Patient Segmentation and How it Adds Value to Your Strategy
Some providers still question using CRM in healthcare as they doubt it is appropriate to use a salesperson’s go-to tool in care delivery. However, the healthcare CRM concept is far from sales automation: it is about knowing your patients and their needs. By adopting healthcare CRM, providers can tap into the various benefits of patient segmentation.
| Providers benefit from | Patients benefit from |
The efficiency of patient health profiling highly depends on the information to be processed by CRM, so its integration with EHR is a must. Leveraging insights from clinical data enables tailoring outreach even further. For example, clinics can automate follow-up reminders for post-operative patients or trigger appointment scheduling prompts for preventive check-ups. The integration will also automatically keep the segmentation up-to-date.
Key criteria for patient segmentation in CRM
Patient segmentation helps define narrow groups based on set rules and get deeper insights from health analytics and BI tools. This allows providers to enhance engagement by sending personalized information via email, patient portals, messaging apps, or other digital channels, alongside traditional phone calls.
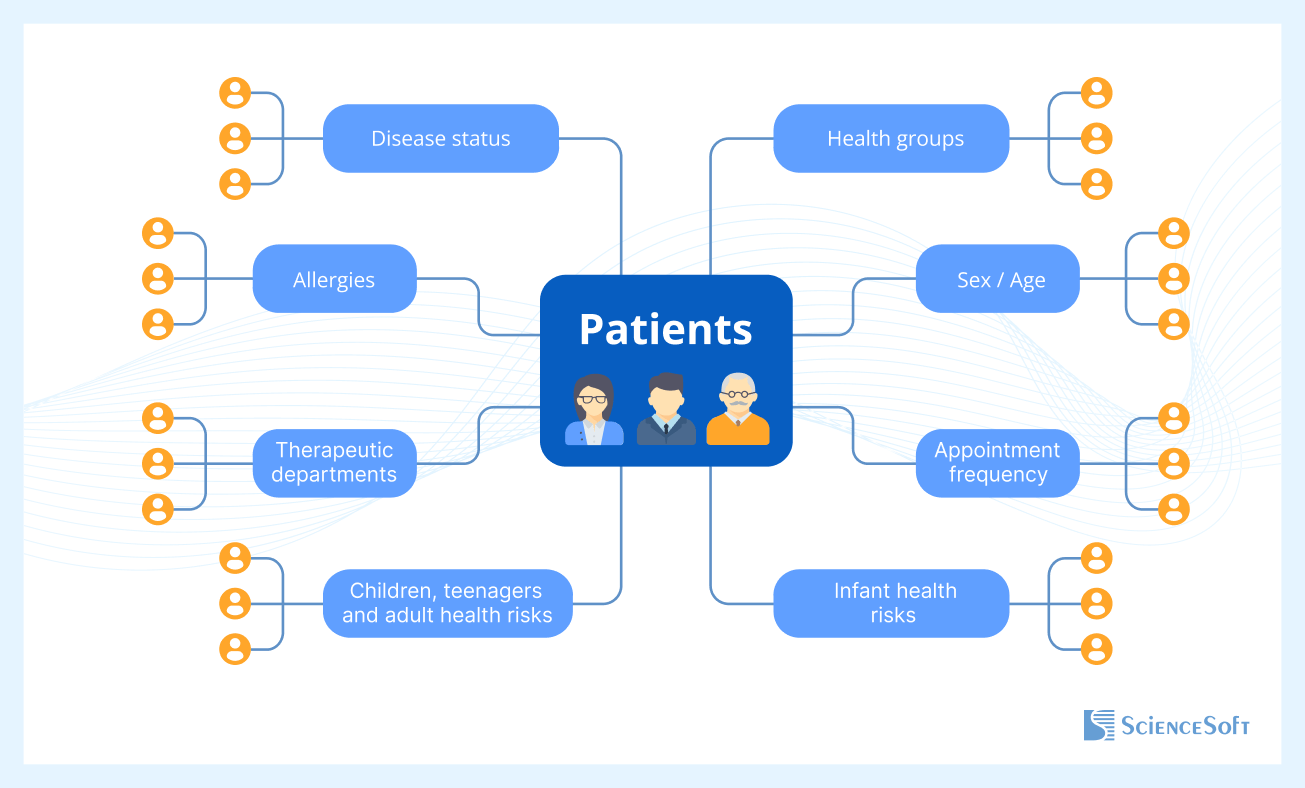
Note: In our concept, all the groups of criteria are equal. They can be used together or separately, and in different combinations. This way, providers can go with wider segments or narrow down their target patient group. Now, let’s review the suggested groups.
Health groups
We built the following patient taxonomy upon the idea of 3 risk-based patient groups (high-risk, low-risk, and rising-risk). It allows providers to decide on a target patient segment and then drill it down to highlight the opportunities for advanced care delivery.
First group
This group includes 2 types of patients:
- individuals without chronic diseases (pathologic conditions) and risk factors for developing any
- patients without chronic diseases (pathologic conditions) but with low or average risk factors for developing any
These patients need to receive preventive care in ambulatory conditions to address the risk factors.
Second group
Patients within this segment don’t have any chronic disease or pathologic condition yet. However, they have high-risk factors for developing any disease or primary symptoms of a pathology.
Such patients may need to receive preventive care in the ambulatory / inpatient setting, including treatment with medications. Systematic medical supervision and screening are desirable in the future.
Third group
The following types of patients fall into the 3rd category:
- patients diagnosed with any of the chronic diseases (conditions) that require systematic supervision and specialty medical care
- individuals with a suspected chronic disease (condition) that requires further examination (upon determining the diagnosis, such a patient’s group can be changed)
These two types are under the highest risk of developing complications leading to disabilities and premature deaths. Consequently, such patients will most likely need inpatient care, including treatment plans supported by medications and rehabilitative care. Systematic medical supervision and screening are possible as well.
Sex / Age
The following structure of basic demographics is built by revising the Piaget stages of intellectual development, Erikson’s stages of human development, as well as Carl Jung’s and Daniel Levinson's theories altogether. We used multiple sources to create the criteria that will not only reflect both psychological and physical development, but also allow healthcare providers to narrow down the patient segments to work with.
Children and teenagers:
Girl / Boy:
- 0-1
- 2-3
- 4-5
- 6-11
- 12-18
Adults:
Woman / Man:
- >65
- <=65:
- 19-25
- 26-35
- 36-50
- 51-64
Appointment frequency
This classification is created to achieve a number of patient analytics goals, such as
- highlighting both satisfied and dissatisfied patients, and
- identifying the patients with acute cases only, who discontinued using a particular provider’s services once the care cycle was completed.
Other criteria below also contribute to this segmentation to some extent. However, only ‘appointment frequency’ enables finding those patients who weren’t engaged during the care process and to act on gaining their loyalty.
- Rare: a single appointment can range from a single appointment in the past 6 months to a single appointment in the past 12 or 36 months, depending on the provider
- Acute cases: 2-5 acute appointments related to one primary condition / disease in the past 6 months, 12 months or 36 months, depending on a provider
- Regular: 2-5 appointments related to a chronic disease / pathology / condition in the past month, 3 months, or 6 months, depending on the particular provider
Health risks
Infant health risks
We aim this classification at providers who are focused on enhancing their prenatal and birth care. The criteria are based on CDC’s and PRB’s maternal and infant health materials that highlight the importance of addressing the problem of perinatal and infant mortality.
- Intranatal
- Perinatal
- Neonatal
- Newborn development - possible to introduce a range from 1 to 10 according to an infant's development in the following domains:
- Feeding / nutrition
- Physical development
- Psychomotor development
Children, teenagers, and adult health risks
This classification addresses healthcare providers’ focus on preventive care and a strong need to monitor their patients with certain health risks. We used the global health risks report as well as CDC’s Prevention Status Reports for reference and guidance.
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- High blood glucose
- Physical inactivity
- Overweight and obesity
- Alcohol consumption
- Sexual preferences
- Genetic
- Professional (stress, depression)
- Environment
- Cardiovascular event risks according to the WHO prediction charts:
- Low (<10%; 10% to <20%)
- Medium (20% to <30%; 30% to <40%)
- High (> 40%)
Allergies
These criteria are composed of common allergies, allowing providers to single out patients with one or multiple allergies.
- Food
- Pollen
- Medications
- Dust
- Pets
- Insect sting
- Mold
- Latex and more
Therapeutic departments
This is only a sample of therapeutic departments within a health organization to be tailored to particular providers. The patient segment can be filtered down to a certain department or a number of departments at once. If, for example, there is a necessity to target patients with diabetes and visual impairment, then endocrinology and ophthalmology are chosen for analysis.
These criteria don’t target patients who are fully recovered, for example, individuals with a broken leg healed.
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- ENT
- Ophthalmology
- Cardiology and more
Disease status
Providers can either combine the ‘disease status’ with ‘therapeutic departments’ criteria sets or use them separately. This particular set consists of multiple dimensions. To create it, we used the general qualities that are not necessarily sufficient for the clinical-only purpose, yet they allow a quite narrow segmentation of patient health profiles.
Disease status:
- acute
- subacute
- chronic (each section can be drilled down to specific conditions, pathologies, disorders, etc.)
Comorbidities:
- yes (can be filtered to a list of particular diseases)
- no
Outcomes:
- recovery
- complications / exacerbations (can be filtered to a particular negative outcome)
Disabilities:
- yes (can be filtered to a specific disability)
- no
The need for systematic supervision:
- yes (then the list of exact supervision types, e.g., regular follow-up appointments or home care, can be provided)
- no
Step-by-step guide to segmentation
Strategy planning
The first step in patient segmentation is defining clear goals and understanding the purpose behind the analysis. Healthcare providers must consider what they want to achieve: Is the primary objective to reduce readmission rates? Improve chronic care management? Enhance preventive care strategies? The answers to these questions shape the selection of segmentation criteria and influence the methods used to analyze patient data.
There are two main ways to approach patient segmentation: data-driven and non-data-driven. Data-driven segmentation uses statistical analysis and machine learning to find patterns in large datasets. It gathers information from sources like EHR, insurance claims, and patient surveys, and uses algorithms to discover groupings that might not be obvious at first glance. On the other hand, non-data-driven segmentation relies on expert knowledge and clinical experience. Healthcare professionals create groups based on known risk factors, demographics, or specific medical needs.
Criteria selection
Once the goals are clear, the next step is to select the criteria that will be used to group patients. There is no universal formula for this; the right choice depends on the healthcare provider’s objectives and the available data.
To be effective, segments should meet three conditions:
- their number must be limited to avoid dilution of focus.
- each segment should include all patients who meet its criteria.
- members within a segment should share similar healthcare needs and behaviors.
Patient data collection
The success of patient segmentation largely depends on the quality and quantity of the data used. EHRs are often the most accessible and extensive data source. However, the choice of sources should align with the segmentation's end goals. For instance, if you aim to focus on patient lifestyle and behavior, adding survey data or wearable device metrics may be necessary.
After identifying data sources, the next step is to clean and prepare the data. This process involves removing duplicates, filling in missing information, and standardizing formats to ensure consistency. For example, patient age should be represented in a uniform format, and health conditions should follow the same coding structure. Health systems may choose to develop their own segmentation models using this data or turn to off-the-shelf solutions that simplify the process.
Leveraging segmentation insights
Once segmentation is complete, healthcare providers must analyze each group to understand their unique needs and design tailored interventions. For example, a clinic wants to offer a personalized discount to its one-time and rare patients from the ophthalmology department. They will only need to:
- select the appointment history (rare and possible to filter back to the past 6 months).
- pick the department (ophthalmology).
Then, the health specialists can send the segmented patients an email, a push notification inside their mHealth patient app, a text message, or make a call to offer them a discount.
Next, a provider finds out that they have a significant number of patients with pollen allergy. When spring is approaching, the provider can choose all their patients with the allergy, remind them to take care during this period, and refill their prescription if needed. This will definitely help to win a few bonus patient loyalty points.
Another provider focuses on maternity care services. They can work with an ‘infant health risks’ criteria group to define the mothers-to-be who need a special approach. As pregnant women with average and high health risks need to see their doctor more often, the provider can send them a personalized follow-up message. It can be a delicate concern about their well-being, supported with short nutrition and activity tips. Of course, a discount on a prenatal massage or special yoga classes can also help to effectively reach out to this group of patients.
Monitoring and refining the results
Patient segmentation is not a one-time exercise. It should be continuously monitored and refined as more data is collected and patient needs evolve. Regularly revisiting segmentation criteria and adjusting strategies ensures that healthcare delivery remains responsive and effective.
Assembling the puzzle
Having tons of data is a questionable benefit if it is unstructured. To identify the levers to pull for the most effective results in communication with patients, every bit of information has to bring value.
While EHR helps to tap into individual patients’ data, an EHR-integrated CRM allows bringing all patients’ details into this multifaceted puzzle (click here to see how it works). By twisting and turning the criteria as well as by dividing and combining segments, providers can highlight one, two, and more patient groups that can and should be targeted with relevant services.
And after the segmentation algorithm is up and running, CRM comes in handy again by giving providers access to all their patient communication channels at once. So once a provider decides on target segments, they can act immediately.

