Partner Portals
Features, Integrations, AI Tools, and Costs
With 20 years of experience in web portal development, ScienceSoft delivers partner portals that streamline onboarding, collaboration, and knowledge sharing. Designed for secure integration with core systems, such portals ensure partners work with up-to-date information and simplify program operations.
Partner Portals in Brief
Partner portals are secure online workspaces for companies that work with distributors, resellers, service partners, subcontractors, or franchisees. Partner portal solutions replace scattered emails and one-off spreadsheets with a single place where partners can onboard, access current materials, submit work and requests, exchange documents, and track task status, making day-to-day collaboration easier to manage.
Compared to out-of-the-box partner management software, a custom-built portal can fit non-standard workflows and integration needs without forcing program redesigns.
For midsize organizations, platform-based portals typically start around $50,000, with more advanced configurations that add complex workflows and AI features often requiring $100,000 or more. Use our free online calculator to get a cost estimate for your case.
Key Features of Partner Portals
The features below reflect capabilities most frequently requested by ScienceSoft’s clients for partner portal software. Every portal is configured to match the company’s workflows, industry requirements, and partner mix, so the final combination of capabilities may differ from one implementation to another.
Partner experience
Access and onboarding
Partners join via portal forms with company details, contacts, and cooperation scope, while existing partners can be added directly. Internal teams review submissions, link agreements, and activate accounts. Designated partner administrators manage users and roles, with central policies governing data and tool access.
Partner knowledge base and training
Partners access structured materials — product guides, technical documentation, procedures, and compliance information. Required training and knowledge checks allow to unlock certain tools or high-impact activities. The portal records course completion so internal teams understand partner readiness.
Program tiers and partner status
Partner program managers configure tier or status levels in the portal and link them to measurable criteria such as performance, capabilities, compliance steps, volume thresholds, or specialization. The portal shows each partner’s current level, highlights gaps, and records status changes over time to keep benefit decisions and partner reviews consistent.
Partner earnings and incentives
Partners can view performance-linked incentives where applicable, including deal-based commissions, payout history, and progress toward earning thresholds. This allows each partner to track both activity metrics and the financial outcomes associated with their work.
Support center
Partners can use a dedicated support area to browse help articles, submit issues, and track progress. Each support case has a dedicated view with updates, comments, attachments, and activity history. Internal teams can create support articles via portal authoring tools or an integrated knowledge system, with tagging and publishing workflows.
Responsive layouts
Menus, pages, and data views can be adjusted based on partner type, user role, tier, region, and language, so each user sees workspaces and resources relevant to their responsibilities. Responsive layouts keep key tasks usable on both desktop and mobile.
Collaboration
Incoming work queue
Partners can view new items that require their action in a dedicated dashboard or section of the portal (e.g., sales leads, project inquiries, bid invitations, service requests, or shipment offers). They can accept or decline, update essential details, and request assistance, so both sides stay aligned on ownership and next steps.
Work registration
Partners register pieces of work they intend to pursue through a dedicated portal form that collects key details (e.g., customer, scope, timelines, products involved). Internal teams can see these submissions in the corresponding portal workspace, spot overlaps, and decide where additional support is needed.
Standardized partner requests
Partners use guided templates to submit standardized actions: pricing or quote requests, project or scope changes, returns, or shipment-related requests. The portal routes submissions to the right owner and lets partners track the status of each request without separate email threads.
Funding requests
Partners submit funding requests with objectives, planned activities, and budgets. Partner program managers review, comment, approve, or decline in their approval workspace. After execution, partners upload proof of performance (e.g., invoices, reports, screenshots). The portal provides partners with request summaries and gives managers consolidated views by partner and period.
Secure document exchange and compliance files
Partners use a dedicated document area in the portal to exchange sensitive materials, such as contracts, certifications, drawings, reports, and operational documents, according to the permissions defined for their company. Role-based access rights, version tracking, and expiry reminders ensure each partner sees only the files intended for them and always works with the latest approved materials.
Co-branding assets and marketing resources
Partners can access co-branding tools and approved marketing materials for customer-facing campaigns. The portal provides ready-to-use templates, brand-compliant graphics, and usage guidelines, helping partners prepare consistent promotional content without separate requests to internal teams.
Dashboards and analytics
Internal teams see aggregated views of activity and outcomes across the partner ecosystem, including sales pipelines, project performance, order volume, service levels, and compliance metrics. Partners see their own performance data and trends, supporting planning and continuous improvement.
How AI Tools Can Enhance Partner Portals
Copilots for search and support
In-portal copilots let partners ask questions in natural language across documentation, knowledge articles, and program policies. Virtual agents draft responses, surface relevant articles, and summarize complex cases, while assistive tools propose replies and next steps for human support teams, speeding up resolution without giving up decision control to AI.
Intelligent compliance, incentives, and MDF monitoring
LLM-based assistants can review incentive claims, MDF requests, and activity evidence to detect anomalies such as duplicate claims, mismatched spend patterns, or activities that do not align with program rules. In regulated industries, models can also assist with partner risk scoring and regulatory mapping, reducing manual audit effort and fraud risk.
Integration Map for Partner Portals
The integration landscape for a partner portal is typically shaped around the CRM, training, content, financial, and other systems already used to run the partner program. In the schema below, ScienceSoft’s architects outline the most common integration pathways, though the final architecture will depend on the existing enterprise systems and tech stack.
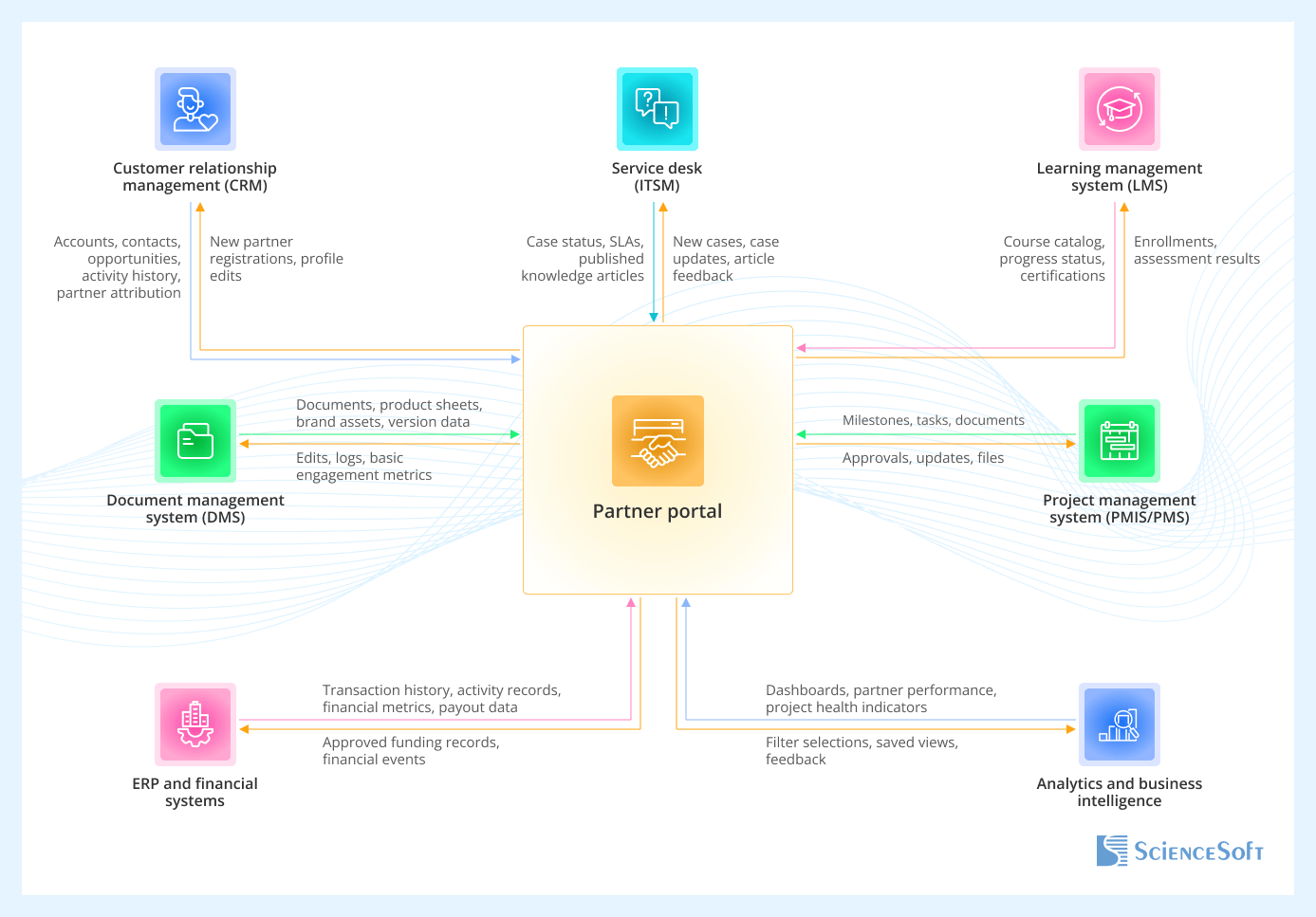
- Customer relationship management (CRM) remains the system of record for accounts, contacts, and commercial opportunities; the portal surfaces a partner-safe view and collects partner input on work they handle.
- Service desk (ITSM) tools stay the source of truth for support cases. The portal provides a partner-facing support center and exposes a curated knowledge base.
- Learning management system (LMS) manages partner courses, exams, and certifications. The portal embeds learning access and uses LMS data to show readiness and limit access to certain tools until required training is completed.
- Document management system (DMS) stores source files, product documentation, and brand assets. The portal exposes approved, partner-ready versions and tracks their use.
- Project management system (PMIS/PMS) exposes a partner-safe view of project data in the portal and collects their updates and approvals.
- ERP and financial systems provide the portal with authoritative records on transactions, operational activities, and partner-related performance. The portal uses this information to support tiers, reporting, and funding decisions.
- Analytics and business intelligence consolidate metrics across CRM, service, training, and finance. The portal surfaces partner and internal views based on these consolidated models.
Partner Portals: Development Tips
From ScienceSoft’s experience in building partner relationship management software, we’ve selected field-tested practices that streamline collaboration, reduce administrative effort, and support consistent partner experiences across regions and partner types.
Established portal platforms as a base
Most successful partner portals are built on enterprise platforms that already support external identities, permissions, and content delivery (e.g., SharePoint, Microsoft Power Pages, Salesforce Experience Cloud). Built-in services will cover sign-in, storage, and simple forms, and you can add custom components only for partner-specific workflows like deal registration, tier tracking, and co-branding.
Structured request handling
Replace scattered email exchanges with structured portal forms for registrations, pricing questions, scope changes, returns, and service updates. Standard fields and workflows provide predictable processing, give partners a transparent view of status, and generate consistent data that simplifies auditing, reporting, and process optimization.
Roles and data scopes first
Well-designed portals start from clearly defined partner roles, company boundaries, and data scopes. These models govern navigation, permissions, and record visibility, so each user sees only the accounts, documents, and requests that are relevant to them. Clear scoping early on helps avoid redesigns and reduces the risk of accidental data exposure.
How to avoid channel conflict in partner-facing work intake
When several partners work with the same customer, the portal should make task ownership clear. Set it up like this: each opportunity or project has one owning partner, and others can be added only as contributors. Changing the owner goes through an approval step. Partners can see the current owner but cannot change the owner themselves. Internally, the system tracks the owner, contributors, and ownership history to prevent conflicts and reduce manual clean-up later.
Partner Portals: Cost Breakdown
Based on ScienceSoft’s experience with B2B ecosystems of varying sizes and industries, partner portal implementation cost usually ranges from $50,000 to over $100,000. Pricing increases with added workflows, analytics, and customization.
$50,000+
A platform-based portal MVP with configurable onboarding, a structured content hub, role-based access, and a clean workspace for core partner tasks. Suitable when early alignment and fast rollout are priorities. Works well for standard partner programs.
$70,000+
Adds end-to-end commercial and service workflows, co-branding tools, consolidated dashboards, and flexible regional or role-based views. This type of build will fit expanding programs that manage multiple partner roles.
$100,000+
Combines tailored UX, advanced analytics, complex document flows with co-editing options, assistive AI capabilities, and multi-system data sync. Suitable for high-volume, multi-level partner operations.
Why Build Your Partner Portal With ScienceSoft
-
20 years of experience in end-to-end web portal delivery.
- 1,900+ successful web apps released.
- Hands-on experience in assistive AI enablement.
- Long-standing Microsoft partner for SharePoint and Microsoft 365, and a registered ServiceNow partner.
- 240+ web developers. Over 50% of our developers are seniors and leads.










