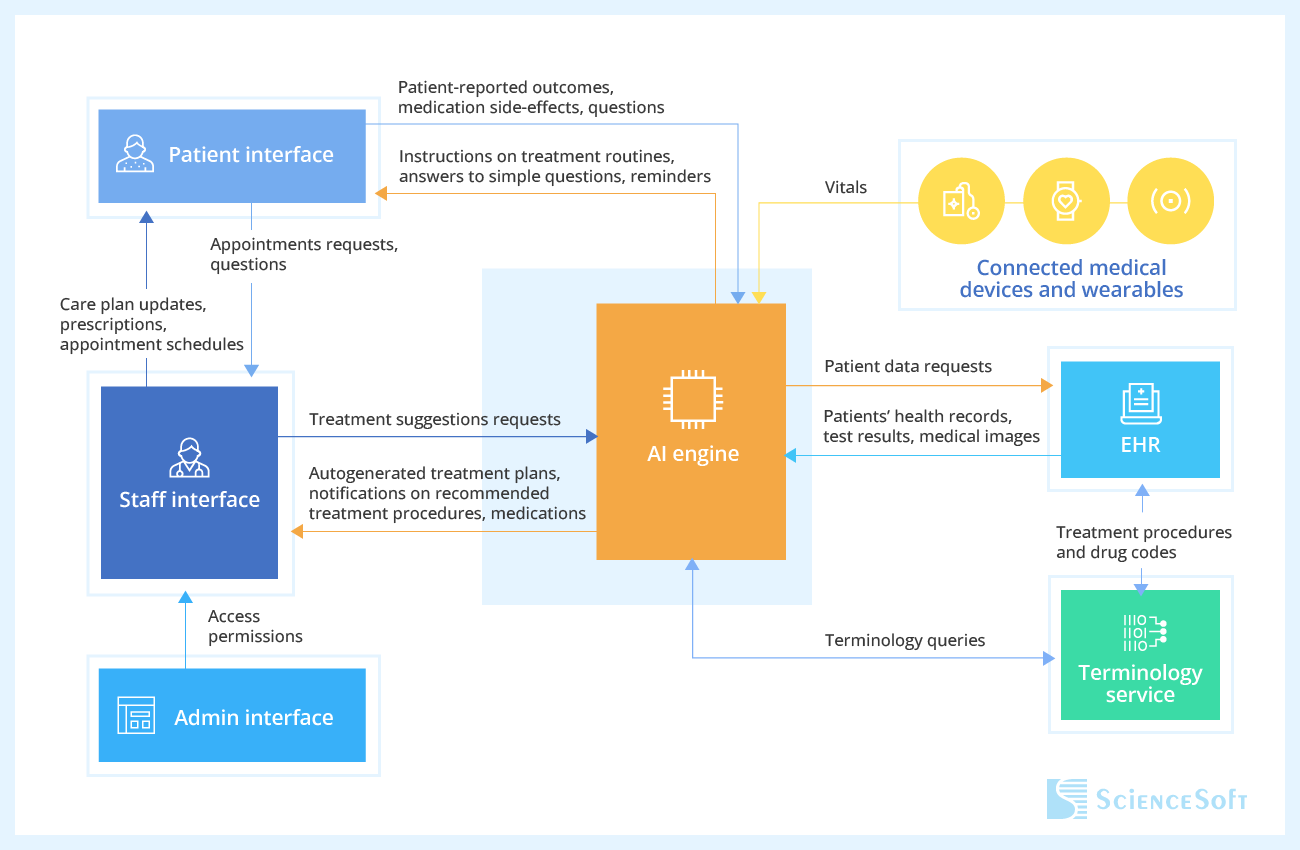
Technology Behind AI-Powered Personalized Care
Machine learning platforms and services
AWS





Azure
Google Cloud Platform
Machine learning frameworks and libraries
Frameworks
Libraries
How to Address the Challenges of AI-Driven Treatment Personalization
Using AI to personalize care delivery leads to better health outcomes and increased patient satisfaction. However, applying AI in healthcare solutions comes with a distinct set of challenges. Here is how we address them:
1
Resistance to adoption
Clinicians’ concerns about AI’s reliability and potential impact on their professional autonomy can hinder its adoption. To address these human barriers to AI adoption, ScienceSoft recommends allocating substantial time to educating staff about AI-driven software usage. Clinicians are more likely to embrace AI if they understand how it works and how it can benefit them. Comprehensive training programs and user guides can facilitate the integration of AI into existing routines. Another measure is establishing clear boundaries between AI-automated tasks and actions that need human approval. For example, AI can suggest a medication, but clinicians must validate this suggestion first.
Regardless of model accuracy, using AI output for such high-risk tasks as treatment planning and medication selection will require human validation. At this point in its evolution, AI should be used as an assistive tool rather than a replacement for a trained clinician. We strongly advise medical professionals to validate AI output before making clinical decisions.
2
PHI security risks
When using proprietary PHI for AI training, healthcare providers must ensure that their IT team or business associates properly de-identify the data.
Another concern comes from using third-party components (e.g., ready-made cloud AI tools). Solution architects must ensure that these tools comply with applicable regulations. To learn more, check our dedicated page about HIPAA-compliant cloud platforms. Additionally, ScienceSoft’s data scientists recommend only using anonymized data where possible to avoid risks.
One more important consideration is who can access an AI solution and with whom it can potentially share data. For example, a virtual assistant might inadvertently disclose sensitive information to other patients. Natural language processing safeguards, such as response filtering, can prevent patient-facing AI solutions from disclosing PHI.
The Costs of Implementing AI for Patient Treatment Personalization
The primary cost drivers of a solution with AI-powered treatment personalization functionality include:
- The scope and complexity of AI functionality.
- The number of data sources and the volume of data to be stored and processed.
- The extent of data cleaning and preprocessing needed.
- The number and complexity of integrations with healthcare IT systems (e.g., EHR, diagnostic software, e-prescribing platforms, etc.).
- The number of integrations with medical devices.
- Security, performance, and UI/UX requirements.
- Output speed (delivering AI insights in batches or in near real time).
- Compliance-associated costs (e.g., for FDA submission of SaMD functionality).
The costs of an AI-driven solution for treatment personalization may vary from $30,000 to $2,000,000. See several examples of solutions that have AI functionality below:
$30,000–$200,000
For a single-purpose AI tool (e.g., a smart drug interaction checker or a medical image analysis module).
$70,000–$250,000
For a patient app with an AI chatbot providing informational support and appointment scheduling assistance.
$300,000–$800,000+
For an EHR-integrated digital therapeutics (DTx) solution with AI-powered treatment planning and real-time patient monitoring features.
$600,000–$2,000,000
For an advanced EHR system with AI-powered clinical decision support, image analysis, and predictive analytics capabilities.