AI for Patient Communication and Access
Capabilities, Integrations, Costs
With healthcare IT experience since 2005, ScienceSoft develops AI-enabled patient communication and access solutions scoped to priority needs: shortening wait times, reducing missed appointments, and automating manual routines without putting PHI at risk.
AI for Patient Communication and Access: Summary
AI-powered patient communication and access solutions help patients get answers and complete common tasks (e.g., scheduling an appointment) independently via chat, SMS, or telephony. AI copilots also help front-desk teams and contact center agents handle requests faster by capturing essential details from phone calls, drafting replies, routing exceptions, and reducing manual documentation.
In most implementations, the AI engine (typically one or several NLP models) is added as a patient-facing layer across existing digital channels. The most critical integrations typically include EHR or EMR, scheduling or practice management, contact center tools, and a governed knowledge base. Safety is enforced through strict boundaries and handoff rules: AI supports request intake, record-based status updates, routing, and documentation, while clinical judgement stays with clinicians and escalations follow defined paths.
The costs of implementing an AI-enabled patient communication and access solution typically range from $15,000 to $300,000+ for midsize and large healthcare organizations, depending on workflow scope, channel coverage, accessibility, and governance. Use our cost calculator to estimate your project budget.
Key AI Capabilities for Patient Communication Automation
Patients can access text-based AI assistants via a website widget, portal or app chat, or text messages. These chatbots typically cover non-clinical Q&A (hours, directions, prep instructions), next-step guidance, and structured intake for requests such as appointment changes, billing questions, referral status, and records access. To keep answers consistent, responses are usually grounded in approved sources (policies, FAQs, SOPs), with clear escalation when a request requires human approval or verification is missing.
Patient voice assistants (AI call center)
Voice assistants support natural, real-time phone conversations for common patient access needs, using short prompts and confirmations to capture the necessary details without making the call feel like a rigid menu. They can answer common FAQs, ask and record key patient information, and complete allowed actions, such as booking or rescheduling, after confirming the caller’s identity. When a call has to be routed to a human, the voice assistant can pass a handoff packet (reason for call, captured data) to reduce repeated questions and after-call documentation.
Scheduling and intake agents
Back-office AI agents help scheduling and registration teams by turning patient requests into structured work and completing routine steps under your rules. They can check visit requirements, find available time slots, prepare booking or rescheduling actions, and pre-fill intake items like demographics, insurance details, and consent. When a task cannot be completed safely, it is sent to the right worklist as a pre-filled task with a short summary and captured details.
Outreach agents
AI agents can run outbound communication workflows, such as appointment confirmations, reminders, prep instructions, and post-visit follow-ups, across different channels. Outreach can be triggered by schedule events, missed pre-visit steps, or staff-defined rules. When a patient responds that they can’t attend or can’t follow prep instructions, the agent can switch workflows (e.g., offering reschedule options or routing to staff). For outbound calls, identity checks can be applied before any patient-specific details are shared.
Staff copilots for messages and calls
Staff-facing AI copilots can support the daily work of front desk staff or call center agents, usually implemented as an interactive sidebar in contact center software, a portal inbox, or an EHR message pool. AI can summarize conversation history, suggest replies aligned to approved content, and prefilled request forms (reason, key fields, next steps) to reduce retyping. This results in faster case handling with consistent wording, especially when staff have to juggle multiple systems. For safety and accountability, drafts remain editable and require staff approval before they are sent or saved.
Task routing and orchestration layer
This essential layer coordinates how work flows across the system when AI cannot complete a request or requires oversight. The orchestration engine classifies patient intent, evaluates urgency and policy rules, and determines the execution path: complete automatically, request additional input, or create a structured case for human follow-up. When human input is required, AI creates a case with a defined owner (team, queue, or role), priority, and SLA based on request type (e.g., access issue, referral, billing question, clinical escalation). Conversation transcripts, summaries, and captured data are attached to each case so that staff can act without re-triage. This enables consistent handoffs, predictable response times, and clear accountability across patient access workflows.
See How This Works in Practice
See how an AI voice scheduler built for one of ScienceSoft’s projects handles appointment booking in a real phone conversation. In the demo, Vadim Belski, ScienceSoft’s Principal Architect and Head of AI, takes on the role of a patient scheduling a visit.
Powered by Amazon Nova Sonic, the assistant conducts real-time voice conversations and can complete common scheduling actions such as booking, rescheduling, and cancellations. The solution is estimated to cut booking time by about 40%, reduce abandonment by about 30%, lower scheduling costs by 50%, and handle roughly 70% more calls per hour than a patient service representative.
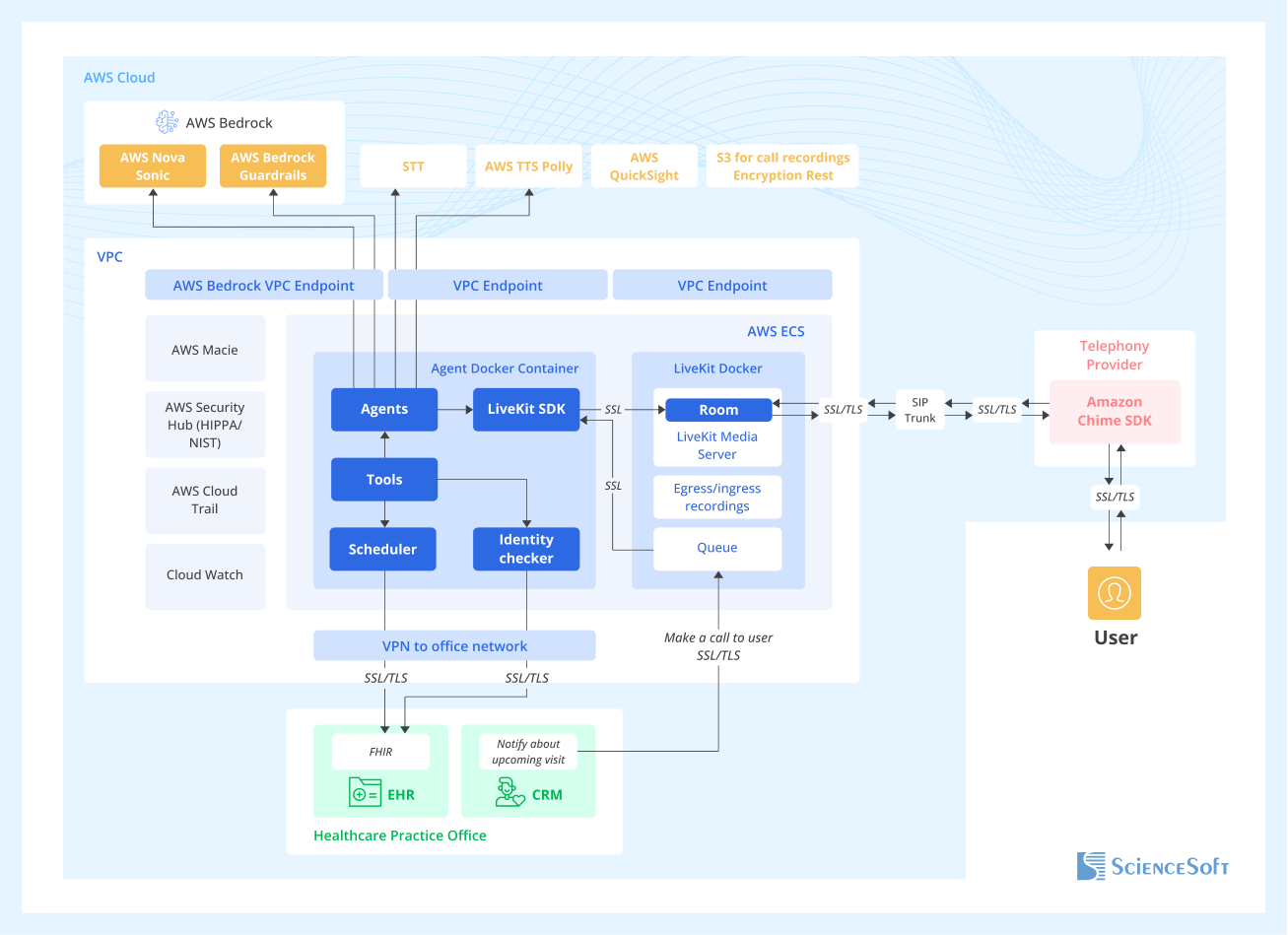
In this project, the voice agent was deployed in a HIPAA-compliant Amazon VPC, routed real-time interactions through LiveKit, and exchanged data with hospital systems such as the EHR, CRM, and scheduling via FHIR-based APIs during the call. While this solution was built on AWS, the architecture is portable and can be deployed on other cloud platforms or hosted in your own data center.
Beyond this setup, the same voice assistant can be integrated with additional systems often used in patient communication workflows: a patient portal or a mobile app, contact center software, HIPAA-ready messaging platforms, or an internal knowledge base.
Development Tips for Building AI Patient Communication Workflows
Below are practical considerations that tend to matter most when introducing AI into patient communication and access. They can help you keep scope under control, avoid common safety and adoption pitfalls, and focus on early wins you can track with clear metrics.
Identity checks for common access scenarios
AI workflows should reuse the same access levels your teams follow, so the assistant only performs actions when the required verification is met. In practice, each AI task is mapped to a verification level, and the workflow asks for the minimum checks needed for that level before sharing information or completing an action. For example, general FAQs can stay anonymous, limited status checks require basic verification, and account actions require stronger verification such as portal login or a one-time passcode.
Proxy and caregiver handling
When someone contacts you on behalf of a patient, the assistant should first identify the caller as a caregiver, parent, or other representative and check whether proxy access is recorded in the portal or EHR. If proxy access is confirmed, the assistant can proceed with the allowed actions for that proxy account. If it is not confirmed, the assistant should avoid patient-specific details and switch to safe paths such as collecting contact information, creating a callback request, or directing the caller to registration to set up proxy access.
Designing for downtime and partial integrations
When scheduling or EHR systems are slow or unavailable, the assistant should not stall the conversation or break it with “try again later.” Instead, it should switch to a fallback flow in the same channel (chat, SMS, or phone call): capture the patient’s request and contact details, confirm the next step, and create a work item for staff.
Grounding answers in approved sources
AI can use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to base answers on structured internal knowledge. This way, the assistant will retrieve relevant passages from approved policies, FAQs, prep instructions, and SOPs, then assemble a reply based only on that content. When no approved answer is found, the assistant should say it cannot confirm the details and switch to a safe path, such as offering to connect the patient to staff or creating a request for follow-up, while logging the question as a content gap for the knowledge base.
The Cost of Implementing AI for Patient Communication
The cost of AI solutions for patient communication and access can range from $15,000 to $100,000+ for chatbot and voice agent builds, with multi-component solutions reaching $300,000+.
$15,000–$100,000+
Agent-side copilot (staff assist only)
An AI assistant that drafts replies and summaries for portal inboxes, contact center desktops, and EHR message pools. Can suggest next steps and structured notes (with staff review before sending or saving).
$15,000–$60,000+
Patient chatbot (Q&A only)
An informational assistant that answers common patient questions (services, doctors, locations, procedures, pricing) using approved content and safety guardrails. Typically limited to knowledge-based responses.
$80,000–$150,000+
Patient assistant (autonomous agent)
A highly autonomous agent that can handle patient scheduling and confirmations, directions, reminders, and pre-visit instructions, with escalation to staff when needed. Real-time speech-to-speech conversation capability typically adds $10,000–$30,000.
$150,000–$300,000+
Enterprise-scale patient access automation
Large solutions that combine multiple AI components across several digital channels. They can handle longer, multi-task conversations (e.g., first-line triage combined with insurance coverage checks and appointment scheduling).
Want a more precise figure?
ScienceSoft's team is ready to provide a quote for your specific case.
Why Choose Sciencesoft for AI in Patient Communication and Access
-
Since 2005 in healthcare IT.
- Since 1989 in AI enablement.
- 150+ completed healthcare projects across clinical and administrative workflows.
- Expertise in healthcare-oriented AI architecture, with controls against common LLM risks and privacy concerns.
- AI delivery aligned to healthcare privacy regulations: HIPAA, GDPR, or PDPL.
- Proficiency in healthcare interoperability for AI workflows: HL7 FHIR and HL7 v2.
Our awards, recognitions, and certifications
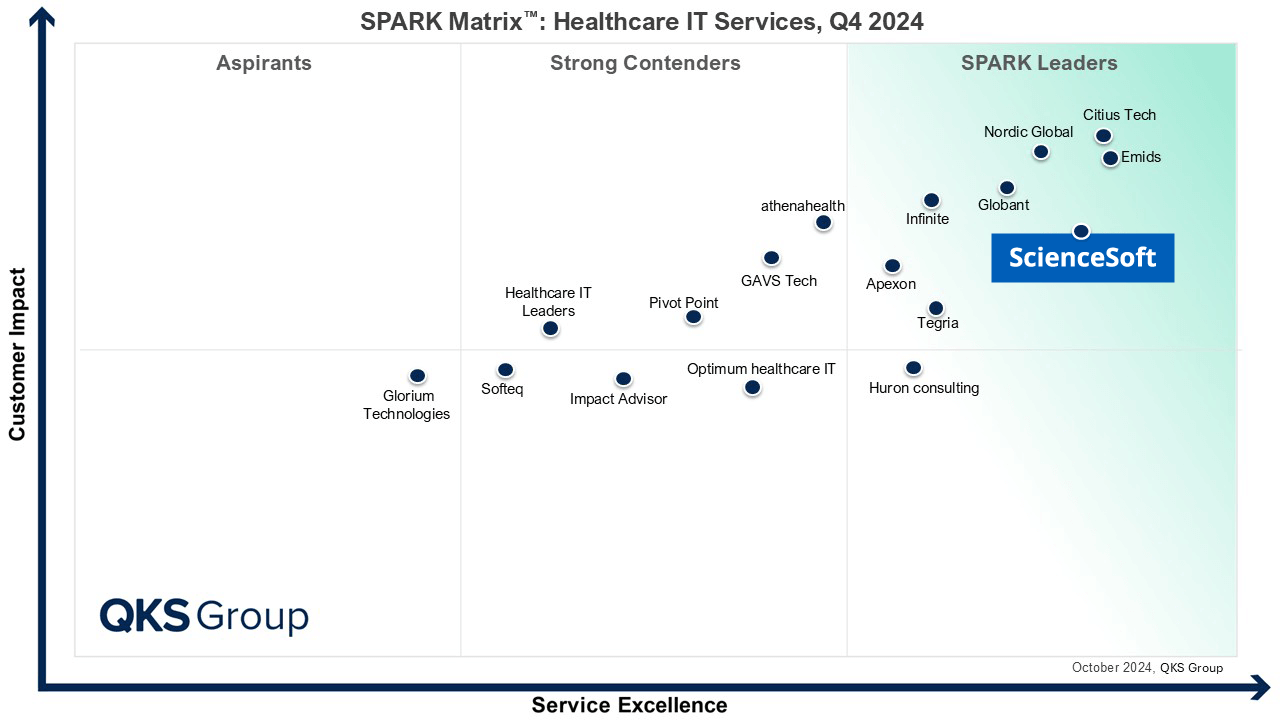
Featured among Healthcare IT Services Leaders in the 2022 and 2024 SPARK Matrix
Recognized for Healthcare Technology Leadership by Frost & Sullivan in 2023 and 2025
Named among America’s Fastest-Growing Companies by Financial Times, 4 years in a row

Top Healthcare IT Developer and Advisor by Black Book™ survey 2023
Four-time finalist across HTN Awards programs

Named to The Healthcare Technology Report’s Top 25 Healthcare Software Companies of 2025

HIMSS Gold member advancing digital healthcare
ISO 13485-certified quality management system
ISO 27001-certified security management system







