EHR for Long-Term Care (LTC)
Capabilities, Integrations, and Development Costs
In healthcare IT since 2005, ScienceSoft designs EHR solutions for SNFs and ALFs that align daily care, reimbursement workflows, and safety programs across facilities and simplify documentation for frontline staff.
EHR for Long-Term Care (LTC) at a Glance
EHR for long-term care provides a shared digital chart that supports long stays, interdisciplinary reviews, and survey-ready records across facilities, backed by pharmacy, lab, and hospital integrations. Advanced platforms may add PDPM optimization, predictive safety and rehospitalization analytics, and AI-assisted documentation to protect reimbursement and reduce clinical workload.
ScienceSoft delivers custom long-term care EHR software as well as targeted LTC EHR modules and extensions for the following skilled nursing facilities and senior care providers:
- Regional SNFs and assisted living groups invest in a chain-wide LTC EHR backbone to replace standard systems that don’t fit specific care pathways, PDPM tactics, and multi-facility reporting.
- Large SNF chains deploy LTC EHR extensions to their existing EHRs to bring together chain-wide safety analytics, rehospitalization control, and PDPM drill-downs in a single cross-facility layer.
- Assisted living and memory care networks implement clinical and safety modules that enhance behavior tracking, fall oversight, and sensor integration beyond what their occupancy-focused senior living platforms support.
Implementation time: 6–12+ months for EHR extension packs and 12–24+ months for a full-scale multi-facility EHR for long-term care.
Development costs: from $250,000 for a targeted LTC EHR extension to $2,500,000+ for an advanced multi-facility platform with SNF reimbursement automation and AI-driven safety and rehospitalization analytics.
Long-Term Care (LTC) EHR Feature Map
Below, ScienceSoft’s consultants present a long-term care EHR feature map that covers most of the clinical, safety, and reimbursement needs of SNFs and long-term care providers we work with. In real projects, clients select and phase in only the functionality that matches their priorities and budget.
Admission, placement, and transfers
Daily care, medication, and safety management
Reimbursement, safety analytics, and staffing planning
AI Tools for Long-Term Care EHR: Popular Use Cases
ScienceSoft helps long-term care providers implement secure, transparent AI tools that automate documentation, make PDPM and survey work more predictable, and identify residents at risk early. The benefits in the examples below are indicative only and depend on data quality, workflow maturity, staff adoption, and governance. ScienceSoft recommends validating impact in a short pilot with clear baseline metrics before scaling.
Each scenario below can be implemented as clinician-in-the-loop decision support, so staff can see key inputs, adjust thresholds, and override suggestions, drawing on FDA Clinical Decision Support guidance and ONC HTI-1 transparency principles where they apply.
We typically deploy these tools on HIPAA-compliant cloud infrastructure with end-to-end encryption, RBAC, audit logging, and bias checks to help providers address CMS nursing home expectations and ACA Section 1557 nondiscrimination rules without adding extra compliance overhead.
AI-assisted clinical documentation and care planning
Ambient AI tools can capture bedside conversations and convert them into draft nursing notes, ADL records, and incident reports. LLM assistants can structure free text into MDS-aligned fields, summarize recent documentation, or suggest prefilled care plan text for the clinician’s review.
Reported benefits: up to 50% less time spent on documentation reported with ambient AI tools.
AI copilot for clinical, MDS, and regulatory tasks
An AI copilot can generate resident, unit, and shift summaries to support rounding, handoffs, and safety reviews. Such tools can support MDS and PDPM “what-if” analysis for coding decisions and draft regulatory narratives for surveys, QAPI reporting, and board communications.
Reported benefits: ~30% less chart review burden with AI assistants.
Predictive AI for rehospitalization and deterioration risk management
Predictive models can calculate near-term rehospitalization and deterioration risk scores from diagnoses, vitals, ADLs, and MDS data. They can flag higher-risk residents for care team review, show which inputs drove each score, and support early warning sign detection.
Reported benefits: ~10–15% fewer 30-day readmissions in AI-supported risk control programs.
AI assistant for acuity-driven nurse staffing
Staffing AI tools can combine census, acuity data, and regulatory rules to estimate required nurse hours and test staffing scenarios. They can draft balanced rosters as well as suggest reassignments or call-ins when acuity spikes or shifts are dropped.
Reported benefits: up to 70–80% less manager time on schedule-building in healthcare AI staffing programs.
Important Integrations for Long-Term Care (LTC) EHR
In EHR systems for long-term care, reliable integrations with hospital records, labs, CMS, and revenue systems often determine whether providers can avoid claim leakage, survey issues, and staff hours lost to retyping. ScienceSoft handles this at the architecture level, using patterns recommended in the ONC ISA and other industry best practices.
In full-scale builds, ScienceSoft defines a canonical clinical and billing data model and connects partner systems via HL7 or FHIR for clinical data, NCPDP for pharmacy, and X12 for eligibility and claims. When a non-interoperable EHR remains in place, we add an integration layer that maps the EHR’s data to the canonical model and exposes standardized file formats or APIs, so providers can connect with partners without double-entry or creating new custom integrations each time.
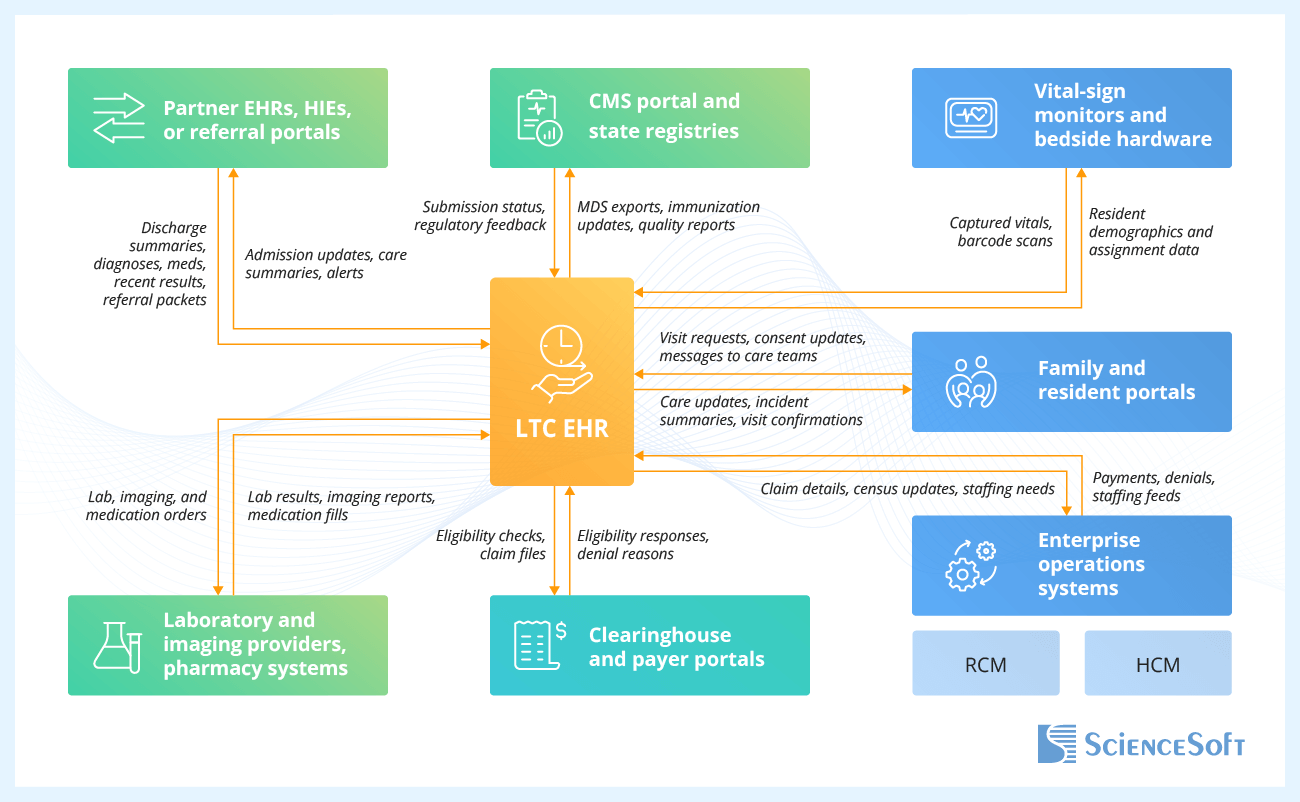
- Hospital EHRs, HIEs, and referral portals — to pull discharge summaries, medication lists, diagnoses, and recent test results straight into admission workflows; to send admission notices and care summaries back when residents transfer.
- Laboratory systems, imaging provider systems, and pharmacy software — to send lab, imaging, and medication orders from the EHR and receive results and fills that update eMAR, infection tracking, and stewardship metrics.
- Family and resident portals — to share near-real-time care updates, incident summaries, and visit schedules with families, and to collect digital consents into the resident chart.
- Revenue cycle management (RCM) system — to export LTC claim data, PDPM rates, and census updates from the EHR, and to import payments and denials that feed posting, analytics, and payer dashboards.
- CMS portal and state registries — to submit MDS, quality measure, and immunization data from the EHR and receive status, error messages, and scores that guide survey preparation and QAPI priorities.
Other frequently requested LTC integrations include single sign-on services, HR and scheduling systems, document scanning tools, and nurse call and safety sensor platforms that centralize alerts and content in the EHR.
Development Tips for Long-Term Care EHR Projects
Below, ScienceSoft’s experts identify three development areas that often lie at the root of common problems LTC providers face with their EHR systems. For each one, we describe engineering practices our teams rely on to keep these platforms’ parts predictable.
PDPM and MDS as a rule engine, not screen code
In EHR systems for SNFs and nursing homes, PDPM and MDS rules should live in a versioned engine that assessment screens and claim builders call through stable APIs. This way, when CMS guidance changes, IT teams can update rules and rerun automated regression tests using reference residents, rather than editing dozens of forms and reports. This keeps PDPM groups, per diem rates, and quality metrics aligned across facilities even during busy regulatory cycles.
eMAR performance shaped around peak med rounds
Stable LTC eMAR deployments start with clear written performance goals for peak med rounds that cover response time, sync frequency, and error handling. If those targets are not agreed upon up front, problems like slow screens, stuck syncs, or lost offline entries usually show up only after nurses lose trust in the system. ScienceSoft links this performance agreement to automated load tests and easy-to-read live metrics, so operations staff can see med pass performance in real time.
Analytics-ready LTC event model and governed metrics
LTC EHR gains more value when daily EHR records feed an event data layer that stores each incident, vital, medication administration, and reimbursement change with resident, unit, and time tags. Without this model, each report pulls from its own mix of tables, exports, and manually edited files, so the same measure is counted in different ways. For example, multi-site providers then see QAPI packs, PDPM reviews, and board reports use different numbers for one period. This weakens trust in analytics, AI output, and internal benchmarking. ScienceSoft defines metrics in this dedicated event layer and adds simple checks, so executives and clinical leaders can work with one trusted set of numbers.
Some LTC EHR modules can be built more economically with low-code tools such as Microsoft Power Apps. For example, you can use Power Apps to build back-office safety and compliance workflows, such as an incident and infection hub with chain-wide safety views and survey-ready documentation packs. Beyond faster rollout, low-code modules also let you make manual tweaks to the software logic when regulations change, often without software developers.
However, it’s important to remember the limitations. When heavy image volumes, offline use, and complex analytics are needed, Power Apps alone may not be enough, so providers still need custom code, separate storage, or reporting layers.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop EHR for Long-Term Care?
The cost of long-term care EHR development typically ranges from $350,000 for focused clinical or safety modules to over $2,500,000 for a full-scale multi-facility platform.
The project budget will depend on the number of communities in scope, the depth of clinical and reimbursement features, the complexity of integrations, and the extent of AI and analytics you plan to introduce.
The options below outline scope bundles and corresponding cost ranges that cover the most common needs of our long-term care clients.
|
|
Clinical and safety LTC EHR module |
LTC EHR extension pack |
Full-scale LTC EHR build |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Best for
|
Assisted living and memory care networks that prioritize safety controls, behavior tracking, and fall reduction. |
SNF chains that need to enhance chain-wide PDPM, rehospitalization, and safety analytics in their existing EHRs. |
SNFs and assisted living groups that want a single clinical and reimbursement backbone across facilities. |
|
Standard functionality / Common extension types
|
$250,000–$800,000 |
$350,000–$900,000 |
$700,000–$1,400,000 |
|
Advanced functionality
|
$750,000–$1,500,000+ |
$900,000–$1,800,000+ |
$1,400,000–$2,500,000+ |
Why Choose ScienceSoft as Your EHR Development Partner
- Since 2005 in healthcare software engineering and IT consulting.
- 150+ successful projects in the domain.
- Architecture and Solutions CoE to design secure, integration-first solutions with offline-tolerant point-of-care features and canonical data models for legacy-heavy environments.
- Proficiency in aligning healthcare software with HIPAA, GDPR, CMS nursing home regulations, and the 21st Century Cures Act.
- Expertise in data exchange standards, including HL7 v2, FHIR, C-CDA, USCDI, NCPDP, and X12; clinical coding standards, such as ICD-10-CM, SNOMED CT, and LOINC; and QRDA/MDS-based quality reporting.
Our awards, recognitions, and certifications
Featured among Healthcare IT Services Leaders in the 2022 and 2024 SPARK Matrix
Recognized for Healthcare Technology Leadership by Frost & Sullivan in 2023 and 2025
Named among America’s Fastest-Growing Companies by Financial Times, 4 years in a row

Top Healthcare IT Developer and Advisor by Black Book™ survey 2023
Four-time finalist across HTN Awards programs

Named to The Healthcare Technology Report’s Top 25 Healthcare Software Companies of 2025

HIMSS Gold member advancing digital healthcare
ISO 13485-certified quality management system
ISO 27001-certified security management system







