Clients can type a question (e.g., “What’s included in Phase 2?”), and an NLP-powered assistant will answer it using approved workspace content, cite sources, and provide links to exact passages. When context is insufficient, AI proposes likely sources or creates a task for review.
Client Portal for Consulting Firms
Features, Implementation Plan, and Costs
In web portal development since 2005, ScienceSoft builds client portals that encourage collaboration, enable fast decisions, and provide helpful guidance to clients from onboarding to long-term partnerships.
Client Portal for Consulting Firms: Overview
A client portal provides consulting firms with a secure space to collaborate with their clients without manual follow-ups and scattered emails. A client portal is most useful for ongoing consulting work: it centralizes file exchange with version history, in-line document reviews and approvals, automates request tracking and notifications, and offers a transparent billing dashboard with online payments.
Typically, web portals for professional services integrate with the firm’s CRM, a project management or ERP platform, and accounting systems to speed up data exchange and give customers real-time visibility into project progress. The cost of developing a portal for consulting generally starts at about $50,000 for an MVP and scales with compliance needs and complexity of system integrations. Try our free online calculator to learn what a tailored solution might cost in your case.
Key Functionality of a Consulting Portal
Document and file management
Each client workspace provides a secure document vault with version history, co-editing roles (editor/reviewer/approver), and review checkpoints that control what becomes client-visible. Expiring share links and private internal notes protect sensitive materials; watermarked, read-only outputs support VDR-like sharing without downloads. Full-text search spans files and comments, with filters by project, author, tag, and date.
E-signatures and approvals
Legally binding e-signatures handle SoWs, change order requests, and deliverable acceptances. Signing workflow supports sequential/delegated signers, identity verification (MFA/KBA), and jurisdictional compliance (ESIGN/UETA, eIDAS). Integrity-protected envelopes produce sealed PDFs with certificate chains and unchangeable audit records. The portal mirrors status and stores the file’s hash; acceptance events post to PM and billing. Optional legal hold and retention policies preserve signing records.
Project tracking
Clients and consultants see a shared, role-based timeline of milestones and status changes. Meeting agendas, notes, and flagged messages get converted into linked action items and a compact decision log with owners, due dates, and references to the call. A focused dashboard shows buckets (new, in review, approved, blocked) and keeps key fields in sync with integrated CRM, PM/ERP, and billing.
Communication and collaboration
Threads attach to documents, tasks, or stages; clients can raise questions in a Q&A queue with service targets and auto-escalation. Role mentions (@Sponsor, @Legal, @PMO) notify the right people. Replies from email, Microsoft Teams, or Slack sync back to the same conversation so that participants can respond directly from the tools they already use.
Engagement governance
Contracts, SoW data, and SLAs sync from CRM so that clients can see applicable terms in the portal. A structured change-request flow captures scope, estimates, and approvals; acceptance events feed PM and billing to keep scope and invoicing aligned. A consulting firm can expose rate cards and retainer balances to its clients via the portal for commercial transparency.
Billing and payments
Invoices generated in accounting appear on the portal with full details and a downloadable copy. Clients are notified and can pay by card or ACH via an integrated gateway, or record an offline payment; disputed items are routed back to finance. Payment and status updates synchronize across systems to keep posted/partial/paid aligned.
Self-service, knowledge, and support
Onboarding checklists, a client-filtered resource library, and a searchable knowledge base help customers go through early steps and answer basic questions independently. When assistance is needed, clients submit support requests and track ownership and status right in the portal. Quick “Was this helpful?” prompts on articles drive continuous content improvement by the editorial team.
Notifications and alerts
Users control alert channels and cadence (real-time or daily/weekly digests) and can apply quiet hours and mute settings per project. The activity feed surfaces new files, comments, approvals, status changes, and assignments automatically. Admins can set org-level defaults; clients and consultants fine-tune personal preferences.
Analytics and reporting
Portal engagement analytics reveal client log-in times and frequency, file access events, and response patterns. Project managers can track approval cycle time and on-time rate directly via the portal or through an integration with PM platforms. Support teams monitor response times and resolution metrics on the portal against their SLAs, while finance receives payment statistics to improve cash flow.
Portal performance and reliability
Large files and heavy activity loads are handled via background processing and streaming previews to minimize wait times. Admin dashboards track response times, error rates, and queue depth, with threshold-based alerts. Storage and retention policies are configurable per client to manage data volume growth without manual clean-ups.
Customization and UX
Each workspace reflects the client’s brand (e.g., logo, colors, domain name) and provides a configurable home page of tasks and updates. The interface is responsive and mobile-friendly, supports multiple languages and locales, and follows WCAG 2.2 with captions/transcripts and no color-only cues.
Access management and security
Granular workspace permissions, secure sign-in with optional MFA, and detailed activity logs support compliance reviews. Privacy policy profiles align data handling controls for each client with engagement context (e.g., HIPAA, GLBA, US state laws). Identity integration (SSO/MFA) provides low-friction, auditable access across roles.
How AI Can Streamline Client Portal Workflows
Context-aware answers
File summarization and data extraction
The AI assistant in the portal can create a short brief of a long file and extract dates, amounts, and counterparties into searchable fields. Summaries link to key sections; extracted fields drive search and deadline reminders.
Request auto-labeling and routing
Portal AI engine can classify incoming Q&A items, support tickets, and intake forms by topic and urgency and route them to the right owner automatically. This way, high-priority requests don’t get held up in general support queues, and clients see more accurate estimates of target response times.
Risk-based nudges and service alerts
AI monitors approvals, Q&A queues, and due dates to detect at-risk items. It recommends next steps (e.g., remind the owner, notify a project manager, schedule a review) and explains the signals behind each suggestion.
On-the-go translation
AI renders threads and articles in the reader’s language without changing the source file. For example, a client in Germany views a Q&A in German; your team sees additional questions and replies from them in English. AI translation is display-only; the source remains canonical.
Sensitive data detection
AI scans files and threads when content is prepared for broader sharing and flags personal or confidential fields (e.g., IDs, bank details, internal rates). A designated owner reviews suggested redactions for a shared copy; the original remains unchanged for authorized roles inside the workspace. Strict policies guide the AI checker on what to flag and in which scenarios (exports, emails, vendor access) to reduce accidental disclosure.
Content insights and article tuning
AI groups similar questions and shows which articles actually resolve them. The resulting content analytics dashboard shows effective content and weak spots, prompt updates, and “trusted answers” for recurring queries. For example, “Onboarding guide” answers 70% of setup questions, while “Pricing FAQ” rarely helps — that means it’s time to rewrite it.
Important Integrations
These are the core integrations most consulting portals start with:
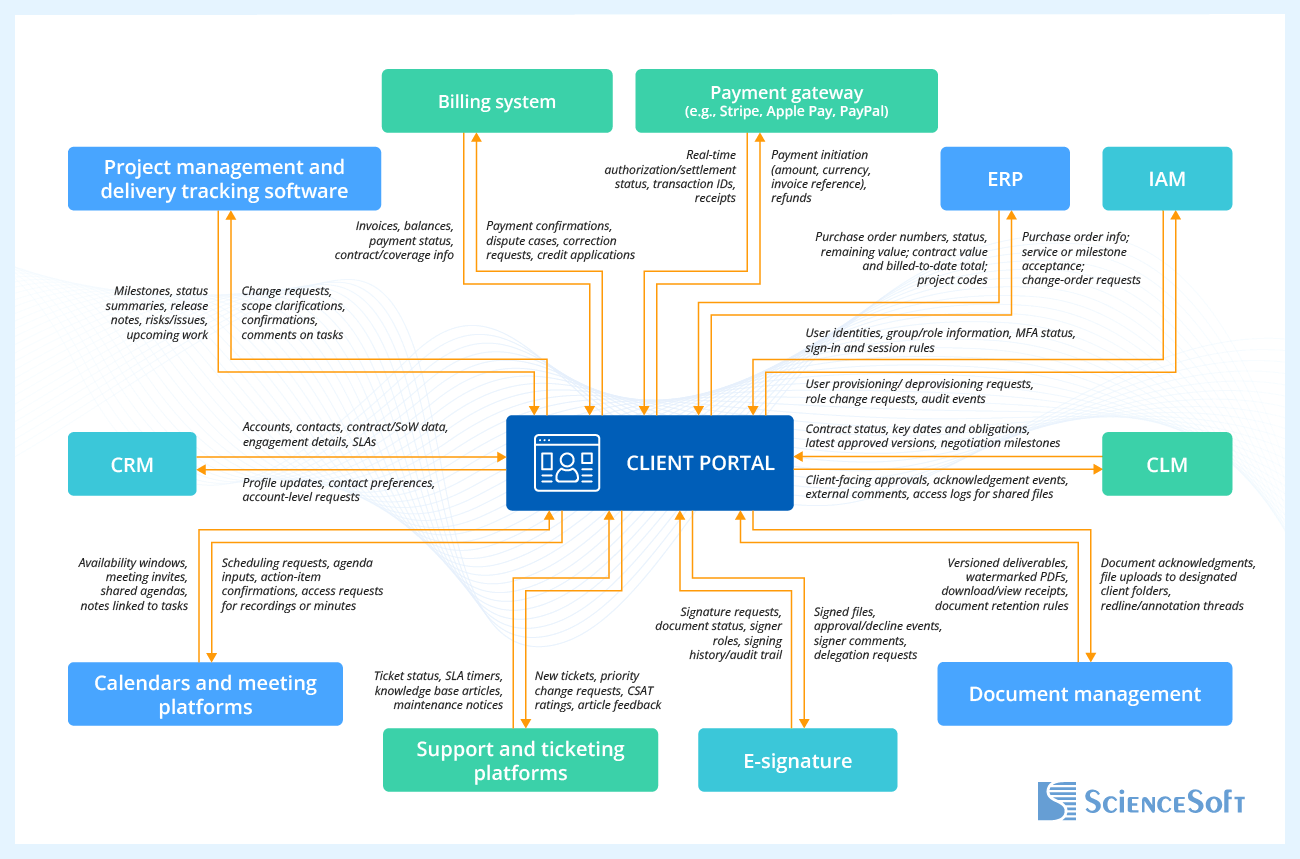
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM). Integration with CRM ensures the portal reflects verified account hierarchies, contacts, contract terms, and engagement details for precise, client-specific content.
- Project management and delivery tracking software. Connecting project management tools to the portal allows clients to see simplified timelines and progress without exposing internal backlogs.
- Payments and billing. Integration with payment gateways and billing systems ensures customers can view invoices and balances in the portal, pay securely via cards, bank transfers, or digital wallets through a payment gateway, and receive instant confirmations and receipts.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). The portal connects to your ERP to surface purchase orders, contract value, project IDs, and billed-to-date information.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM). Integration with enterprise identity providers delivers secure, low-friction access with single sign-on and multi-factor authentication.
- Document management. Integrating the portal with your document management system keeps master files and drafts internal; clients see only approved, share-ready versions.
- E-signature. Direct e-signature integration (e.g., DocuSign, Adobe Sign) means the portal coordinates envelopes and mirrors status; the e-sign tool remains the system of record.
- Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM). Full CLM integration (e.g., clause library, redlining, obligation tracking) is a good idea when you need contract authoring/negotiation, as well as post-signature governance. The portal provides a client view and access to sealed files.
- Support and ticketing platforms. Customer service tools align client questions and incidents with internal queues and SLAs.
- Calendars and meeting platforms. Calendar integrations (Microsoft 365, Google Workspace) make scheduling and meeting prep effortless and tie discussions to work items.
Developing a Client Portal: Roadmap
Building a mid-tier consulting client portal typically takes about 6–8 months: 1–2 months for discovery/design, 3–4 months for core build and integrations, 1–1.5 months for QA/compliance, then a 3-week rollout following a 1-month pilot. For compliance-heavy, VDR-grade implementations, it would be a good idea to plan 9–12 months.
Step 1.
Discovery and planning
- Alignment workshops confirm goals, scope, decision rights, assumptions, and success criteria.
- Together with the portal owner, the development team defines users/roles, document lifecycles, request types, billing flows, visibility rules, and success metrics.
- A business analyst maps required integrations across customer relationship management, project management, accounting, and enterprise resource planning.
- After that, they create and order the feature backlog with user stories and criteria covering file control, approval and payment flows, request handling, and reporting.
- The solution architect drafts the initial architecture and the security approach.
Output: finalized backlog, system design, and integration map.
Step 2.
Design and prototyping
- The UX/UI team builds portal user flows and clickable prototypes for key journeys (sign-in, project dashboard, document review/approval, Q&A, invoices and payments).
- The team coordinates branding, layouts, reusable components, and accessible typography, and defines portal specifics like document states (draft/review/approved), status badges, and notifications.
- The research team validates prototypes with internal stakeholders and a selected client group to confirm roles/permissions, data visibility, and wording, then refines accordingly.
Output: tested portal prototype and visual foundation.
Step 3.
Core build
- The engineering team delivers core features and a multi-tenant architecture (client-level data isolation, role-based permissions) and sets up the portal’s content management system with content types and workflows. A theming framework and admin controls allow per-client branding (logo, colors, optional domain) to be applied later by administrators without code.
- An early version is released to a pilot group of internal project/delivery staff and client approvers who provide structured feedback via test scripts and short surveys.
Output: usable first-release portal, validated internally.
Step 4.
Integrations
- The integration process connects the portal with existing systems (CRM, project/practice management, ERP/billing, file stores, identity) and using vendor APIs and webhooks. Where ready connectors are unavailable, the team develops custom middleware.
- Integration engineers align data models or establish data transformation rules so that keys and statuses match across systems. Account and contact IDs, project codes or WBS, purchase orders, invoice numbers, and user identities are mapped to a shared schema; reference lists are normalized.
- Single sign-on and multi-factor authentication are enabled at this stage.
Output: secure live data flows in the portal.
Step 5.
Quality assurance and compliance
- The quality assurance team runs functional, penetration, performance, and usability tests and tracks fixes to closure. This is done in parallel with development to prevent the propagation of errors into later software builds.
- Testers make sure the portal has the necessary security controls and features to comply with universal and case-specific regulations and standards.
- Engineering and operations teams perform security hardening (patching, secure configuration, least-privilege access) and optimization.
Output: stable, compliant version of the portal.
Step 6.
Pilot launch
- The portal is launched to a limited set of client accounts.
- Customer success and analytics teams gather feedback on adoption, task success, satisfaction, and support cases.
- Portal owner and engineering team refine features, user experience, and integrations based on pilot findings.
Output: pilot feedback and prioritized adjustment list.
Step 7.
Full rollout
- Internal training for consulting staff and client administrators ensures that help desk and support teams are prepared.
- The content team publishes onboarding materials (guides, tutorials, FAQs).
- The portal is released to all clients.
Step 8.
Continuous improvement
- Together with the portal owner, the development team plans regular enhancements based on usage metrics (e.g., approval cycle time, first-response time, client adoption, invoice-to-payment time) and direct client feedback.
- Engineering and integration teams release new modules or deeper integrations when appropriate.
Operations and security teams deliver maintenance, security updates, and scaling.
You can use SharePoint if your portal is mainly about document management (share/review/approve) and the majority of your clients already use Microsoft 365. With light customization, which usually includes branding, content types, approval flows via Microsoft Power Automate, and tailored lists/pages, you get a fast rollout with enterprise search and security, plus a UI that matches your environment without starting from scratch.
Go fully custom if you need complex, multi-step workflows beyond documents, deep integrations outside the Microsoft stack, strict per-client branding and isolation, payments and billing flows, or a highly tailored user experience that SharePoint web parts can’t easily deliver.
Custom Client Portal Development: Cost Estimation
Typical budgets of client portal development for consulting firms range from about $50,000 for a focused portal MVP based on an existing platform (e.g., SharePoint) to $150,000–$250,000+ for multi-integration custom builds with advanced security. The costs are driven mainly by client volume and diversity, the number and complexity of integrations, and the scope of client-facing features.
From $50,000
A platform MVP (e.g., SharePoint) that covers essentials like client workspaces, document vault, approvals, email/Teams alerts, 1–2 integrations, and branding.
From $100,000
A mid build adds custom UX and workflows; 3–5 integrations; role-based approvals, and reporting dashboards. Assistive AI can be added for document summarization, auto-tagging, and meetings-to-actions.
From $150,000
A fully custom solution with advanced security, unique workflows and UX, 6–10 integrations (ERP, CLM, time tracking), and augmented assistive AI (RAG search, PII redaction, translation, intelligent analytics).
Why Develop Your Client Portal With ScienceSoft
- Since 2005 in web portal engineering, delivering end-to-end services covering architecture and UX/UI design, custom and platform-based web development, system integration, quality and security assurance, support, and evolution.
- Established Project Management Office (PMO) and Architecture and Solutions CoE to engineer business-focused solutions that deliver the desired outcomes despite the time and budget constraints and changing priorities.
- 240+ web developers proficient in .NET, Python, Java, PHP, Go, and JavaScript frameworks (Node.js, Angular, React, and more). Over 50% of our talents are senior and lead specialists.
- In-house compliance consultants proficient in jurisdictional (e.g., GDPR, CCPA/CPRA) and sectoral (e.g., HIPAA, GLBA) regulations; cybersecurity experts to enable compliance with ISO 27001, SOC 2, and similar data protection standards.
- Since 1989 in AI and machine learning to add search copilots, summaries, routing, and risk-based alerts grounded in client workspace data.







