Revolving diabetes management: provider-connected mHealth app
The number of mHealth apps designed to ease the lives of diabetes patients is constantly growing. However, disconnected from the care cycles, the majority of them are useless to patients.
Real-life mobile diabetes management
Usually, mobile diabetes software only offers a set of tools mostly useful for self-checking, i.e., tracking vitals such as activity, blood pressure, nutrition, and others. This information stays on a patient’s device, serving as a motivational element at most.
As a result, healthcare providers are unaware of the patient’s health status between appointments, examinations, and tests. Therefore, they can’t recognize a condition pattern, reduce complications, and fulfill the core mission of value-based care – higher outcomes.
Bringing patients and healthcare providers closer requires building a bridge between a mobile diabetes app and a provider's EHR. With this bridge, the care cycle can escape communication and information gaps, and patients will feel permanently connected to their provider.
Below, we come up with a concept of such an EHR-based diabetes management app designed for dealing with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Architecture
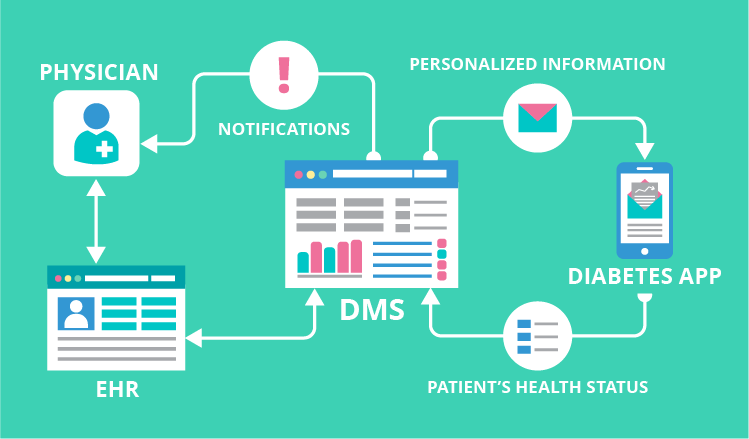
At the concept’s core is a HIPAA-compliant Diabetes Management System (DMS) linked to the EHR and the mobile application (as its backend).
The DMS offers health data analysis, alerting, and information exchange elements. It receives the patient’s data from the EHR and the patient directly, analyzes it, and, if needed, notifies physicians and other care team members (for example, when, according to the last lab results, the HbA1c level is above the predefined threshold).
Physician to patient: treatment plan guidelines
The diabetes management system provides patients with EHR-personalized information, such as:
- Medication intake scheme (according to the treatment plan)
- Recommendations on nutrition (best protein food choices, diabetes diet tips, alcohol drinking guidelines, and more)
- Instructions (the right insulin injection algorithm, blood pressure check scheme, personal hygiene milestones, and more)
- Motivation (gamification elements with achievements, social media sharing, goal-setting, and others)
Patient to physician: health status updates
Between appointments, patients can share their health status information with providers, including data such as:
- Subjective
- Photos of feet
- Objective
- Insulin and medication intake
Patients just input their data into the corresponding fields and tap ‘Send’. Moreover, the app can connect to other diabetes-related devices (instant glucometers, CGMs, insulin pumps) and include the collected insights into the patient’s messages.
Possible usage scenario
A physician creates a personal treatment plan in the EHR or the Diabetes Management System according to a particular patient’s diabetes type, the HbA1c level, comorbidities, allergies, physical activity level, nutrition habits, and more.
The patient receives the treatment plan via the mobile app and follows the guidelines – for example, recommendations and instructions as described above. In the app, they can specify the daily regimen to receive relevant reminders on medication intake. To ensure the most accurate fulfillment of the treatment plan, the patient should journalize and send to the physician such information as daily glucose, blood pressure, diet, physical activity, mood, and medication intake. And the app can do it all.
Based on the processed data, the diabetes management system will monitor the patient’s health status and, if needed, notify the physician or the patient (via the diabetes app like this one).
For example, the app can warn an individual about the risk of complications and recommend an appointment with a doctor when the glucose level is slowly rising due to a gradual growth of insulin resistance or insulin secretion decrease. Moreover, the software can also alert the patient about the risk of hyperglycemia in case the patient's diet contains excessive amounts of carbs, or their physical activity isn’t regular.
Then, the health specialist can adjust the treatment plan accordingly or suggest that the patient schedule an appointment to discuss their condition changes. All these communication elements are held via the DMS-based notifications.
Alternative to a mobile app
In some cases, a medical website can be an alternative to a mobile app, although it is less convenient and engaging. An mHealth diabetes app provides more personalization as it is installed on a patient’s personal device. This way, an individual tends to use the software more often, which is beneficial for both them and the physician.
Revolving diabetes management: benefits
Patients and physicians benefit from the next-gen healthcare mobile app development approach, where applications are tightly integrated into daily chronic condition management.
Particularly, an EHR-connected mHealth app for managing diabetes ensures the following perks:
- Revolutionized care delivery thanks to continuous and constant communication with patients
- Improved health outcomes – reducing the risk of hypoglycemia- and hyperglycemia-caused complications (up to retinopathy, angiopathy, neuropathy, and others)
- Advanced patient engagement
- Educating patients on how to manage their conditions in the comfort of their homes, thus reducing the need for clinic visits (especially useful for a rural population’s health)
If you want to learn more about diabetes mHealth apps as well as the diabetes management system concept and its integration to your EHR, don’t hesitate to contact us. We’ll be happy to offer you a free consultation and a PoC.

