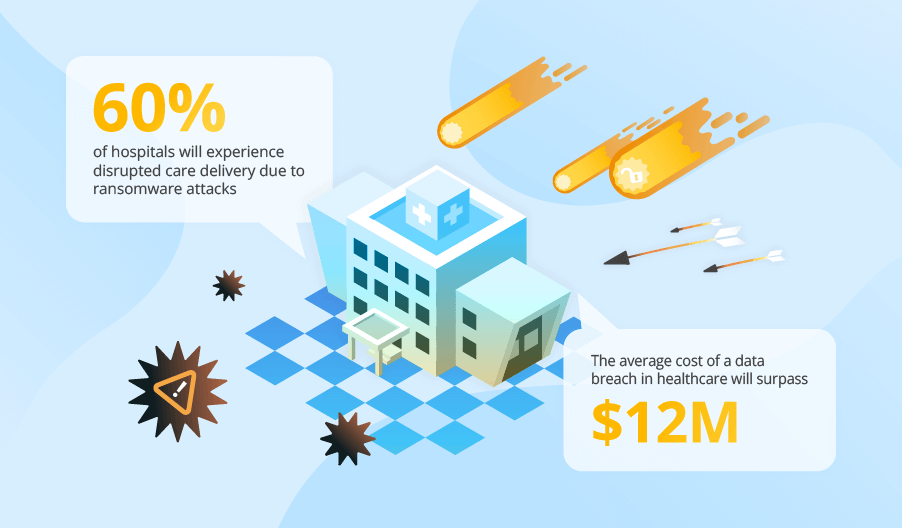
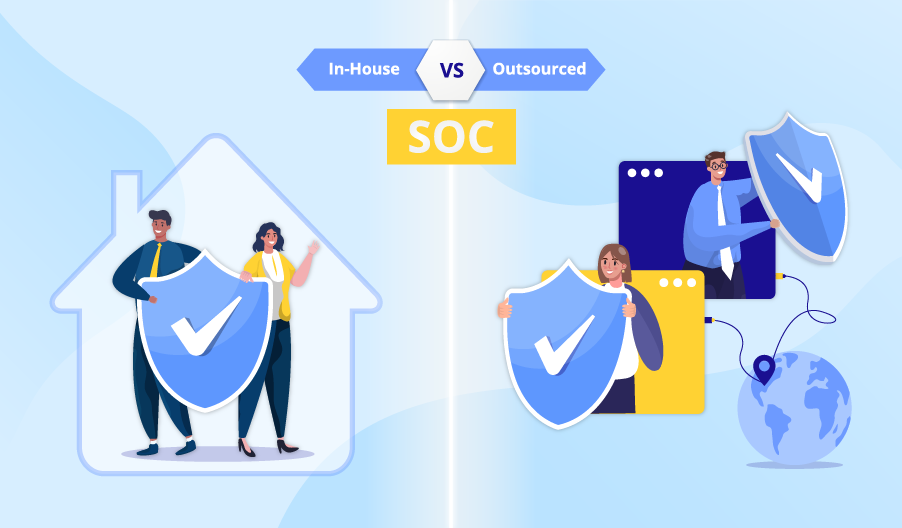
ScienceSoft helps businesses adopt a proactive cybersecurity strategy that includes robust threat detection and incident response mechanisms and continuous evolution of their cyber defenses.
ScienceSoft in Brief
Explore the Full Range of Our Cybersecurity Services
Security consulting
Security testing and vulnerability assessment
Our experts examine every security aspect that standard checklists often miss, including non-obvious, sector-specific attack vectors. We provide actionable mitigation advice and can additionally implement it upon a client’s request.
- Vulnerability assessment for IT infrastructure and applications
- Penetration testing (black box, gray box, white box pentesting)
- Social engineering
- Stress testing (emulation of denial of service attacks)
- Application security assessment
- Cloud infrastructure security assessment
- Security code review
IT security operations
ScienceSoft offers long-term IT security management services with a focus on continuous monitoring and risk mitigation.
Compliance services
ScienceSoft provides comprehensive risk assessments, advisory support, and implementation services to ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
- Compliance assessment
- Compliance consulting
- Compliance program implementation assistance
- Ongoing compliance monitoring and maintenance
We work with mandatory regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, NYDFS, NIST) as well as voluntary security standards (SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI SSF).
IT Components We Secure
On-premises infrastructures
Databases, data warehouses, data lakes
Websites and web portals
APIs and microservices
Development infrastructures, including CI/CD pipelines
Desktops, laptops, mobile devices
System software (e.g., OS, middleware, firmware) and dependencies
IoT devices and infrastructures
Cybersecurity tools
Cyber Threats We Help Prevent
Malware-based attacks
- Viruses, worms, and trojans
- Ransomware
- Spyware and keyloggers
- Advanced persistent threats (APTs)
Identity and access-related attacks
- Identity theft
- Brute-force attacks
- Unauthorized access
- Insider attacks
Injection and code-based attacks
- SQL Injection
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
- Phishing
- Spear phishing
- Whaling
- Vishing
- Smishing
- Business email compromise (BEC)
- DoS and DDoS attacks
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks
- Packet sniffing and eavesdropping
- Session hijacking
- Replay attacks
- Protocol exploitation and manipulation (e.g., DNS spoofing, IP spoofing)
Why Partner With ScienceSoft for Cybersecurity
- 22 years in cybersecurity and 17 years in ITSM.
- Competent multiskilled team: Certified Ethical Hackers, cloud security experts, senior developers, DevSecOps engineers, compliance consultants, SIEM/SOAR/XDR specialists, ITIL-certified specialists, and certified ITSM Professionals.
- Adherence to best security practices outlined by NIST, CIS, OWASP, PTES, and other authoritative sources.
- Proficiency in region- and domain-specific standards and regulations, including HIPAA, GDPR, NYDFS, NIST, SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI DSS/SSF, and more.
- Adherence to data confidentiality and protection ingrained in our code of conduct and upheld by the ISO 27001-certified security management system.
- Recognized as the Top Penetration Testing Company by Clutch.