Vulnerability Assessment vs. Penetration Testing
Editor’s note: IBM reports that $4.88M was the average total cost of a data breach in 2024. To avoid the devastating financial and reputational impacts of data breaches, organizations use vulnerability assessment and penetration testing to verify and strengthen their cyber defenses. But how do these types of security testing compare? In this article, Uladzislau explains the two security services in detail.
Have you ever paid for penetration testing services and got a hundred-page “penetration testing” report listing vulnerabilities detected by a scanning tool? Well, you’re not alone. The problem is quite common, as many providers offer penetration testing that turns out to be a vulnerability assessment.
I believe both types of security testing play a role in a company-wide security strategy. However, confusing them can lead companies to invest in services that don’t effectively address their cybersecurity needs. Worse yet, it can foster a false sense of security — for instance, due to relying on automated scans while some hidden cybersecurity gaps remain unknown and unmitigated.
Vulnerability Scanning vs. Penetration Testing: A Brief Overview
| Vulnerability assessment | Penetration testing | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus on broad coverage | ||
| Focus on in-depth analysis | ||
| Detecting complex issues | ||
| Impact analysis | ||
| Execution speed | ||
| Accuracy | ||
| Affordable pricing | ||
| Mostly automated | ||
| Mostly manual | ||
| No risk of disruptions (e.g., due to hiring an incompetent vendor) |
- Vulnerability assessment comprises automated scanning to detect weaknesses in software and hardware, manual validation of scanning findings to confirm the identified vulnerabilities, and classification of the vulnerabilities according to OWASP, CVSS, and other frameworks.
Best for: Organizations with limited security maturity and budget constraints but still needing regular security evaluations. - Penetration testing simulates a real-life cyberattack. The testers identify as many vulnerabilities as possible using automated tools and vulnerability assessment techniques. Then, they validate the detected vulnerabilities and, most importantly, attempt to exploit them, finding hidden, non-obvious security gaps and assessing their potential impact.
Best for: Organizations managing sensitive data across complex IT infrastructures with cyber protection defenses already in place.
Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability assessment, also known as vulnerability testing, aims to identify, validate, and classify vulnerabilities in networks, desktops, servers, applications, and mobile devices.
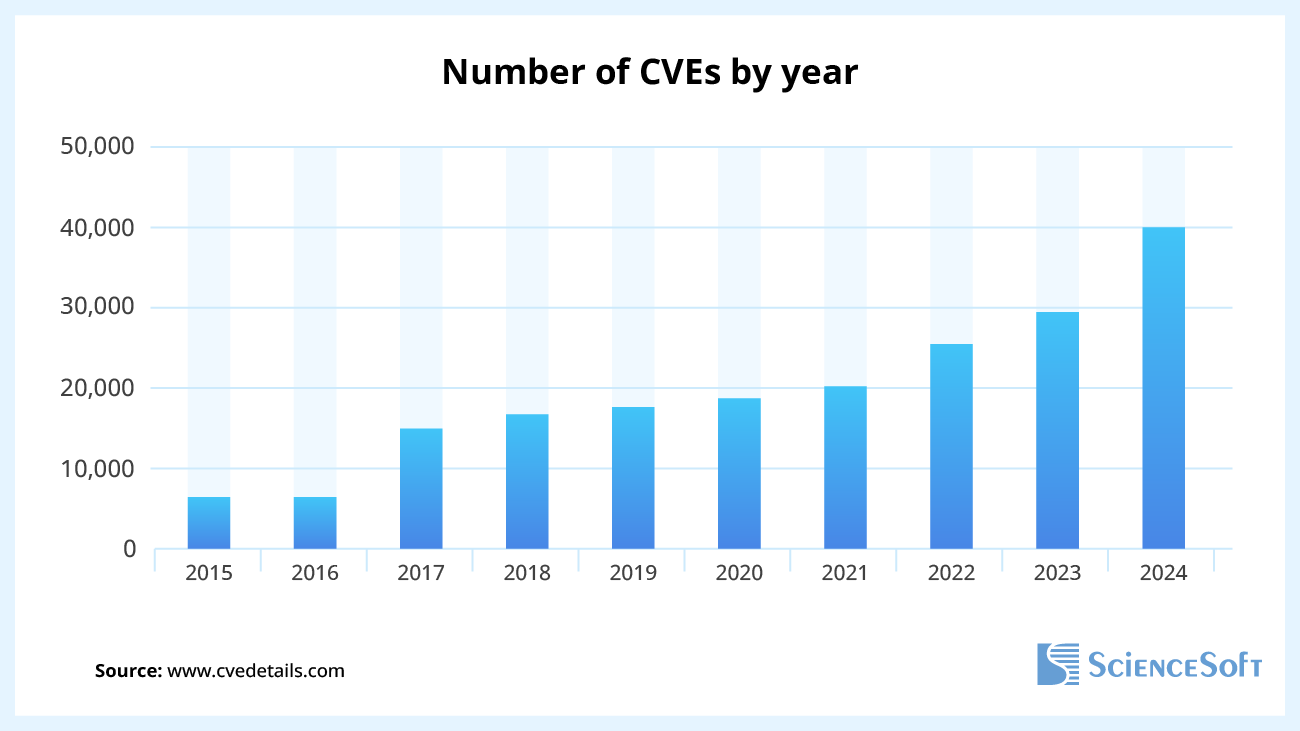
First, security experts use network security and software scanning tools that leverage a CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) database to identify known security flaws, such as outdated software and weak default configurations. The CVE databases are constantly updated as new vulnerabilities emerge, e.g., in 2024, over 40,000 new CVEs were reported.
The next step is vulnerability analysis. The security testing team manually validates the findings to eliminate false positives and reports only confirmed weaknesses. However, not all false positives may be completely filtered out without exploiting weaknesses later during a pentest.
Lastly, the team prioritizes the identified security issues based on severity using the OWASP Testing Guide, WASC Threat Classification, CVSS, and other vulnerability classifications.
A vulnerability assessment can be followed by penetration testing. This security testing approach is called Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT). It offers the benefits of VA and PT and can provide a holistic view of your cybersecurity posture.
Vulnerability assessment pros and cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Penetration Testing
In contrast to vulnerability assessment, penetration testing involves attempting to exploit the vulnerabilities discovered in software, hardware, or network systems to get unauthorized access to the systems and data.
Exploiting weaknesses is the key difference between vulnerability scanning and penetration testing. It requires a lot of manual effort but helps examine existing security measures in depth and prioritize remediation efforts.
The penetration testers, also known as ethical hackers, leverage the same techniques as real-world hackers. That could include using default credentials like ‘admin’ for username and popular passwords like ‘password123 or applying brute-forcing, i.e., sending multiple login requests, using tools like Burp Suite Intruder. Other techniques involve using open ports to access network services and manipulating input data (e.g., injecting SQL queries, triggering buffer overflow).
During application security testing, pentesters can use Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools to simulate real attack scenarios on a running web application to find insecure API endpoints, cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection vulnerabilities, and other security flaws. Both DAST and a penetration test simulate cyberattacks, but, unlike pentesting, DAST is highly automated (allowing for easy integration into CI/CD pipelines), focuses on web applications and APIs, and does not actively exploit the detected vulnerabilities.
Penetration testing pros and cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Vulnerability Assessment vs. Penetration Testing
| Vulnerability assessment | Penetration testing | |
|---|---|---|
| Breadth vs. depth coverage | Vulnerability assessment focuses on uncovering as many security weaknesses as possible (a breadth-over-depth approach). It should be employed regularly to maintain robust security protection, especially when changes are introduced (e.g., new equipment installed, services added, ports opened). | Penetration testing is preferable when the customer asserts that security defenses are strong but wants to check if they are hack-proof (a depth-over-breadth approach). |
| The degree of automation | Vulnerability assessment is usually automated, which allows for a wider vulnerability coverage. | Penetration testing combines automated and manual techniques, which helps dig deeper into the weakness. |
| The choice of professionals | Automated testing, which is widely used in vulnerability assessment, doesn’t require deep expertise, so your security department members can perform it. However, the company’s security employees may find some vulnerabilities they can’t patch and purposefully not include them in the report. A third-party vulnerability assessment vendor might be more unbiased. | Penetration testing is manual and requires a considerably higher level of expertise. It’s always best to outsource pentesting to a professional penetration testing services provider. |
As mentioned above, vulnerability assessment (VA) can be combined with penetration testing (PT) to create a comprehensive VAPT approach. However, you can also take it further and consider a red team campaign that includes social engineering simulation.
According to the Cyberthreat Predictions for 2025 report, cybercriminals are leveraging AI to level up their social engineering attacks from creating highly convincing phishing email campaigns to realistic, deepfake-assisted voice phishing (vishing). That’s why testing and raising cybersecurity awareness of employees is equally important as setting up firewalls and anti-malware. Red teaming examines cyber defenses against multi-layered attacks and is best suited for organizations with mature security programs.
Penetration Testing vs. Vulnerability Assessment at a Glance
| Vulnerability assessment | Penetration testing | |
|---|---|---|
| How often should the service be performed? | Once a month. Plus, additional testing is required after changes in the network. | Once a year, at the least. |
| What’s in the report? | A comprehensive list of vulnerabilities, which may include false positives. | A “call to action” document. It lists the vulnerabilities that were successfully exploited. |
| Who performs the service? | In-house security staff or a third-party vendor. | A provider of penetration testing services. |
| What’s the value of the service? | Uncovers a wide range of possible vulnerabilities. | Shows exploitable vulnerabilities and assesses the potential impact of security gaps. |
The Choice of Vendor
The comparison of vulnerability assessment and penetration testing shows that both security testing services are worth using to guard cybersecurity. Vulnerability assessment is good for security maintenance, while penetration testing can help to explore the possible impact of cyberattacks and uncover less obvious weaknesses requiring multi-step attacks.
It’s possible to take advantage of both services only if you contract a high-quality vendor who understands and, most importantly, translates the difference between penetration testing and vulnerability assessment to the customer. A good vendor providing vulnerability assessment services not only uncovers a wide range of possible vulnerabilities but also validates them to reduce false positives and classifies them according to OWASP, CVSS, and other relevant classifications. It also provides detailed reports that specify affected systems, recommended fixes, and mitigation steps for each finding.
At the same time, in penetration testing, a good vendor combines automated tools with a predominantly manual approach to simulate real-world attack scenarios and uncover vulnerabilities that require complex, multi-step attacks to exploit. A vendor’s report should detail the business impact of each vulnerability, provide a transparent account of the testing procedure and attack paths, and offer tailored remediation steps. A good vendor should also be able to implement all the changes and provide a follow-up testing to check if all the fixes have been applied correctly. Though it may raise the cost of penetration testing, it is highly recommended to engage certified pentesting engineers (e.g., Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)).

